Lansoprazole
"Cheap lansoprazole 15 mg with amex, gastritis in spanish".
By: S. Rasul, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Deputy Director, University of Nevada, Reno School of Medicine
Provision of services and assistance during or immediately after a specific emergency in order to save lives gastritis eating before bed order lansoprazole canada, reduce health impacts chronic gastritis symptoms treatment lansoprazole 15 mg on-line, ensure public safety gastritis diet 50 purchase lansoprazole 15mg free shipping, maintain human dignity and meet the basic subsistence needs of the people affected gastritis diet mayo clinic 15mg lansoprazole otc. Procuring the undocumented entry of a person into a State of which the person is not a national or permanent resident, in exchange for a direct or indirect financial or other material benefit. These effects can be economic, socio-cultural, institutional, environmental, technological or of other types. Glossary 108 Inclusive In humanitarian action refers to actions taken to ensure the right to information, protection and assistance for all persons affected by crisis, irrespective of age, sexual and gender identity, disability status, nationality, or ethnic, religious or social origin or identity. Inclusive action focuses on identifying and removing barriers so that those individuals and groups who are more vulnerable, marginalized and/or excluded can participate in decision-making and benefit from humanitarian action on an equal basis with others. Scientific approach and practical solution designed to prevent harm caused by infection to patients and health workers. Intentional combining of two or more sector interventions in the design and implementation of programmes to achieve humanitarian outcomes. Persons or groups of persons who have been forced or obliged to flee or leave their homes, or places of habitual residence, in particular as a result of armed conflict, situations of generalized violence, violations of human rights or natural or human-made disasters, and who have not crossed an internationally recognized state border. This reflects a number of considerations, including: the number of people arriving, the economic, social and geographical context, the capacity of a receiving State to respond and the impact of a movement that is sudden or prolonged. Level 2: the scale of an emergency is such that a country office needs additional support from other parts of the organization (headquarters, regional office and country offices) to respond and that the regional office must provide leadership and support. It focuses on a healthy start to life and targets the needs of people at critical periods throughout their lifetime. It adopts a temporal and societal perspective on the health of individuals and generations, including intergenerational determinants of health. Skills and abilities that enable individuals to adapt to and deal effectively with the demands and challenges of everyday life. They help people think, feel, act and interact as individuals and as participating members of society. Any type of local or outside support that aims to protect or promote psychosocial well-being and prevent or treat mental health conditions. Glossary 110 Negotiations Process of influencing individuals or groups through joint decision-making. It requires the consent of all parties to participate in the process and to accept and respect the agreed outcome. Processes and activities that allow crisis-affected people to play an active role in all decision-making processes that affect them. It includes a multidimensional range of measures and interventions that seek to reduce the risk of lapse or relapse into violent conflict, by addressing the dynamics and underlying causes and consequences of conflict, and by strengthening national capacities to lay the foundations for sustainable peace and resilient development. Glossary 111 (Emergency) Preparedness Mechanisms and systems put in place in advance to enable an effective and timely emergency response to humanitarian crisis, based on analysis of the risks in a particular context, taking into account national and regional capacities. Approach that involves determining which programmes are the most critical in a given part of a country (in terms of saving lives or requiring immediate delivery) and therefore warrant accepting a greater level of risk or a greater allocation of resources to mitigate these risks. The term "sexual abuse" means the actual or threatened physical intrusion of a sexual nature, whether by force or under unequal or coercive conditions. In the humanitarian sector, quality means effectiveness (impact), efficiency (timeliness and costs), appropriateness (taking account of rights, needs, culture, age, gender, disabilities and context), and equity (non-discrimination and equal access) of elements of a humanitarian response. Glossary 112 Refugees All persons who are outside their country of origin who have been granted protection in another country for reasons of a well-founded fear of persecution on one of the grounds listed in the 1951 Convention (on account of race, religion, nationality, membership in a particular social group, or political opinions), or because a conflict, generalised violence or other circumstances that have seriously disturbed public order, and who, as a result, require international protection. It is the probability of external and internal threats occurring in combination with the existence of individual vulnerabilities. Risk management includes activities to realize opportunities while mitigating the negative consequences of events. It is based on a robust analysis of shocks (sudden and potentially damaging phenomenon or hazard) and stresses (chronic in nature and can occur over a longer period of time) as well as the underlying vulnerabilities and capacities in a given risk-prone, conflict-affected or fragile context. It recognizes the collectively experienced security threats and the importance of collaboration to ensure the safe delivery of humanitarian and development assistance. It can be physical, emotional, psychological, or sexual in nature, and can take the form of a denial of resources or access to services. Groups can be distinguished in terms of regional, ethnic or socio-cultural identities, religious and political beliefs, social class or economic sector, or on the basis of characteristics such as gender and age.
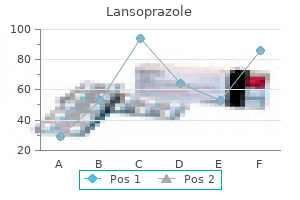
Lowering the target range represents an "easing" of monetary policy gastritis diet zinc buy generic lansoprazole 30mg on line, while increasing the target range is a "tightening" of policy gastritis and duodenitis purchase lansoprazole 30mg amex. Longer-term interest rates and the prices for a wide range of financial and nonfinancial assets gastritis on x ray discount 15mg lansoprazole fast delivery, including stocks gastritis vs heart attack lansoprazole 15 mg visa, bonds, and real estate, respond to changes in the current and expected path of the federal funds rate. That is, medium- and longerterm interest rates are affected by how people expect the federal funds rate to change in the future. The federal funds rate over time the effective federal funds rate is the interest rate at which depository institutions-banks, savings institutions (thrifts), and credit unions-and government-sponsored enterprises borrow from and lend to each other overnight to meet short-term business needs. The target for the federal funds rate-which is set by the Federal Open Market Committee-has varied widely over the years in response to prevailing economic conditions. The level of longer-term interest rates affects household and business spending decisions, which in turn influence the level of economic output, employment, and inflation. For example, lowering mortgage rates will make buying a house more affordable, encouraging some individuals who were previously renters to purchase homes. As more individuals purchase homes, employment rises among homebuilders and many other types of home-supply industries. Lower mortgage rates may also allow some existing homeowners to refinance their mortgages at lower rates and thus free up income for spending on many other types of goods and services. In addition, lower interest rates on consumer loans may spur greater spending on durable goods (long-lasting manufactured goods) such as televisions and automobiles. The increased demand for all goods and services will boost employment across a variety of industries. Corresponding to the increased demand and change in employment, prices will adjust. Anticipated Factors Many factors affect spending, output, employment, and inflation. For example, the government influences demand in the economy through changes in taxes and spending programs, which are often anticipated. Indeed, the economic effects of a tax cut may precede its actual implementation if businesses and households increase their spending in anticipation of lower taxes. In addition, forward-looking financial markets may build anticipated fiscal events into the level and structure of interest rates. Demand Shocks Other factors that affect spending on goods and services can come as a surprise and can influence the economy in unforeseen ways. Examples of these "demand shocks" include shifts in consumer and business confidence or unexpected changes in the credit standards that banks and other lenders apply when they consider making loans. This public health crisis disrupted economic activity, significantly affected financial conditions, and posed risks to the economic outlook. Because traditional changes in the stance of monetary policy affect the economy with a lag, policy actions today may take several quarters or more before their effects on spending and inflation take hold. Conducting Monetary Policy 27 Supply Shocks Other shocks can affect the production of goods and services and their prices by altering the costs associated with production or the technology used in production. Examples of such "supply shocks" include crop losses due to extreme weather and slowdowns in productivity growth relative to what would have occurred otherwise-these sorts of adverse supply shocks tend to raise prices and reduce output (and also employment). A disruption in the oil market that reduces the supply of oil and increases its price substantially can also raise other prices and reduce output because oil is an input to the production of many products. In the face of these adverse supply shocks, policymakers can attempt to counter the loss of output by easing monetary policy and making financial conditions more conducive to spending; alternatively, policymakers can attempt to counter the rise in prices by tightening policy. Of course, the economy can also experience beneficial supply shocks, such as technological breakthroughs or reductions in the cost of important raw materials, and these beneficial supply shocks can both lower prices and boost output. How Monetary Policy Decisions Are Made: the Deliberative Process How are monetary policy decisions made Participants also consult business, consumer, and financial industry contacts to hear their perspectives on economic and financial conditions and the outlook. The staff of the Federal Reserve Banks collect and summarize information on current economic conditions in their Districts. Economic research groups at the Reserve Banks separately brief their Bank presidents on relevant economic developments and policy choices. During the first part of the meeting, the Federal Reserve governors and Reserve Bank presidents receive briefings that review the operations of the System Open Market Desk at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York and recent economic and financial developments in the United States and abroad.
What are the requirements for educating health professionals to practice in health care delivery teams What are the obstacles to educating health professionals to practice in health care delivery teams However gastritis diet forum purchase lansoprazole 30mg without prescription, such programs remained largely elective gastritis of the antrum discount 30 mg lansoprazole with visa, dependent on this external support nervous gastritis diet generic 30 mg lansoprazole free shipping, and targeted small numbers of students gastritis skin symptoms discount lansoprazole online american express. Several intra- and interprofessional factors limited "mainstreaming" of interprofessional education during this time (Schmitt, Baldwin, & Reeves, forthcoming). Compelling larger-scale practice issues that emerged in the past decade have prompted broad-based support for changes in health professions education, including interactive learning to develop competencies for teamwork and team-based care. The focus on workforce retraining to build interprofessional teamwork and teambased care continues, particularly in the context of improving institutional quality (effectiveness) and safety (Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, 2008; Baker et al. Growing evidence supports the importance of better teamwork and team-based care delivery and the competencies needed to provide that kind of care. The passage of the Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (Steinbrook, 2009) and the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010 (Kaiser Family Foundation, 2010) has stimulated new approaches, such as the "medical home" concept, to achieving better outcomes in primary care, especially for high-risk chronically ill and other at-risk populations. Improved interprofessional teamwork and team-based care play core roles in many of the new primary care approaches. The idea of primary care and its relationship to the broader context of health is itself being reconsidered. Second, health care delivery professionals jointly with public health professionals share roles and responsibilities for addressing health promotion and primary prevention needs related to behavioral change. Third, health care professionals and public health professionals work in collaboration with others on behalf of persons, families and communities in maintaining healthy environments, including responding to public health emergencies. All of these elements link direct health care professionals more closely with their public health colleagues. Therefore, the principles from which we worked included both patientcenteredness and a community/population orientation. Teamwork training for interprofessional collaborative practice in health professions education has lagged dramatically behind these changes in practice, continually widening the gap between current health professions training and actual practice needs and realities. Recognizing that health professions schools bear the primary responsibility for developing these core competencies, considerable emphasis also was placed on better coordinated oversight processes (accreditation, licensure, and certification) and continuing education to ensure the development, demonstration, and maintenance of the core competencies. The report indicated that although the accrediting standards of most professions reviewed contained content about interdisciplinary teams, few of these were outcomes-based competency expectations. Interprofessional education, by profession Policy, curricular, and/or accreditation changes to strengthen teamwork preparation are at various stages of development among the six professions represented in this report. Pilot work is ongoing by the American Board of Internal Medicine to evaluate hospitalist teamwork skills (Chesluk, 2010). Among those competencies is "participate with dental team members and other health care professionals in the management and health promotion for all patients" (American Dental Education Association, 2008). Interprofessional education has been identified as a critical issue in dental education. Authors of a position paper have explored the rationale for interprofessional education in general dentistry and the leadership role of academic dentistry and organized dentistry in this area (Wilder et al. Accreditation standards for dental education programs adopted in August 2010 for implementation in 2013 contain language promoting collaboration with other health professionals (Commission on Dental Accreditation, 2010). National pharmacy education leaders completed intensive study of interprofessional education and its relevance to pharmacy education (Buring et al. Curricular guidance documents (American Association of Colleges of Pharmacy, 2004), a vision statement for pharmacy practice in 2015 (Maine, 2005), and accreditation requirements (Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education, 2011) now incorporate consistent language. Phrases such as "provide patient care in cooperation with patients, prescribers, and other members of an interprofessional health care team," "manage and use resources in cooperation with patients, prescribers, other health care providers, and administrative and supportive personnel," and "promote health improvement, wellness, and disease prevention in cooperation with patients, communities, at-risk populations, and other members of an interprofessional team of health care providers" appear throughout those documents. The most explicit of the four learning outcomes relevant to interprofessional education is: "Engage in collaborative and interdisciplinary approaches and teamwork for improving population health" (Association of Schools of Public Health, 2011, p. Interprofessional education has received some attention in the osteopathic medical literature. An exploratory analysis of the relationship between the principles of osteopathic medicine and interprofessional education is in press, as part of a description of a three-phase interprofessional education program underway involving one osteopathic medical school and eight other health professions (Macintosh, Adams, Singer-Chang, & Hruby, forthcoming, 2011). However, the need remains to identify, agree on, and strengthen core competencies for interprofessional collaborative practice across the professions.
Purchase lansoprazole 15mg with amex. 5 Yoga Poses for Stomach Problems | Swami Ramdev.
Syndromes
- Flank pain on one or both sides
- Serum prolactin levels
- Vision problems
- Cooked lean beef
- Nausea and vomiting
- Talk to your baby about objects and people in his or her environment
- Diabetes
- Common side effects of Tdap and Td include pain and swelling at the injection site and mild fever.
- Fasciitis
- Are in the last half of your pregnancy and notice the baby is moving less or not at all
In addition gastritis y colitis nerviosa sintomas buy generic lansoprazole 15mg on-line, urbanization is likely to exacerbate urban-rural societal divides gastritis reddit generic lansoprazole 30mg on-line, while the expanding role for local and city governance may undermine policy coherence when local and national strategies for problem solving diverge gastritis diet àâèòî discount 30mg lansoprazole mastercard. The combination of widespread public discontent and major crises or shocks could create conditions that are ripe for significant shifts or transformations in the models gastritis diet êèíîïîèñê buy 30mg lansoprazole overnight delivery, ideologies, or ways of governing. Historically, ideological shifts across regions have taken place at moments of catastrophic crisis, such as in the wake of a major war or economic collapse, because people are more willing to embrace bold systemic changes to address overarching problems. However, the emergence of a new unifying ideology or system-on the scale of communism or economic liberalism-is rare. Other stresses, such as another pandemic or a major environmental catastrophe, that expose governance shortcomings might create conditions ripe for new or alternative models to gain traction if widespread dysfunction is sustained. Pervasive discontent and major crises probably are necessary forcing functions for transformations but not sufficient. Transforming discontent into something new also requires the combination of inspiring and unifying leadership with compelling ideas or ideology to build political coalitions and garner socie- tal consensus. Short of a new ideology, new approaches-or even more combinations or blends of systems-could occur along several axes, from centralized to localized governance, from a strong state role to a strong nonstate role, from democratic to authoritarian, from secular to religious, or from nationalist to internationalist. These shifts or transformations would spur inevitable contestation between the constituencies holding onto the old orders and those embracing the new ones. The precise nature of these shifts, transformations, or new models is uncertain and difficult to foresee. Moreover, compelling new governance models or ideologies that have not yet been envisioned or identified could emerge and take hold. No single state is likely to be positioned to dominate across all regions or domains, opening the door for a broader range of actors to advance their interests. The United States and China will have the greatest influence on global dynamics, supporting competing visions of the international system and governance that reflect their core interests and ideologies. This rivalry will affect most domains, straining and in some cases reshaping existing alliances, international organizations, and the norms and rules that have underpinned the international order. In this more competitive global environment, the risk of interstate conflict is likely to rise because of advances in technology and an expanding range of targets, new frontiers for conflict and a greater variety of actors, more difficult deterrence, and a weakening or a lack of treaties and norms on acceptable use. Accelerating power shifts-as well as hardening ideological differences and divisions over governance models-are likely to further ratchet up competition. The lack of a preponderant power or global consensus on some key areas will offer opportunities for other actors to lead or pursue their own interests, especially within their regions. This more competitive environment with rapidly emerging technologies is likely to be more volatile with a heightened risk of conflict, at least until states establish new rules, norms, and boundaries for the more disruptive areas of competition. States will face a combination of highly destructive and precise conventional and strategic weapons, cyber activity targeting civilian and military infrastructure, and a confusing disinformation environment. Regional actors, including spoilers such as Iran and North Korea, will jockey to advance their goals and interests, bringing more volatility and uncertainty to the system. At the same time, states may struggle to establish stable deterrence with these new systems, particularly if the rules and treaties governing them continue to erode or lag. During the next two decades, the intensity of competition for global influence is likely to reach its highest level since the Cold War. No single state is likely to be positioned to dominate across all regions or domains, and a broader range of actors will compete to advance their ideologies, goals, and interests. Expanding technological, network, and information power will complement more traditional military, economic, and soft power aspects in the international system. These power elements, which will be more accessible to a broader range of actors, are likely to be concentrated among leaders that develop these technologies. These power dynamics are likely to produce a more volatile and confrontational geopolitical environment, reshape multilateralism, and widen the gap between transnational challenges and cooperative arrangements to address them. The United States, along with its longstanding allies, and China will have the greatest influence on global dynamics, supporting competing visions of the international system and governance that reflect their core interests and ideologies. In an even more hyperconnected world, power will include applying technology, human capital, information, and network position to modify and shape the behavior of other actors, including states, corporations, and populations.