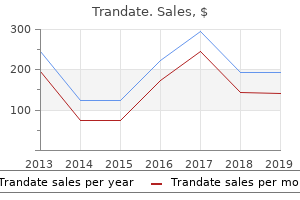
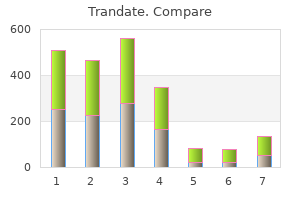
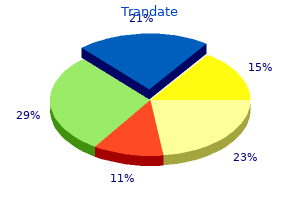
Trandate
"Generic 100 mg trandate with visa, blood pressure medication bananas".
By: P. Gembak, M.A.S., M.D.
Medical Instructor, New York University School of Medicine
Early microscopes were simple but they opened an exciting new field of observation blood pressure medication starting with x trandate 100mg overnight delivery. Undoubtedly blood pressure tea trandate 100mg without prescription, the small chambers that de Graaf described were blastocysts arteria vesicalis buy trandate no prescription. He also described vesicular ovarian follicles blood pressure medication with food cheap trandate 100 mg with visa, which are still sometimes called graafian follicles. A young medical student in Leiden, Johan Ham van Arnheim, and his countryman Anton van Leeuwenhoek using an improved microscope in 1677. They thought the sperm contained a miniature preformed human being that enlarged when it was deposited in the female genital tract. The object was held in front of the lens on the point of the short rod, and the screw arrangement was used to adjust the object under the lens. The miniature human being within it was thought to enlarge after the sperm entered an ovum. Other embryologists at this time thought the oocyte contained a miniature human being that enlarged when it was stimulated by a sperm. Caspar Friedrich Wolff refuted both versions of the preformation theory in 1759, after observing parts of the embryo develop from "globules" (small spherical bodies). He proposed the layer concept, whereby division of what we call the zygote produces layers of cells (now called the embryonic disc) from which the embryo develops. His ideas formed the basis of the theory of epigenesis, which states that development results from growth and differentiation of specialized cells. He also observed embryonic masses of tissue that partly contribute to the development of the urinary and genital systems-Wolffian bodies and Wolffian ducts-now called the mesonephros and mesonephric ducts, respectively (see Chapter 12). The preformation controversy ended in 1775 when Lazaro Spallanzani showed that both the oocyte and sperm were necessary for initiating the development of a new individual. From his experiments, including artificial insemination in dogs, he concluded that the sperm was the fertilizing agent that initiated the developmental processes. Heinrich Christian Pander discovered the three germ layers of the embryo, which he named the blastoderm. Etienne Saint Hilaire and his son, Isidore Saint Hilaire, made the first significant studies of abnormal development in 1818. They performed experiments in animals that were designed to produce developmental abnormalities, initiating what we now know as the science of teratology. He also observed cleaving zygotes in the uterine tube and blastocysts in the uterus. He contributed new knowledge about the origin of tissues and organs from the layers described earlier by Malpighi and Pander. Von Baer formulated two important embryologic concepts: corresponding stages of embryonic development and that general characteristics precede specific ones. His significant and far-reaching contributions resulted in his being regarded as the Father of Modern Embryology. Mattias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann were responsible for great advances being made in embryology when they formulated the cell theory in 1839. The cell theory soon led to the realization that the embryo developed from a single cell, the zygote, which underwent many cell divisions as the tissues and organs formed. Wilhelm His (1831-1904), a Swiss anatomist and embryologist, developed improved techniques for fixation, sectioning, and staining of tissues and for reconstruction of embryos. His method of graphic reconstruction paved the way for producing current three-dimensional, stereoscopic, and computergenerated images of embryos. Mall (1862-1917), inspired by the work of His, began to collect human embryos for scientific study. For his discovery of the phenomenon of primary induction-how one tissue determines the fate of anotherSpemann received the Nobel Prize in 1935. Over the decades, scientists have been attempting to isolate the substances that are transmitted from one tissue to another, causing induction. Edwards and Patrick Steptoe pioneered one of the most revolutionary developments in the history of human reproduction: the technique of in vitro fertilization. These studies resulted in the birth of Louise Brown, the first "test tube baby," in 1978.
Scholar Using Poems of Jibanananda Das and Rabindranath Tagore in the Language Classrooms of Bangladesh 48 4 heart arrhythmia 4 year old generic trandate 100 mg without a prescription. After the groups finish their work ulterior motive quotes cheap 100mg trandate visa, the teacher then asks the group members to answer the questions set previously by the teacher and corrects the answers hypertension journal purchase discount trandate on-line. At the end of the class the teacher informs the students that the next class would be based on spoken English in which the groups would either debate on the "racial issues" traced in the poem "Krishnakali" (as it is about an adorable "dark" girl) or how beauty is "perceived" by the society blood pressure medication one kidney 100mg trandate otc. Topic for Discussions the racial issues are not forgone and forgotten, rather rampant worldwide and the learners of this subcontinent seem to be aware of the discriminations enacted by the issues of race, color, gender and so on. In Bangladesh, most discrimination towards girls occurs due to predetermined notions of race and color. Moreover, in a developing country like Bangladesh students come to tertiary level from all strata of society. The students who come from villages or Bengali Medium background are by and large discriminated. Findings After the methodology was applied in the class, the reaction of the students was noted down. They were asked few questions (see Appendix-3) based on the classes in which two poems were used as materials and invited to express their opinion on them. Personal Experience "I loved the personal touch of the poet that is found in "Krishnakali", said a student. Scholar Using Poems of Jibanananda Das and Rabindranath Tagore in the Language Classrooms of Bangladesh 50 Since the students have known the poems "Banalata Sen" and "Krishnakali" from their childhood in Bengali, finding the poems in English gives them a sense of prestige and confidence, for they can now share their ideas in English amongst friends. Poetry can be used only in few classes to remove the boredom of the students and to make the language learning enjoyable. However, poetry cannot be used always to teach the other formal aspects of the English language. We posit that a language classroom would be more interacting and interesting if we could use authentic and contextualized materials. Our teachers would do their best to select and use materials, not culturally alienating or shocking, in the classroom where the learners would keep their anxiety level normal and not be engaged in rote learning. Scholar Using Poems of Jibanananda Das and Rabindranath Tagore in the Language Classrooms of Bangladesh 51 revise our materials while teaching Bangladeshi learners English, applying eclectic methods at our discretion. We are well aware that selecting and using literary texts for language teaching is not an easy job to accomplish. However, if selected sensibly and used pragmatically, considering linguistic, cultural and pedagogical implications, it would be a great experience in the context of language learning and teaching for both the learners and the teachers. To conclude we can state that using poems in the language class can be entertaining and engaging if the learners find interest in the texts and are able to relate them to their personal experience, cultural orientations, and social backgrounds. In fact, a culturally common text that has literary qualities and that the learners are familiar with in their mother tongue can enhance their linguistic skills. Scholar Using Poems of Jibanananda Das and Rabindranath Tagore in the Language Classrooms of Bangladesh 52 Secondary level in Bangladesh- A Communicative Approach to Curriculum Development. The Inward Ear: Poetry in the Language Classroom: Cambridge Handbooks for Language Teachers. I remember a cloud-laden day and a glance from her eyes, her veil trailing down at her feet her braided hair loose on her back. Scholar Using Poems of Jibanananda Das and Rabindranath Tagore in the Language Classrooms of Bangladesh 54 She is the surprise of cloud in the burning heart of May, a tender shadow on the forest in the stillness of sunset hour, a mystery of dumb delight in the rain-loud night of June. As in a far-off sea, the ship-wrecked mariner, lonely, and no relief in sight, Sees in a cinnamon isle sings of a lush grass-green valley, Did I see her in darkness; said she, "Where had you been Which poem did you like more out of Give reasons for your choice Did you like the idea of using poetry Do you think it is helpful to use Language in India Scholar Using Poems of Jibanananda Das and Rabindranath Tagore in the Language Classrooms of Bangladesh 56 5. Did you like the methodology of Who do you like more- Banalata or Comment on the use of lexis. Scholar and English Language Teacher the English and Foreign Languages University Hyderabad-500605 Andhra Pradesh India mehedi 08@hotmail.
Laser treatments are effective at preventing or slowing the progress of wet type degeneration by sealing the leaking blood vessels blood pressure chart american heart association generic 100 mg trandate overnight delivery, but no treatment restores vision loss hypertension 2 symptoms cheap trandate online american express. Diabetic retinopathy is a degenerative disease of the retina and a leading cause of blindness associated with diabetes mellitus pulse pressure therapy trandate 100 mg lowest price. The background type (the earliest phase) is marked by microaneurysms blood pressure by palpation purchase genuine trandate, intraretinal dot-like hemorrhages, exudates (as a result of leaky vessels), cotton-wool spots, and macular edema. The proliferative type is characterized by neovascularization (proliferation of new, abnormal vessel growth) of the retina and optic disk, which may project into the vitreous, proliferation of fibrous tissue, vitreous hemorrhage, and retinal detachment. It can be treated with laser photocoagulation to seal off leaking blood vessels and destroy new growth. Aqueous Humor Is formed by the ciliary processes and provides nutrients for the avascular cornea and lens. Passes through the pupil from the posterior chamber (between the iris and the lens) into the anterior chamber (between the cornea and the iris) and is drained into the scleral venous plexus through the canal of Schlemm at the iridocorneal angle. Its impaired drainage causes an increased intraocular pressure, leading to atrophy of the retina and blindness. The increased pressure causes impaired retinal blood flow, producing retinal ischemia or atrophy of the retina; degeneration of the nerve fibers in the retina, particularly at the optic disk; defects in the visual field; and blindness. Glaucoma can be treated by surgical iridectomy or laser iridotomy for drainage of aqueous humor or by use of drugs to inhibit the secretion of aqueous humor. Is held in position by radially arranged zonular fibers (suspensory ligament of the lens), which are attached medially to the lens capsule and laterally to the ciliary processes. Flattens to focus on distant objects by pulling the zonular fibers and becomes a globular shape to accommodate the eye for near objects by contracting the ciliary muscle and thus relaxing zonular fibers. Cataract is a clouding (opacity or milky white) of the crystalline eye lens or of its capsule, which must be removed. It results in little light being transmitted to the retina, causing blurred images and poor vision. It is caused by the loss of elasticity of the crystalline lens, occurs in advanced age and is corrected with bifocal lenses. Neuroectoderm of the diencephalon evaginates to form the optic vesicle, which in turn invaginates to form the optic cup and optic stalk. Surface ectoderm invaginates to form the lens placode, which forms the lens and anterior epithelium of cornea. Mesoderm forms the sclera, portions of the cornea, vitreous body, and extraocular muscles. Neural crest cells form the choroids, sphincter pupillae muscle, dilator pupillae muscle, and ciliary muscle. Oral Vestibule Is bounded by lips and cheeks externally and teeth and gums internally and receives opening of parotid duct at the parotid papilla opposite second maxillary molar. Is bounded anteriorly and laterally by teeth and gums, its roof is formed by the palate, and its floor is formed by the tongue and the mucosa, supported by the geniohyoid and mylohyoid muscles. Hard Palate Is the anterior four-fifths of the palate and forms a bony framework covered with a mucous membrane between the nasal and oral cavities. Consists of the palatine processes of the maxillae and horizontal plates of the palatine bones. Contains the incisive foramen in its median plane anteriorly and the greater and lesser palatine foramina posteriorly. Receives sensory innervation through the greater palatine and nasopalatine nerves and blood from the greater palatine artery. Soft Palate Is a fibromuscular fold extending from the posterior border of the hard palate and makes up one-fifth of the palate. Moves posteriorly against the pharyngeal wall to close the oropharyngeal (faucial) isthmus when swallowing or speaking. Receives blood from the greater and lesser palatine arteries of the descending palatine artery of the maxillary artery, the ascending palatine artery of the facial artery, and the palatine branch of the ascending pharyngeal artery. Receives sensory innervation through the lesser palatine nerves and receives skeletal motor innervation from the vagus nerve. Lesion of the vagus nerve causes deviation of the uvula toward the opposite side of the lesion on phonation because of paralysis of the musculus uvulae. Is divided by a V-shaped sulcus terminalis into two parts-an anterior two-thirds and a posterior one-third-which differ developmentally, structurally, and in innervation.
The nerves of the second to sixth pharyngeal arches have little cutaneous distribution arrhythmia definition medical buy trandate online. The endoderm of the pharynx lines the internal aspects of the pharyngeal arches and passes into diverticula-the pharyngeal pouches blood pressure chart emergency trandate 100mg with amex. The first pair of pouches blood pressure 7030 effective trandate 100mg, for example heart attack 3 28 demi lovato heart attack single pop purchase trandate 100mg, lies between the first and second pharyngeal arches. There are four well-defined pairs of pharyngeal pouches; the fifth pair is rudimentary or absent. The endoderm of the pouches contacts the ectoderm of the pharyngeal grooves and together they form the double-layered pharyngeal membranes that separate the pharyngeal pouches from the pharyngeal grooves. Derivatives of the Pharyngeal Pouches the endodermal epithelial lining of the pharyngeal pouches gives rise to important organs in the head and neck. The First Pharyngeal Pouch the first pharyngeal pouch expands into an elongate tubotympanic recess. The expanded distal part of this recess contacts the first pharyngeal groove, where it later contributes to the formation of the tympanic membrane (eardrum). The cavity of the tubotympanic recess becomes the tympanic cavity and mastoid antrum. The connection of the tubotympanic recess with the pharynx gradually elongates to form the pharyngotympanic tube (auditory tube). The Second Pharyngeal Pouch Although the second pharyngeal pouch is largely obliterated as the palatine tonsil develops, part of the cavity of this pouch remains as the tonsillar sinus or fossa. The endoderm of the second pouch proliferates and grows into the underlying mesenchyme. The central parts of these buds break down, forming tonsillar crypts (pitlike depressions). The pouch endoderm forms the surface epithelium and the lining of the tonsillar crypts. At approximately 20 weeks, the mesenchyme around the crypts differentiates into lymphoid tissue, which soon organizes into the lymphatic nodules of the palatine tonsil. B, Sketch of the head and neck regions of a 20-week fetus showing the superficial distribution of the two caudal branches of the first arch nerve (cranial nerve V). C, Sagittal section of the fetal head and neck showing the deep distribution of sensory fibers of the nerves to the teeth and mucosa of the tongue, pharynx, nasal cavity, palate, and larynx. The third pharyngeal pouch expands and develops a solid, dorsal bulbar part and a hollow, elongate ventral part. By the sixth week, the epithelium of each dorsal bulbar part of the pouch begins to differentiate into an inferior parathyroid gland. The epithelium of the elongate ventral parts of the pouch proliferates, obliterating their cavities. The bilobed form of this lymphatic organ remains throughout life, discretely encapsulated; each lobe has its own blood supply, lymphatic drainage, and nerve supply. The developing thymus and parathyroid glands lose their connections with the pharynx. The brain and associated structures expand rostrally while the pharynx and cardiac structures generally expand caudally. This causes the derivatives of pharyngeal pouches two to four to become displaced caudally. Later, the parathyroid glands separate from the thymus and lie on the dorsal surface of the thyroid gland. Histogenesis of the Thymus this primary lymphoid organ develops from epithelial cells derived from endoderm of the third pair of pharyngeal pouches and from mesenchyme into which epithelial tubes grow. The tubes soon become solid cords that proliferate and give rise to side branches. Some cells of the epithelial cords become arranged around a central point, forming small groups of cells-the thymic corpuscles (Hassall corpuscles). Other cells of the epithelial cords spread apart but retain connections with each other to form an epithelial reticulum.
Carotid endarterectomy is the excision of atherosclerotic thickening of intima of the internal carotid artery for the prevention of stroke in patients with symptoms of obstructive disease of the carotid artery heart arrhythmia 4 year old purchase trandate on line amex. In the middle cranial fossa blood pressure yoga ramdev trandate 100 mg mastercard, gives rise to the ophthalmic artery and the anterior and middle cerebral arteries and participates in the formation of the circulus arteriosus (circle Chapter 8 Head and Neck 333 of Willis) blood pressure kit walgreens order trandate 100mg on line, which is an important polygonal anastomosis between four arteries: the two vertebrals and the two carotids low pressure pulse jet bag filter discount trandate 100mg online. It is formed by the posterior cerebral, posterior communicating, internal carotid, anterior cerebral, and anterior communicating arteries. External Carotid Artery Extends from the level of the upper border of the thyroid cartilage to the neck of the mandible, where it ends in the parotid gland by dividing into the maxillary and superficial temporal arteries. Superior Thyroid Artery Arises below the level of the greater horn of the hyoid bone. Descends obliquely forward in the carotid triangle and passes deep to the infrahyoid muscles to reach the superior pole of the thyroid gland. Gives rise to an infrahyoid, sternocleidomastoid, superior laryngeal, cricothyroid, and several glandular branches. Arises at the level of the tip of the greater horn of the hyoid bone and passes deep to the hyoglossus to reach the tongue. Arises just above the lingual artery and ascends forward, deep to the posterior belly of the digastric and stylohyoid muscles. Hooks around the lower border of the mandible at the anterior margin of the masseter to enter the face. Arises from the deep surface of the external carotid artery in the carotid triangle and ascends between the internal carotid artery and the wall of the pharynx. Arises from the posterior surface of the external carotid artery, just above the level of the hyoid bone. Passes deep to the digastric posterior belly, occupies the groove on the mastoid process, and appears on the skin above the occipital triangle. Gives rise to the following: (1) Sternocleidomastoid Branch Descends inferiorly and posteriorly over the hypoglossal nerve and enters the substance of the muscle. Its deep branch anastomoses with the deep cervical artery of the costocervical trunk. Arises from the posterior surface of the external carotid artery just above the digastric posterior belly. Ascends superficial to the styloid process and deep to the parotid gland and ends between the mastoid process and the external acoustic meatus. Arises behind the neck of the mandible as the larger terminal branch of the external carotid artery. Arises behind the neck of the mandible as the smaller terminal branch of the external carotid artery. Ascends in front of the external acoustic meatus into the scalp, accompanying the auriculotemporal nerve and the superficial temporal vein. Temporal (giant cell) arteritis is granulomatous inflammation with multinucleated giant cells, affecting the medium-sized arteries, especially the temporal artery. Symptoms include severe headache, excruciating pain in the temporal area, temporal artery tenderness, visual impairment, transient diplopia, jaw claudication, fever, fatigue, and weight loss. Its cause is unknown, but it is diagnosed by a temporal artery biopsy and can be treated with corticosteroids such as prednisone. Is formed by the union of the posterior auricular vein and the posterior branch of the retromandibular vein. Crosses the sternomastoid obliquely under the platysma and ends in the subclavian (or sometimes the internal jugular) vein. Internal Jugular Vein (Figure 8-7) Begins in the jugular foramen as a continuation of the sigmoid sinus, descends in the carotid sheath, and ends in the brachiocephalic vein. Has the superior bulb at its beginning and the inferior bulb just above its termination. Subclavian artery Descending aorta Recurrent laryngeal nerve Ascending aorta Central venous line is an intravenous needle and catheter placed into a large vein such as the internal jugular or subclavian vein to give fluids or medication. A central line is inserted in the apex of the triangular interval between the clavicle and the clavicular and sternal heads of the sternocleidomastoid muscle into the internal jugular vein through which the catheter is threaded into the superior vena cava (a large central vein in the chest).
Purchase 100 mg trandate with mastercard. This is what happens to your lungs lungs and air when you diffuse essential oils.