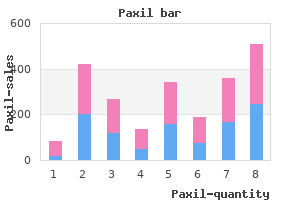
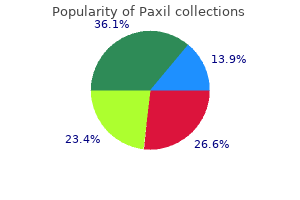
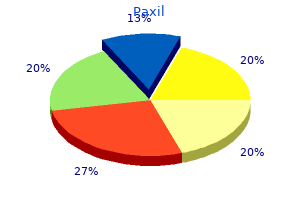
Paxil
"Order 10mg paxil amex, medications that cause tinnitus".
By: D. Kent, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Medical Instructor, Palm Beach Medical College
Even though the mechanism of the high mortality is not known treatment gastritis purchase 40 mg paxil, it is clear that a judicious approach to diagnosis and treatment of hypernatremia is imperative (Box 8 treatment action group buy paxil 40 mg with amex. Detailed clinical examples showing the step-by-step approach to hypernatremia are shown in Cases 8 treatment 3 nail fungus cheap 20 mg paxil fast delivery. As discussed earlier medicine used to treat chlamydia order paxil now, neurologic sequelae can occur both with hypernatremia and with its correction. Decreased cell volume impairs tissue function, and overly rapid correction can cause cerebral edema if adaptation has occurred. In addition to the adverse central nervous system effects, hypernatremia also inhibits insulin release and increases insulin resistance, thereby predisposing patients to hyperglycemia. Hypernatremia also decreases hepatic gluconeogenesis, lactate clearance, and cardiac function. Adverse sequelae associated with hypernatremia are often underappreciated and frequently lead to a delay in treatment. Studies have shown that fewer than 50% of patients with hospital-acquired hypernatremia receive free water replacement within 24 hours of the first identified elevated serum [Na+], and the majority take longer than 72 hours to treat. Furthermore, patients whose hypernatremia is corrected within 72 hours had a lower mortality than those whose hypernatremia was not corrected within 72 hours. Chassagne P, Druesne L, Capet C, et al: Clinical presentation of hypernatremia in elderly patients: a case control study, J Am Geriatr Soc 54:1225-1230, 2006. Liamis G, Kalogirou M, Saugos V, et al: Therapeutic approach in patients with dysnatraemias, Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:1564-1569, 2006. Lindner G, Funk G, Schwarz C, et al: Hypernatremia in the critically ill is an independent risk factor for mortality, Am J Kidney Dis 50:952957, 2007. Polderman K, Schreuder W, van Schijndel R, et al: Hypernatremia in the intensive care unit: an indicator of quality of care? The anticonvulsant topiramate also inhibits carbonic anhydrase and therein can cause metabolic acidosis. Unless other treatment options do not exist, patients with a history of renal calculi or known renal tubular acidosis should not receive topiramate except with caution. Chlorothiazide, which became available in 1958, ushered in the modern era of diuretic therapy, initially for the treatment of edematous states and shortly thereafter for the treatment of hypertension. Diuretics are currently recommended as a first-line therapy for the treatment of hypertension by the Joint National Commission on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of Hypertension of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program. In addition, they remain an important element of the treatment regimen for volume overload states, such as nephrotic syndrome, cirrhosis, and heart failure, because they improve the congestive symptomatology that typifies these disease states. This chapter reviews the various diuretic classes and the physiologic adaptations that accompany their use, and establishes the basis for their use in the treatment of volume overload and hypertension. Thiazides also inhibit NaCl and fluid reabsorption in the medullary-collecting duct. In addition to these varied effects on Na+ excretion, thiazide diuretics impair urinary diluting capacity without affecting urinary concentrating mechanisms, reduce calcium (Ca++) and urate excretion, and increase magnesium (Mg++) excretion. This latter feature creates a depot for chlorthalidone streaming (red cell plasma tubular secretion). Diuretic classes of note include proximal tubular, distal tubular, and loop diuretics, potassium (K+)sparing agents, and osmotic diuretics. Its use is constrained by its transient action and because prolonged use results in a metabolic acidosis. Notably, acetazolamide at doses of 250 to 500 mg daily can correct the metabolic alkalosis that sometimes occurs with thiazide or loop diuretic therapy. Color patterns identify sites of action along the nephron and corresponding cell types affected. Spironolactone and eplerenone (not shown) are competitive mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists and act primarily in the cortical collecting tubule. V2 receptors facilitate insertion of aquaporin-2 water channels in the apical membrane.
Diseases
- Mucormycosis
- Ankylosis of teeth
- Pneumonoultramicroscopicsilicovolcanoconiosis
- Juvenile temporal arteritis
- Gelatinous ascites
- Spastic paraplegia type 4, dominant
- 3-hydroxy 3-methyl glutaryl-coa lyase deficiency
- Keratoderma palmoplantar deafness
- Hypertrichosis atrophic skin ectropion macrostomia
- Microcephaly lymphoedema syndrome
Perpetrators are more often male than female and include parents treatment of uti discount 30 mg paxil, relatives medicine quiz buy 10mg paxil with mastercard, teachers treatment 5th toe fracture cheap paxil 20 mg without a prescription, family friends treatment zygomycetes cheap 40mg paxil with amex, members of the clergy, and other individuals who have access to children. All perpetrators strive to keep the child from disclosing the abuse and often do so with coercion or threats. Approximately 80% of victims are girls, although the sexual abuse of boys is underrecognized and underreported. Children generally come to attention after they have made a disclosure of their abuse. They may disclose to a nonoffending parent, sibling, relative, friend, or teacher. Children commonly delay disclosure for many weeks, months, or years after their abuse, especially if the perpetrator has ongoing access to the child. Sexual abuse also should be considered in children who have behavioral problems, although no behavior is pathognomonic. Hypersexual behaviors should raise the possibility of abuse, although some children with these behaviors are exposed to inappropriate sexual behaviors on television or videos or by witnessing adult sexual activity. Sexual abuse occasionally is recognized by the discovery of an unexplained vaginal, penile, or anal injury or by the discovery of a sexually transmitted infection. In most cases, the diagnosis of sexual abuse is made by the history obtained from the child. Many communities have systems in place to ensure quality investigative interviews of sexually abused children. However if no other professional has spoken to the child about the abuse, or the child makes a spontaneous disclosure to the physician, the child should be interviewed with questions that are open-ended and non-leading. In all cases, the child should be questioned about medical issues related to the abuse, such as timing of the assault and symptoms (bleeding, discharge, or genital pain). The physical examination should be complete, with careful inspection of the genitals and anus. Most sexually abused children have a normal genital examination at the time of the medical evaluation. Genital injuries are seen more commonly in children who present for medical care within 72 hours of their most recent assault and in children who report genital bleeding, but they are diagnosed in only 5% to 10% of sexually abused children. Many types of sexual abuse (fondling, vulvar coitus, oral genital contact) do not injure genital tissue, and genital mucosa heals so rapidly and completely that injuries often heal by the time of the medical examination. For children who present within 72 hours of the most recent assault, special attention should be given to identifying acute injury and the presence of blood or semen on the child. Forensic evidence collection is needed in a few cases and has the greatest yield when collected in the first 24 hours after an acute assault. Few findings are diagnostic of sexual assault, but findings with the most specificity include acute, unexplained lacerations or ecchymoses of the hymen, posterior fourchette or anus, complete transection of the hymen, unexplained anogenital scarring, or pregnancy in an adolescent with no other history of sexual activity. Universal screening for sexually transmitted infections for prepubertal children is unnecessary because the risk of infection is low in asymptomatic young children. The type of assault, identity and known medical history of the perpetrator, and the epidemiology of sexually transmitted infections in the community also are considered. The diagnosis of most sexually transmitted infections in young children requires an investigation for sexual abuse (see Chapter 116). Crimes that are committed against children also are investigated by law enforcement, so the police become involved in some, but not all, cases of suspected abuse. Physicians occasionally are called to testify in court hearings regarding civil issues, such as dependency and 74 Section 5 u Psychosocial Issues pregnancy and continue through early childhood may reduce the risk of abuse and neglect. Physician training in screening for risk factors in parents has shown to be supportive of families and reduce child maltreatment in some populations. Ultimately physicians always need to remain cognizant of the diagnosis, aware of their professional mandates, and willing to advocate on behalf of these vulnerable patients. Visiting home nursing programs that begin during Yes Is history consistent with injuries?
Furthermore medicine video buy paxil 10mg visa, those patients who continue to experience active disease generally have only mild to moderate symptoms medications you can give dogs purchase paxil 10mg with mastercard. The mechanisms responsible for this apparent remission of systemic lupus in kidney failure remain unclear treatment 5th metatarsal fracture purchase discount paxil on-line. Patients with end-stage renal disease due to lupus nephritis should be dialyzed for at least 3 to 6 months before kidney transplantation is performed; this recommendation holds particular importance for those patients with relatively rapid progression to kidney failure symptoms tracker order 20mg paxil overnight delivery. This period allows for a potential further reduction in lupus activity before transplantation and affords patients with acute kidney injury sufficient time to recover kidney function if therapy is effective. Overall graft survival in patients with lupus who receive a kidney transplant is similar to those in patients with other kidney diseases, despite a recurrence rate of lupus nephritis that ranges from 5% to 30% depending on the indications for kidney allograft biopsy. Recurrence can occur as early as the first week to as late as 10 to 15 years after transplantation. Recurrent lupus nephritis does not necessarily follow the pattern of the native disease but often takes the form of a milder, nonproliferative lesion. Miyasaka N, Kawai S, Hashimoto H: Efficacy and safety of tacrolimus for lupus nephritis: a placebo-controlled double-blind multicenter study, Mod Rheumatol 19:606-615, 2009. The mortality rate of patients with diabetic nephropathy is high, with a marked increase in cardiovascular risk accounting for more than half of the increased mortality risk among these patients. Accordingly, there has been intensive research into early pathophysiologic mechanisms of diabetic kidney injury, predictors of risk for diabetic nephropathy, and early intervention strategies. Studies in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes have shown that improved glycemic control can reduce the risk of diabetic nephropathy. Moreover, the development of the earliest diabetic kidney lesions can be slowed or prevented by strict glycemic control, as was demonstrated in a randomized trial in type 1 diabetic kidney transplant recipients. Similarly, intensive insulin treatment decreased the progression rates of glomerular lesions in a controlled trial in microalbuminuric type 1 diabetic patients. Finally, established diabetic glomerular lesions in the native kidneys of type 1 diabetic patients regressed with prolonged normalization of glycemic levels after successful pancreas transplantation. In sum, these studies strongly suggest that hyperglycemia is necessary for the development and maintenance of diabetic nephropathy, as correction of hyperglycemia allows expression of reparative mechanisms that facilitate healing of the original diabetic glomerular injury. Although hemodynamic mechanisms may be also involved in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy, patients with other causes of hyperfiltration (such as unilateral nephrectomy) do not develop diabetic lesions. Therefore, glomerular hyperfiltration alone cannot fully explain the genesis of the early lesions of diabetic nephropathy; however, clinical observations do suggest that hemodynamic factors may be important in modulating the rate of progression of diabetic lesions that are already well established. Systemic blood-pressure levels and a lack of normal nocturnal blood-pressure dipping both may be implicated in the progression and genesis of diabetic nephropathy. Supporting this hypothesis is the association between intensive blood-pressure control and decreased rates of progression from normoalbuminuria to microalbuminuria and from microalbuminuria to proteinuria in both normotensive and hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients. Genetic predisposition to diabetic nephropathy has been strongly suggested in multiple cross-sectional studies in type 1 and type 2 diabetic siblings concordant for diabetes. Importantly, diabetic sibling pairs, known to be concordant for diabetic nephropathy risk, are also highly concordant for diabetic glomerulopathy lesions, and this risk is in part independent of glycemia. Accordingly, there are ongoing searches for genetic loci related to diabetic nephropathy susceptibility through genomic scanning and candidate gene approaches. There is also growing evidence that oxidative stress is increased in diabetes and is related to diabetic nephropathy, mediated through altered nitric oxide production and action, and endothelial dysfunction. The same time frame is present when a normal kidney is transplanted into a diabetic patient. The changes in kidney structure caused by diabetes are specific, creating a pattern not seen in any other disease, and the severity of these diabetic lesions is related to the functional disturbances of the clinical kidney disease as well as to diabetes duration, glycemic control, and genetic factors. However, the relationship between the duration of type 1 diabetes and extent of glomerular pathology is not precise. This is consistent with the marked variability in susceptibility to this disorder, such that some patients may develop kidney failure after having diabetes for 15 years whereas others escape kidney complications despite having type 1 diabetes for decades. In about 40% to 50% of patients developing proteinuria, there are areas of extreme mesangial expansion called Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules (nodular mesangial expansion). Mesangial cell nuclei in these nodules are palisaded around masses of mesangial matrix material with compression of surrounding capillary lumina. Nodules are thought to result from earlier glomerular capillary microaneurysm formation. Notably, about half of patients with severe diabetic nephropathy do not have these nodular lesions; therefore, although Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules are diagnostic of diabetic nephropathy, they are not necessary for severe kidney disease to develop. The severity of these lesions is directly related to the frequency of global glomerulosclerosis, perhaps as the result of glomerular ischemia.
More sensitive and specific tests for light chains symptoms 8 days after iui generic paxil 30 mg mastercard, such as immunoelectrophoresis or immunoprecipitation medicine 4 you pharma pvt ltd purchase genuine paxil line, are preferred 5 medications related to the lymphatic system paxil 10mg mastercard. If the urine is very concentrated symptoms neuropathy paxil 20 mg with amex, the presence of a modest protein reaction is less likely to correspond to significant proteinuria in a 24-hour collection or when assessed by spot urine protein:creatinine ratio. Even so, it is unlikely that a 3+ or 4+ reaction would be seen solely because of a high urine concentration or, conversely, that the urine would be dilute enough to yield a negative reaction despite significant proteinuria. The protein indicator used for routine dipstick analysis is not sensitive enough to detect microalbuminuria. False-positive reactions occur if the urine is contaminated with other oxidants such as povidone-iodine, hypochlorite, or bacterial peroxidase. A urine sample that is positive for blood by dipstick analysis, but shows no red cells on microscopic examination, is suspect for myoglobinuria or hemoglobinuria. Pink discoloration of serum may occur with hemolysis, but free myoglobin is seldom present in a concentration sufficient to change the color of plasma. However, the degree of glycosuria occurring in diabetic ketoacidosis is sufficient to prevent false-negative results despite ketonuria. False-positive results may occur in patients who are taking levodopa or drugs such as captopril or mesna that contain free sulfhydryl groups. In obstructive jaundice, bilirubin does not reach the bowel, and urinary excretion of urobilinogen is diminished. The urobilinogen test is based on the Ehrlich reaction in which diethylaminobenzaldehyde reacts with urobilinogen in acid medium to produce a pink color. Sulfonamides may produce false-positive results, and degradation of urobilinogen to urobilin may yield false-negative results. False-positive results may be observed in patients receiving chlorpromazine or phenazopyridine. False-negative results occur with infection with enterococcus or other organisms that do not produce nitrite, when ascorbate is present, or when urine has not been retained in the bladder long enough (approximately 4 hours) to permit sufficient production of nitrite from nitrate. False-negative results occur with glycosuria, high specific gravity, cephalexin or tetracycline therapy, or excessive oxalate excretion. Contamination with vaginal material may yield a positive test result without true urinary tract infection. The most accurate screening occurs when first morning specimens are examined, because exercise can increase albumin excretion. One type of dipstick uses colorimetric detection of albumin bound to gold-conjugated antibody. Normally, the urine albumin concentration is less than the 20 mcg/L detection threshold for these strips. Unless the urine is very dilute, a patient with no detectable albumin by this method is unlikely to have microalbuminuria. Because urine concentration varies widely, however, this assay has the same limitations as any test that only measures concentration. This strip is useful only as a screening test, and more formal testing is required if albuminuria is found. A second type of dipstick has tabs for measurement of both albumin and creatinine concentration that permits calculation of the albumin-to-creatinine ratio. In contrast to the other dipstick tests described in this chapter, these strips cannot be read by simple visual comparison with a color chart. When present on more than one determination, an albumin-to-creatinine ratio of 30 to 300 mcg/mg signifies microalbuminuria. The accuracy and reproducibility of this semiquantitative method depends on using the correct volume of urine. Twelve milliliters of urine should be spun in a conical centrifuge tube for 5 minutes at 1500 to 2000 rpm (450 g). The pellet is resuspended in the few drops of urine that remain in the tube after inversion by flicking the base of the tube gently with a finger or with the use of a pipette. The drop should be of sufficient size so that a standard 22 Ч 22 mm coverslip just floats on the urine with a thin rim of urine at the edges. If an excess of urine is applied, it will spill onto the microscope objective or stream distractingly under the coverslip. Rapid commercial urine stains, or the Papanicolaou stain, may be used to enhance detail. When the urine is dilute and few formed elements are present, detection of motion of objects suspended in the urine ensures that the focal plane is correct.
Buy paxil without a prescription. The Shed Roof - An Architect's Review of a Modern Classic.