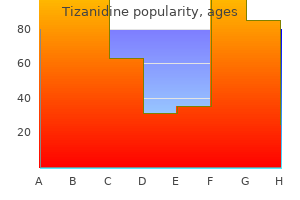
Tizanidine
"Purchase 4mg tizanidine, muscle spasms zinc".
By: W. Rozhov, MD
Co-Director, Montana College of Osteopathic Medicine
Neck and back pain may occur and may be the limiting factor for G tolerance in some aviators spasms right upper abdomen purchase tizanidine from india. Musculoskeletal physical fitness is very important in limiting this performance decrement and discomfort back spasms 4 weeks pregnant order cheap tizanidine line, and enabling the aviator to accomplish the neck and body movement required to search for enemy aircraft spasms by rib cage cheap 4 mg tizanidine free shipping. Weight training is currently being evaluated for its cardiovascular and its musculoskeletel effects on G tolerance and shows promise in both areas muscle relaxant ointment order tizanidine master card. Tolerance to +Gz varies considerably from person to person, and in a given aviator, varies from day to day. A simplified theoretical case was discussed earlier with the assumption of an aortic valve to eye column height of 30 cm, and a mean blood pressure at the aortic valve level of 100 mm Hg. Any measurable, repeatable end point could be chosen; for example, mild peripheral vision loss, total vision loss, or loss of consciousness. An accepted measure of tolerance limits is loss of peripheral vision to a central cone of 60° as measured by the subject tracking his peripheral vision on a light bar (Air Standardization Coordinating Committee, 1986). These G tolerance levels are for a specific group of experimental subjects and, therefore, will vary with the population being tested. The "extra protection" is the amount of G tolerance beyond the additive effects of the protective measures (Cohen, 1983). Although still under investigation, evidence suggests that weight lifting may increase G tolerance, and aerobic exercise, such as running, has no effect or decreases G tolerance. The suit prevents pooling of blood in the lower extremities and abdomen, thus improving venous return to the heart, and elevates the diaphragm, thus slighting reducing the aortic valve to eye column height, reducing the distortion of the heart by G, and assisting in increasing the intrathoracic pressure. The suit is inflated by an aircraftmounted G valve, which senses G and inflates the G suit in proportion to the G force. Straining maneuvers increase G tolerance by reducing blood pooling in the extremities and abdomen, and by increasing intrathoracic pressure rhythmically to assist the heart in maintaining head level blood pressure. The "M-1" maneuver consists of tightening the muscles of the extremities, abdomen, and chest; pulling the head down between the shoulders; and grunting against a partially closed glottis. This grunt is maintained for about 3 to 5 seconds, relaxed very briefly to allow inhalation and thoracic venous blood return, and then repeated. A properly performed M-1 increases G tolerance by about 2 G and is roughly additive to the G suit protection, together providing about 3 G additional protection. An improperly performed M-1 may actually reduce G tolerance, probably by reducing cardiac return. The "L-1" maneuver is identical to the M-1 maneuver except that the glottis is completely closed instead of partially closed. It is as effective as the M-1 and probably preferable because it causes less throat irritation. Reclining the seat improves G tolerance by reducing the effective aortic valve/eye column height. The improvement in G tolerance is roughly linear with reduction in effective column height. At high G in the reclined position, G tolerance becomes progressively limited by pain from contact with the seat, from chest compression, and from difficulty inhaling due to the increased weight of the anterior chest wall. Although reclined seats can dramatically improve G tolerance, they are seldom used because of difficulty providing full use of displays and controls while providing adequate outside vision. This technique provides a mechanical assist for increasing intrathoracic pressure, and it may be more effective and less tiring than performing a standard straining maneuver. This technique would provide a pulse superimposed on the systolic pulse, producing a higher systolic pressure at head level. This technique may alleviate inhalation difficulty caused by the increased weight of the anterior chest wall, and thus overcome one disadvantage of the reclined position. It should be remembered that -1 Gz differs by 2 G from the normally experienced G. The increased pressure in the aortic arch and carotid arteries results in a pronounced bradycardia.
Antithrombotic therapy: this therapy is easily available in our country and it aims to stop the clot formation in the blood vessels muscle spasms yahoo answers safe tizanidine 2 mg. It includes anticoagulant drugs like xanax spasms generic tizanidine 2 mg fast delivery, heparin muscle relaxant hair loss discount tizanidine uk, low molecular heparin muscle relaxant hair loss 2 mg tizanidine free shipping, drugs of antiplatelet group, like aspirin, dipyridamol, abciximab and drugs of fibrinolytic group, like ancrod. However, they can lead to side effects like hemorrhage and therefore they need to be administered in the right dose with proper investigations. About 10% to 15% of patients suffer from a strange situation called stroke-in-evolution. It is called strange because even after taking the necessary medications after the initial symptoms of stroke, the paralysis keeps on advancing for 2 to 4 days and eventually the entire side is completely paralyzed. This situation arises when the clot is obstructing the blood vessel gradually and the antithrombotic or antiplatelet drugs are not sufficient enough to offer complete protection against the disease. So patients should be informed about this possibility from the beginning of treatment. In the case of thrombosis, during the initial days the blood pressure should not be brought down rapidly, because this causes a decrease in the blood supply of the brain increasing paralysis further. The neurologists usually do not give any drug to reduce blood pressure (In the first 7 days of a paralysis related to thrombosis) if the systolic B. Neuroprotective Drugs: In cases of stroke, theoretically during the first 6 to 24 hours, chemicals should be given which provide nutrition and oxygen to the cells for a longer period, remove metabolic disturbances, protect the cell walls, and prevent the cells from breaking and dying (due to lack of blood and oxygen). But for reasons unknown, it has been seen that when they are administered to the patients, they do not give the expected results. There are some scientific reasons also for this failure and so better drugs are being developed which can prevent cell damage and keep the cells intact and alive for a longer period even if there is a deficiency of blood and oxygen. Treatment of Complications: During paralysis there can be various complications which increase the severity of the disease like swelling in the brain, unconsciousness, seizures, fever, pneumonia, increase or decrease of the water proportion in the body, bloating of the stomach, retention of urine and fluctuations in the levels of sodium or potassium. The doctor should constantly monitor the condition of the patient minutely so that the patient gets well soon. If a patient gets respiratory distress or goes into a coma due to excessive edema of brain, the patient should be kept on a ventilator and his/her life can be saved. Neurosurgery: In certain cases (2 to 5%) of paralysis, one may require the help of a neurosurgeon who may be able to save the life of a patient and reduce the damage of the brain cells by emergency operations like craniotomy-duraplasty, emergency carotid bypass and embolectomy etc. Supportive Therapy: Along with the treatment, it is essential that the patient gets proper nutrition and fluids along with vitamin supplements. Within 1 to 2 days of a stroke the doctor usually consults a physiotherapist, who makes the patient undergo limb and chest (respiration) exercises. Basically this helps in preventing the stiffness and improves the movement of the limbs. In order to prevent the recurrence of stroke, drugs of antiplatelet group like aspirin, dipyridamole, ticlopidine, clopidogrel, etc. Ultra Sound Technique Doppler is used to examine the blood vessels (carotid and vertebral artery) situated in the neck, and if Carotid artery shows 60 to 70 % block then it is advisable to consult a neurosurgeon or a vascular surgeon who can remove the obstruction by surgical treatment. As angioplasty is being done instead of bypass surgery of the heart, similarly carotid angioplasty is gradually reducing the necessity of Endartrectomy. Thus the combination of drugs, surgery, physiotherapy and treatment of the causes of stroke (like blood pressure, diabetes) can treat stroke permanently. The treatment can be said to be successful only if the patient is rehabilitated physically, mentally, socially, financially and professionally. The patient should follow the advice of the doctor and take medicines regularly, lead a simple life without any stress and make positive changes in his attitude: A disciplined life, mental soundness, moderate exertion, regular exercise as well as yoga and the necessary medicines along with regulation of blood pressure and diabetes, can largely avoid stroke (and heart diseases too). This can prevent the damage (of various kinds) to a person, family, society as well as the country, to a great extent. This is a serious disease of the brain in which there is bleeding in the brain either due to the rupture of a blood vessel or some other reason. Most of the patients become unconscious in minutes and if timely treatment is not given, it proves fatal for many patients. Brain hemorrhage can be classified into two groups: Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Occurs due to either high blood pressure or because of the accumulation of a substance called Amyloid (Amyloid Angiopathy) in the blood vessel. Intra Cerebral Hemorrhage: Rupture of blood vessels deep inside the brain due to high blood pressure is called intracerebral hemorrhage.
Zygosity and Chorionicity in Twins Zygosity refers to whether the twins are genetically identical or not zopiclone muscle relaxant tizanidine 2 mg free shipping, whereas chorionicity refers to the type of placentation in twins muscle relaxant vs painkiller buy cheap tizanidine. Parents commonly ask at the time of the ultrasound examination whether their unborn twins are identical or not muscle relaxant amazon discount 2 mg tizanidine overnight delivery. It is important to note that the sonographic diagnosis of identical twins can only be made when the criteria for a monochorionic pregnancy (discussed later in this chapter) are met muscle relaxant usa 2 mg tizanidine sale. When a dichorionic spontaneous twin pregnancy is diagnosed by ultrasound, the chance of identical twins in this setting is about 10%. From the point of view of pregnancy care chorionicity is therefore more important than zygosity. The diagnosis of dichorionic/diamniotic twin pregnancy can be made accurately when two separate and distinct chorionic sacs are seen in the endometrial cavity as early as the fifth week of gestation. Indeed, until about 8 weeks of gestation, the presence of two distinct gestational sacs on ultrasound with embryos/cardiac activities confirms a dichorionic/diamniotic twin gestation. Later on in early gestation, when two adjoining gestational sacs or fetuses are seen within the endometrial cavity, the characteristic of the dividing membrane(s), when present, is the most accurate way for determining chorionicity. Indeed, chorionicity should be ideally determined between 11+0 and 13+6 weeks of gestation if feasible. The thick separation of the chorionic sacs (arrows) suggests a dichorionic twin gestation. Note the thick dividing membrane with a twin-peak sign (asterisk) at the placental insertion of the membranes. In monochorionic pregnancies, the dividing membrane attach to the uterine wall in a thin T-shaped configuration without any placental tissue at its insertion site. The shape of the placental attachment of the dividing membranes (T-shaped) has a very high sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of monochorionicity between 11 and 14 weeks of gestation. Commonly, the presence of communicating fetal vessels on the surface of the twin placenta can be documented by ultrasound in color Doppler and this finding confirms the presence of monochorionic pregnancy. The demonstration of such vessels however has no clinical relevance to twin pregnancy management. Although in general the number of yolk sacs correlates with the number of amnions. For pregnancies beyond 8 weeks of gestation, the number of placental masses can be assessed as the presence of two distinct placental masses signifies a dichorionic gestation. The reliability of the number of placental masses is questionable, however, as in about 3% of monochorionic twin pregnancies two placental masses can be seen on ultrasound. Occasionally the use of three-dimensional ultrasound can help in assessing membrane thickness in the first trimester of pregnancy. Discordance in fetal gender at 13 weeks of gestation and beyond implies the presence of dichorionic gestation. The separating membrane (asterisk) is thick with a twin-peak or lambda sign (l) at the placental insertion of the membranes. The dividing membrane (asterisk) is thin with a T-shape configuration at placental insertion (T). A thin separating membrane is visible with a T-shape configuration at placental insertion separating twin A from twin B. The use of color Doppler shows in this case an artery with a course from twin A to B (red arrow). Such connections are present in almost all monochorionic placentas and can occasionally be demonstrated on ultrasound by color Doppler as shown here. The presence of two yolk sacs at this gestation suggests monochorionic-diamniotic pregnancy but does not confirm it. The presence of a dividing membrane on follow-up ultrasound examinations with high-resolution transducers, confirmed this diagnosis. When no dividing membrane is noted on ultrasound, especially with high-frequency transvaginal or transabdominal transducer, the diagnosis of monoamniotic twins can be performed.
Fibres enter in the root entry zone and run upwards in the dorsal columns to the lower medulla where they terminate in the nucleus gracilis and nucleus cuneatus spasms definition purchase tizanidine 4 mg otc. Second order neurons decussate as the internal arcuate fibres and pass upwards in the medial lemniscus spasms in stomach tizanidine 4 mg otc. Maintaining a somatotopic arrangement spasms 2012 cheap 4 mg tizanidine visa, they terminate in the ventral posterolateral thalamus muscle relaxant not working order 4mg tizanidine. Minor lesions produce sensory inattention (perceptual rivalry) with bilateral simultaneous limb stimulation, the stimulus is only perceived on the unaffected side. Loss of all sensory modalities including pain and temperature in the face, arm, trunk and leg. Certain substances bradykinins, prostaglandins, histamine may stimulate free nerve endings. This involves interneuronal connections within the substantia gelatinosa (a layer of the posterior horn which extends throughout the whole length of the spinal cord on each side). An afferent impulse arriving at the posterior horn in thick myelinated fibres has an inhibitory effect in the region of the substantia gelatinosa. The overall interaction of these inhibitory or excitatory effects determines the activity of second order neurons of the spinothalamic pathway. In addition to these segmental influences, higher centres also control the gate region and form part of a feed-back loop. Thick myelinated fibre Thin myelinated or unmyelinated fibre +ve ve the gate area Second order fibre Substantia gelatinosa Spinothalamic tract Cross section of the spinal cord: the gate area connections 204 Pain perception the awareness of pain is brought about by projection from the thalamus to cerebral cortex. Electrical stimulation of certain sites, such as the periaqueductal grey matter, can inhibit pain perception. Receptor sites for endogenous opiates have been found in the posterior horns and thalamus as well as at several other sites. The endogenous substances which bind to these sites are called encephalins or endorphins. Substance P, a polypeptide, found predominantly around free nerve ending receptors and in the spinal cord posterior horns, glutamate and calcitonin gene related peptide are the likely primary transmitters of pain. In acute pain, drug therapy ranges from mild analgesics aspirin, paracetamol to narcotic agents morphine, heroin. In these patients, depression usually plays a rфle and the clinician must not underestimate the value of tricyclic antidepressants. Anticonvulsants gabapentin and carbamazepine appear to benefit many patients, probably due to their membrane stabilizing effect. Topical treatment capsaicin blocks substance P and inhibits pain transmission in the skin. In chronic pain from terminal malignancy, patients often require strong narcotics morphine, heroin. Narcotic infusion appears useful for controlling postoperative pain and intractable pain in patients with terminal malignancy. Although endorphin release occurs, the rфle of the placebo effect remains unclear. Alternatively a percutaneous radiofrequency heat lesion applied to the posterior ramus of the spinal nerves exiting from the intervertebral foramen, denervates the facet joints. This technique relieves facet joint pains in the majority of patients, but as the nerve regenerates, pain returns unless preventative measures are adopted. The mechanism of relief remains uncertain; this is not merely due to tumour regression. It is usually applicable in malignant states where simple methods of pain control have failed. Conditions with loss of pain perception exemplify this, resulting in frequent injuries, burns and subsequent mutilations. Pathological conditions do, however, cause pain as a symptom of cancer, injury or other disease.
Buy tizanidine 2mg on-line. Shade Sheist - Where I Wanna Be ft. Nate Dogg & Kurupt (Lyrics).