Ondansetron
"Buy ondansetron 4mg on line, medicine jobs".
By: A. Kasim, MD
Professor, Chicago Medical School of Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science
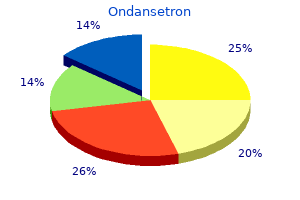
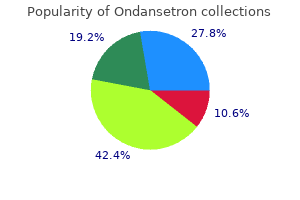
Secondary outcome measures included determination of relationships between preoperative blood glucose measurements treatment resistant depression ondansetron 4 mg sale, glucose control and postoperative readmission for resalvage medicine journal impact factor buy discount ondansetron line. Relationships between average blood sugar levels or HgbA1C levels and rates of readmission for resalvage procedures were also determined medications gout discount 8 mg ondansetron fast delivery. We found a poor correlation between average preoperative blood sugar and Hgb A1C levels (r =0 medications zoloft ondansetron 4mg on line. Similarly, we found a poor correlation between Hgb A1C levels and rates of readmission for resalvage (r=0. We hypothesized that the exclusive use of high quality, high enrolling sites in a multicenter trial may significantly reduce variability. We extracted our site specific data from a multicenter trial to compare our treatment effect with the aggregate data generated by the remaining 28 sites. In order to determine if the observed treatment effect was greater in our single center as compared to a multicenter environment, a post-hoc analysis was performed of (a) patients enrolled by our site and (b) of the remaining patients enrolled by the remaining 28 sites. For each group, we then calculated the odds ratio for the comparison of the two aprepitant doses versus ondansetron and calculated the number of patients necessary to demonstrate a significant difference compared to ondansetron, the active control (using standard type I error of 0. When the odds ratio of complete response for aprepitant (both doses) compared to ondansetron was calculated utilizing our site data exclusively, the result was significantly greater than the odds ratios calculated utilizing aggregate data from the 28 remaining sites. Because study n has an inverse non-linear relationship with the odds ratio, large differences in the calculated value of the required patients per group are apparent (table 1). This may be a spurious finding; however we observed a similar effect in another other clinical trial. J Clin Pharmacol 2010; 50:1068 Treatment Assignment) Single High Enrolling Site Complete response (yes/total) Complete response (%) Odds ratio compared to ondansetron 1. Although propofol has anti-emetic properties, studies on low-dose infusion combined with inhalational agents have had mixed results. Patients received a standardized anesthetic of sevoflurane, fentanyl and hydromorphone. The intraoperative anesthesiologist was blinded to the intervention as propofol was administered in a concealed fashion into either the distal portion of a separate intravenous line (group P) or directly into a reservoir bag (group C). One patient in group P required further surgery and thus we were missing their data at 24 hours. There were no significant differences between the groups in terms of patient characteristics (Table 1). Patients were randomized to receive 8 mg Dex (group 2) or an equivalent volume of saline (group 1) after induction of general anesthesia. Complete response (no vomiting, no rescue medication) was not different between treatment groups for any time intervals. Nausea scores (4 point ordinal scale) were not different between groups for any time intervals. In this study the relations between occurrence of propofol-induced yawning, sex and the falls in arterial blood pressure were examind. Routine monitors consisted of an automated blood-pressure cuff, electrocardiogram, and pulse oximeter. As the only clinical end point, the occurrence of the yawning response (characterized by mouth opening) was observed continuously after the start of the anesthetic infusion. Clonidine and magnesium could achieve hemodynamic stability during intubation and surgical incision. However, it has not been proven if fentanyl has a complication-free, dose-dependent effect on cough suppression during emergence from sevoflurane anesthesia. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the relationship between fentanyl dose and cough suppression during emergence from sevoflurane anesthesia. The relationship between fentanyl dose and incidence of emergence cough was analyzed using the Cochran-Armitage trend test. In some clinical situations, bolus administration may be easier to apply, and fentanyl can be more compatible than is remifentanil in this situation. Effect of a remifentanil bolus dose on the cardiovascular response to emergence from anaesthesia and tracheal extubation.
Effector enzymes include adenylyl cyclase symptoms celiac disease order ondansetron visa, guanylyl cyclase treatment tinnitus discount ondansetron 8mg mastercard, phospholipase C symptoms of strep order ondansetron american express, and others (Figure 7 symptoms influenza order discount ondansetron on line. The second messengers produced by these enzymes trigger the complex biochemical signaling cascades discussed in the next section. Because each of these cascades is activated by specific Gprotein subunits, the pathways activated by a particular receptor are determined by the specific identity of the G-protein subunits associated with it. As well as activating effector molecules, G-proteins can also directly bind to and activate ion channels. For example, some neurons, as well as heart muscle cells, have G-protein-coupled receptors that bind acetylcholine. Because these receptors are also activated by the agonist muscarine, they are usually called muscarinic receptors (see Chapters 6 and 20). Activation of muscarinic receptors can open K+ channels, thereby inhibiting the rate at which the neuron fires action potentials, or slowing the heartbeat of muscle Figure 7. In all three examples shown here, binding of a neurotransmitter to such a receptor leads to activation of a G-protein and subsequent recruitment of second messenger pathways. These inhibitory responses are believed to be the result of subunits of G-proteins binding to the K+ channels. The activation of subunits can also lead to the rapid closing of voltage-gated Ca2+ and Na+ channels. Because these channels carry inward currents involved in generating action potentials, closing them makes it more difficult for target cells to fire (see Chapters 3 and 4). In summary, the binding of chemical signals to their receptors activates cascades of signal transduction events in the cytosol of target cells. Within such cascades, G-proteins serve a pivotal function as the molecular transducing elements that couple membrane receptors to their molecular effectors within the cell. The diversity of G-proteins and their downstream targets leads to many types of physiological responses. By directly regulating the gating of ion channels, G-proteins can influence the membrane potential of target cells. Second Messengers Neurons use many different second messengers as intracellular signals. These messengers differ in the mechanism by which they are produced and removed, as well as their downstream targets and effects (Figure 7. This section summarizes the attributes of some of the principal second messengers. The calcium ion (Ca2+) is perhaps the most common intracellular messenger in neurons. Indeed, few neuronal functions are immune to the influence-direct or indirect-of Ca2+. One of the most thoroughly studied targets of Ca2+ is calmodulin, a Ca2+-binding protein abundant in the cytosol of all cells. Binding of Ca2+ to calmodulin activates this protein, which then initiates its effects by binding to still other downstream targets, such as protein kinases. In addition to these plasma membrane mechanisms, Ca2+ is also pumped into the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. These organelles can thus serve as storage depots of Ca2+ ions that are later released to participate in signaling events. Finally, nerve cells contain other Ca2+-binding proteins-such as calbindin-that serve as Ca2+ buffers. Such buffers reversibly bind Ca2+ and thus blunt the magnitude and kinetics of Ca2+ signals within neurons. The Ca2+ ions that act as intracellular signals enter cytosol by means of one or more types of Ca2+-permeable ion channels (see Chapter 4). These can be voltage-gated Ca2+ channels or ligand-gated channels in the plasma membrane, both of which allow Ca2+ to flow down the Ca2+ gradient and into the cell from the extracellular medium.
Order 4 mg ondansetron fast delivery. Lundy Bancroft Quotes Part 4; Long Term Verbal Abuse Symptoms.
Angelicae Fructus (Angelica). Ondansetron.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What other names is Angelica known by?
- Dosing considerations for Angelica.
- Upset stomach (dyspepsia), when a combination of angelica and five other herbs is used (Iberogast, Medical Futures, Inc).
- Intestinal cramps and gas, nerve pain, arthritis-like pain, fluid retention, menstrual disorders, promoting sweating, and increasing urine production (diuretic).
- How does Angelica work?
- Premature ejaculation, when applied directly to the skin of the penis in combination with other medicines.
- What is Angelica?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96304
The sample is then placed onto a microscope slide and a smear is made in the manner described for concentrating cells in a smear medications covered by blue cross blue shield purchase ondansetron 4 mg fast delivery. Special cytocentrifuge equipmenta is available for concentrating cells on microscope slides while absorbing the fluid onto filter paper counterfeit medications 60 minutes order genuine ondansetron line. This equipment is expensive and not practical for the average veterinary laboratory symptoms yeast infection women order discount ondansetron on line. Because centrifugation distorts the appearance of the cells symptoms 5 weeks into pregnancy order generic ondansetron pills, a cell concentration method that utilizes gravity provides a concentrated sample with normal appearing cells. A simple, inexpensive sedimentation device can be made for use in the veterinary laboratory. This device consists of a base to support the slide and a clamping mechanism to hold the fluid column onto the microscope slide (Figure 10. The column that holds the fluid is made from a one millimeter tuberculin syringe barrel with the tip removed. The base of the syringe barrel allows for the syringe to be held in place by a clamp (usually made of wood). A piece of filter paper (eg, Whatman #2) is cut to the dimensions of the microscope slide and a standard 2 mm paper hole punch is used to create a hole in the center of the filter paper. Fluid samples having low cellularity require a concentration procedure for easier examination of the cells. A simple method is to marginate the cells on a smear made by the conventional wedge technique used for making blood films. A drop of the fluid sample is placed on a microscope slide and spread slowly using a spreader slide. Just prior to reaching the end of the smear, the spreader slide is quickly backed slightly into the advancing smear, just before lifting it from the surface of the slide containing the smear. This should produce a slide with the marginated cells concentrated at the end of the film. A simple device that uses gravity to concentrate cells provides cytologic samples of better quality than centrifugation (courtesy of Terry Campbell). When allowed to stand undisturbed, the fluid is drawn by gravity and absorbed into the filter paper. Once the fluid has drained from the column, the apparatus is disassembled and the slide is allowed to air dry. After staining, the cells can be found concentrated in the two millimeter circle created by the filter paper and column. Cytologic evaluation of the ingluvies (crop) can be performed from samples obtained by aspiration. This is indicated in birds showing clinical signs of regurgitation, vomiting, delayed emptying of the crop or other crop disorders. A crop aspirate is obtained by inserting a sterile plastic, metal or rubber feeding tube through the mouth and esophagus into the ingluvies (see Figure 15. Passage of the tube is facilitated by extending the head and neck to straighten the esophagus. The crop content is gently aspirated into the tube using a syringe attached to the free end. In cases where material cannot be aspirated for examination, a wash sample can be obtained by infusing a small amount of sterile isotonic saline into the crop and aspirating the fluid back into the tube and syringe. Aspiration of the infraorbital sinus of birds suffering from sinusitis can provide diagnostic material for culture and cytologic examination. One technique of sinus aspiration in psittacine birds samples the large sinus between the eye and the external nares (Figure 10. With the head and body properly restrained, a needle (eg, 22 ga one-inch) is passed through the fleshy skin at the commissure of the mouth. The needle is directed toward a point midway between the eye and external nares, keeping parallel with the side of the head. The needle passes under the zygomatic bone, which lies between the lower corner of the rhinotheca (upper beak) and the ear. This procedure requires some practice and complete restraint to prevent damage to the globe.
The involuntary movements are initiated by abnormal discharges of upper motor neurons that are receiving less tonic inhibition from the basal ganglia symptoms ectopic pregnancy buy discount ondansetron 4mg on line. Another circuit within the basal ganglia system entails the dopaminergic cells in the pars compacta subdivision of substantia nigra and modulates the output of the corpus striatum symptoms zika virus ondansetron 4 mg without prescription. The medium spiny neurons of the corpus striatum project directly to substantia nigra pars compacta treatment lyme disease best order for ondansetron, which in turn sends widespread dopaminergic projections back to the spiny neurons medications given to newborns ondansetron 8mg otc. These dopaminergic influences on the spiny neurons are complex: the same nigral neurons can provide excitatory inputs mediated by D1 type dopaminergic receptors on the spiny cells that project to the internal globus pallidus (the direct pathway), and inhibitory inputs mediated by D2 type receptors on the spiny cells that project to the external globus pallidus (the indirect pathway). Since the actions of the direct and indirect pathways on the output of the basal ganglia are antagonistic, these different influences of the nigrostriatal axons produce the same effect, namely a decrease in the inhibitory outflow of the basal ganglia. The modulatory influences of this second internal circuit help explain many of the manifestations of basal ganglia disorders. As mentioned earlier, the normal effects of the compacta input to the striatum are excitation of the medium spiny neurons that project directly to the internal globus pallidus and inhibition of the spiny neurons that project to the external globus pallidus cells in the indirect pathway. Normally, both of these dopaminergic effects serve to decrease the inhibitory outflow of the basal ganglia and thus to increase the excitability of the upper motor neurons (Figure 17. Thus, Parkinsonian patients tend to have diminished facial expressions and lack "associated movements" such as arm swinging during walking. Indeed, any movement is difficult to initiate and, once initiated, is often difficult to terminate. Described by James Parkinson in 1817, this disorder is characterized by tremor at rest, slowness of movement (bradykinesia), rigidity of the extremities and neck, and minimal facial expressions. Walking entails short steps, stooped posture, and a paucity of associated movements such as arm swinging. To make matters worse, in some patients these abnormalities of motor function are associated with dementia. Following a gradual onset between the ages of 50 and 70, the disease progresses slowly and culminates in death 10 to 20 years later. The defects in motor function are due to the progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta, a population that projects to and innervates neurons in the caudate and putamen (see text). Although the cause of the progressive deterioration of these dopaminergic neurons is not known, genetic investigations are providing clues to the etiology and pathogenesis. Familial forms of the disease caused by single gene mutations account for less than 10% of all cases, However, identification of these rare genes is likely give some insight into molecular pathways that may underlie the disease. Identification of these genes provides an opportunity to generate mutant mice carrying the mutant form of the human gene, potentially providing a useful animal model in which the pathogenesis can be elucidated and therapies can be tested. This spatial restriction, combined with the defined and relatively homogeneous phenotype of the degenerating neurons. Gene therapy refers to the correction of a disease phenotype through the introduction of new genetic information into the affected organism. Although still in its infancy, this approach promises to revolutionize treatment of human disease. An alternative strategy to treating Parkinsonian patients involves "neural grafts" using stem cells. Stem cells are self-renewing, multipotent progenitors with broad developmental potential (see Chapters 21 and 24). Instead of isolating mature dopaminergic neurons from the fetal midbrain for transplantation, this approach isolates neuronal progenitors at earlier stages of development, when these cells are actively proliferating. Critical to this approach is to prospectively identify and isolate stem cells that are multipotent and self-renewing, and to identify the growth factors needed to promote differentiation into the desired phenotype. The prospective identification and isolation of multipotent mammalian stem cells has already been accomplished, and several factors likely to be important in differentiation of midbrain precursors into dopamine neurons have been identified. Although therapeutic strategies like these remain experimental, it is likely that some of them will succeed. The resulting increase in tonic inhibition reduces the excitability of the upper motor neurons in the superior colliculus and causes saccades to be reduced in both frequency and amplitude. Furthermore, a second lesion placed in the subthalamic nucleus results in significant improvement in the ability of these animals to initiate movements, as would be expected based on the circuitry of the indirect pathway (see Figure 17. In both cases, the balance of inhibitory signals in the direct and indirect pathways is altered, leading to a diminished ability of the basal ganglia to control the thalamic output to the cortex. The result of this change in the direct pathway is to sustain the tonic inhibition from the globus pallidus (internal segment) to the thalamus, making thalamic excitation of the motor cortex less likely (thinner arrow from thalamus to cortex).