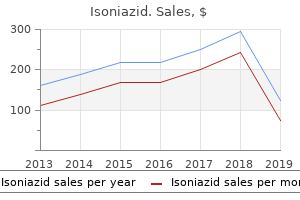
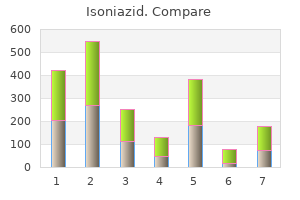
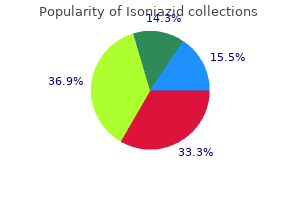
Isoniazid
"Order isoniazid 300 mg, medications adhd".
By: W. Sanford, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Deputy Director, West Virginia School of Osteopathic Medicine
Laboratory Diagnosis 207 with meningococci carriers treatment 99213 discount isoniazid online american express, before surgery involving massive bacterial contamination medicine to stop runny nose isoniazid 300mg without a prescription, in heavily immunocompromised patients medicine qid buy isoniazid 300mg online, in cardiac surgery or in femoral amputations due to circulatory problems medications not covered by medicare discount isoniazid 300mg. Immunomodulators Despite the generally good efficacy of anti-infective agents, therapeutic success cannot be guaranteed. Complete elimination of bacterial pathogens also requires a functioning immune defense system. In view of the fact that the number of patients with severe immunodeficiencies is on the rise, immunomodulators are used as a supportive adjunct to specific antibiotic therapy in such patients. The reliability of laboratory results is characterized by the terms sensitivity and specificity, their value is measured in terms of positive to negative predictive value. In direct laboratory diagnosis, correct material sampling and adequate transport precautions are an absolute necessity. The classic methods of direct laboratory diagnosis include microscopy and culturing. Identification of pathogens is based on morphological, physiological, and chemical characteristics. Among the latter, the importance of detection of pathogen-specific nucleotide sequences is constantly increasing. Development of sensitive test systems has made direct detection of pathogen components in test materials possible in some cases. The molecular biological methods used are applied with or without amplification of the sequence sought as the case warrants. Direct detection can also employ polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies & to detect and identify antigens. Modern medical practice, and in particular hospital-based practice, is inconceivable without the cooperation of a special microbiological laboratory. To ensure optimum patient benefit, the physician in charge of treatment and the laboratory staff must cooperate closely and efficiently. The preconditions include a basic knowledge of pathophysiology and clinical infectiology on the part of the laboratory staff and familiarity with the laboratory work on the part of the treating physician. The following sections provide a brief rundown on what physicians need to know about laboratory procedures. The accuracy and value of each of the available diagnostic methods are characterized in terms of sensitivity, specificity, and positive or negative predictive value. Sampling and Transport of Test Material It is very important that the material to be tested be correctly obtained (sampled) and transported. In general, material from which the pathogen is to be isolated should be sampled as early as possible before chemotherapy is begun. Transport to the laboratory must be carried out in special containers provided by the institutes involved, usually containing transport mediums- either enrichment mediums (e. An invoice must be attached to the material containing the information required for processing (using the form provided). It analyzes the positive test results both in the infected collective and in the noninfected collective (vertical addition). Expectorated sputum is usually contaminated with saliva and the flora of the oropharynx. Since these contaminations include pathogens that may cause infections of the lower respiratory tract organs, the value of positive findings would be limited. Morning sputum from flushing the mouth or after induction will result in suitable samples. Midstream urine is in most cases contaminated with the flora of the anterior urethra, which often corresponds to the pathogen spectrum of urinary tract infections. Bacterial counts must be determined if "contamination" is to be effectively differentiated from "infection. The dipstick method, which can be used in any medical practice, is a simple way of estimating the bacterial count: a stick coated with nutrient medium is immersed in the midstream urine, then incubated. The colony count is then estimated by comparing the result with standardized images. Uncontaminated bladder urine is obtainable only by means of a suprapubic bladder puncture.
Antimicrobial drugs are effective in the treatment of infections because of their selective toxicity; that is treatment 3rd degree burns discount 300 mg isoniazid overnight delivery, they have the ability to injure or kill an invading microorganism without harming the cells of the host medications used to treat bipolar disorder buy isoniazid 300mg with amex. In most instances treatment of strep throat order isoniazid 300 mg with visa, the selective toxicity is relative rather than absolute medications that cause high blood pressure purchase 300mg isoniazid otc, requiring that the concentration of the drug be carefully controlled to attack the microorganism while still being tolerated by the host. Identification of the infecting organism Characterization of the organism is central to selection of the proper drug. However, it is generally necessary to culture the infective organism to arrive at a conclusive diagnosis and to determine the susceptibility of the bacteria to antimicrobial agents. Thus, it is essential to obtain a sample culture of the organism prior to initiating treatment. Empiric therapy prior to identification of the organism Ideally, the antimicrobial agent used to treat an infection is selected after the organism has been identified and its drug susceptibility established. However, in the critically ill patient, such a delay could prove fatal, and immediate empiric therapy is indicated. Therapy is initiated after specimens for laboratory analysis have been obtained but before the results of the culture are available. Broad-spectrum therapy may be needed initially for serious infections when the identity of the organism is unknown or the site makes a polymicrobial infection likely. The choice of agents may also be guided by known association of particular organisms with infection in a given clinical setting. For example, a gram-positive coccus in the spinal fluid of a newborn infant is unlikely to be Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) and most likely to be Streptococcus agalactiae (Group B), which is sensitive to penicillin G. By contrast, a gram-positive coccus in the spinal fluid of a 40-year-old patient is most likely to be S. This organism is frequently resistant to penicillin G and often requires treatment with a third-generation cephalosporin (such as cefotaxime or ceftriaxone) or vancomycin. Determination of antimicrobial susceptibility of infective organisms After a pathogen is cultured, its susceptibility to specific antibiotics serves as a guide in choosing antimicrobial therapy. Some pathogens, such as Streptococcus pyogenes and Neisseria meningitidis, usually have predictable susceptibility patterns to certain antibiotics. In contrast, most gram-negative bacilli, enterococci, and staphylococcal species often show unpredictable susceptibility patterns to various antibiotics and require susceptibility testing to determine appropriate antimicrobial therapy. The minimum inhibitory and bactericidal concentrations of a drug can be experimentally determined (Figure 30. Because of their more aggressive antimicrobial action, these agents are often the drugs of choice in seriously ill patients. Note that viable organisms remain even in the presence of the bacteriostatic drug. By contrast, addition of a bactericidal agent kills bacteria, and the total number of viable organisms decreases. Although practical, this classification may be too simplistic, because it is possible for an antibiotic to be bacteriostatic for one organism and bactericidal for another. For example, chloramphenicol is bacteriostatic against gram-negative rods and is bactericidal against other organisms, such as S. Minimum bactericidal concentration: this quantitative assay determines the minimum concentration of antibiotic that kills the bacteria under investigation. The minimum bactericidal concentration is the lowest concentration of antimicrobial agent that results in a 99. Effect of the site of infection on therapy: the blood-brain barrier Adequate levels of an antibiotic must reach the site of infection for the invading microorganisms to be effectively eradicated. For example, the endothelial cells comprising the walls of capillaries of many tissues have fenestrations (openings that act like windows) that allow most drugs not bound by plasma proteins to penetrate. Of particular significance are the capillaries in the brain, which help to create and maintain the blood-brain barrier.
Return to full-power state from a sleep mode takes only a few processor clock cycles medications qt prolongation discount generic isoniazid canada. Because the time base has been inactive during the sleep mode it is necessary to update from an external reference upon exiting sleep medicine 75 yellow buy 300 mg isoniazid amex. Furthermore medicine werx isoniazid 300 mg without a prescription, nap and sleep modes require all outstanding bus operations to be completed before these modes are entered symptoms 5 weeks pregnant cramps discount isoniazid. The frequency change occurs in one clock cycle and no idle waiting period is required to switch between modes. This feature may or may not be used in combination with voltage derating by a system to reduce the power consumption of the processor. The applied system clock frequency also does not need to change for this power reduction step. Additional details are also documented in the hardware specifications for the individual device. When used with dynamic power management, instruction cache throttling provides the system designer with a flexible way to control device temperature while allowing the processor to continue operating. The instruction cache throttling mechanism simply reduces the instruction dispatch rate. Note also when instruction cache throttling is enabled, to reduce overall junction temperature, the performance does degrade. These devices use the negative temperature coefficient of a diode operated at a constant current to determine the temperature of the microprocessor and its environment. The count of such events (that may be an approximation) can be used to trigger the performance monitor exception. Its priority is below the trace exception and above the AltiVec unavailable exception. The priority of the performance monitor exception is below the trace exception and above the AltiVec unavailable exception. Exception handling for the performance monitor exception is described in Section 4. An explicit synchronization instruction, such as sync, should be placed before and after an mfspr or mtspr of one of these registers to guarantee an accurate count. The supervisor-level registers in Table 11-1 are accessed through the mtspr and mfspr instructions. Attempting to write to one of these registers in either supervisor or user mode causes a program exception. Performance monitor exception enable 0 Performance monitor exceptions are disabled. The use of the trigger and freeze counter conditions depends on the enabled conditions and events described in Section 11. Selects the time-base bit that can cause a time-base transition event (the event occurs when the selected bit changes from 0 to 1). By varying the threshold value, software can obtain a profile of the characteristics of the events subject to the threshold. Counters overflow when the high-order (sign) bit becomes set; that is, they reach the value 2,147,483,648 (0x8000 0000). This enables statistics to be gathered only during the execution of the marked process. The counter can increment by 0, 1, 2, or 3, depending on the number of dispatched instructions per cycle. This event includes instructions dispatched directly to the completion queue, Counts times the processor begins to generate its performance monitor exception condition. This count does not include the following instructions, which do not perform a load or store: sync, eciwx, ecowx, eieio, dcbf, dcbi, dcbst, dcbt, dcbtst, dcbz, icbi, tlbie, tlbld, tlbli, tlbsync, dcba, dst, dstt, dstst, dststt, dss, and dssall. This includes branches in a speculative path that might later be thrown away due to another previously predicted branch that mispredicts. This count may be greater than the sum of link-stack-correctly-resolved and link-stack-mispredicted because another branch may mispredict and cause this branch to be thrown off the link stack before the resolution occurs. Load strings and load multiples are only counted once regardless of how many pieces they are broken into. This also includes table search operations caused by dst, dstt, dstst, and dststt instructions.
Control activities involve detecting deviations from the predetermined reference point and stimulating compensatory responses in the muscles and glands of the body medications 44 175 discount 300 mg isoniazid overnight delivery. The major organs affected are the heart treatment lead poisoning order isoniazid with visa, lungs 86 treatment ideas practical strategies order isoniazid master card, kidneys symptoms yeast infection women order isoniazid with a mastercard, liver, gastrointestinal tract, and skin. When stimulated, these organs alter their rate of activity or the amount of secretions they produce. The cells detect a change in their immediate environment and initiate an action to counteract its effect. For example, the accumulation of lactic acid in an exercised muscle stimulates dilation of blood vessels in the area to increase blood flow and improve the delivery of oxygen and removal of waste products. A steady state is achieved by the continuous, variable action of the organs involved in making the adjustments and by the continuous small exchanges of chemical substances among cells, interstitial fluid, and blood. For example, an increase in the carbon dioxide concentration of the extracellular fluid leads to increased pulmonary ventilation, which decreases the carbon dioxide level. On a cellular level, increased carbon dioxide raises the hydrogen ion concentration of the blood. This is detected by chemosensitive receptors in the respiratory control center of the medulla of the brain. The chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in the rate of discharge of the neurons that innervate the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, which increases the rate of respiration. Excess carbon dioxide is exhaled, the hydrogen ion concentration returns to normal, and the chemically sensitive neurons are no longer stimulated. Homeostasis, Stress, and Adaptation 89 Positive Feedback Another type of feedback, positive feedback, perpetuates the chain of events set in motion by the original disturbance instead of compensating for it. There are some exceptions to this; blood clotting in humans, for example, is an important positive feedback mechanism. The maintenance function refers to the activities that the cell must perform with respect to itself; specialized functions are those that the cell performs in relation to the tissues and organs of which it is a part. Cells can adapt to environmental stress through structural and functional changes. Some of these adaptations are hypertrophy, atrophy, hyperplasia, dysplasia, and metaplasia (Table 6-2). Hypertrophy and atrophy lead to changes in the size of cells and hence the size of the organs they form. Compensatory hypertrophy is the result of an enlarged muscle mass and commonly occurs in skeletal and cardiac muscle that experiences a prolonged, increased workload. Atrophy can be the consequence of a disease or of decreased use, decreased blood supply, loss of nerve supply, or inadequate nutrition. Cell size and organ size decrease; structures principally affected are the skeletal muscles, the secondary sex organs, the heart, and the brain. As cells multiply and are subjected to increased stimulation, the tissue mass enlarges. It is a mitotic response (a change occurring with mitosis), but it is reversible when the stimulus is removed. This distinguishes it from neoplasia or malignant growth, which continues after the stimulus is removed. An example is the increase in the size of the thyroid gland caused by thyroid-stimulating hormone (secreted from the pituitary gland) when a deficit in thyroid hormone is detected. Dysplasia is the change in the appearance of cells after they have been subjected to chronic irritation. Dysplastic cells have a tendency to become malignant; dysplasia is seen commonly in epithelial cells in the bronchi of smokers. Metaplasia is a cell transformation in which a highly specialized cell changes to a less specialized cell. This serves a protective function, because the less specialized cell is more resistant to the stress that stimulated the change. For example, the ciliated columnar epithelium lining the bronchi of smokers is replaced by squamous epithelium.
Cheap isoniazid on line. Teens' tics: Mysterious illness or hysteria?.