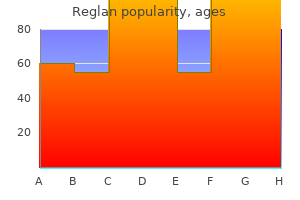
Reglan
"Purchase reglan 10 mg amex, gastritis symptoms palpitations".
By: S. Daro, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Co-Director, Cooper Medical School of Rowan University
Ramelteon appears to be a promizing novel hypnotic gastritis root word buy reglan once a day, provided its efficacy is established gastritis loose stools generic reglan 10 mg with mastercard. However gastritis mind map purchase 10 mg reglan overnight delivery, on certain nights he keeps lying in bed for 23 hours before getting sleep gastritis symptoms blood best buy for reglan. Such episodes are unpredictable, and he cannot relate them to any disturbance, anxiety, worry or physical illness. He has tried relaxing, getting up and walking around or reading, but nothing helps. As a result, next day he feels lethargic, impaired, unable to concentrate and has poor creativity. If so, which drug would be suitable for late night intake without next morning sedation? Epilepsy has a focal origin in the brain, manifestations depend on the site of the focus, regions into which the discharges spread and postictal depression of these regions. Absence seizures (minor epilepsy, petit mal): prevalent in children, lasts about 1/2 min. Momentary loss of consciousness, patient apparently freezes and stares in one direction, no muscular component or little bilateral jerking. Atonic seizures (Akinetic epilepsy): Unconsciousness with relaxation of all muscles due to excessive inhibitory discharges. Myoclonic seizures Shock-like momentary contraction of muscles of a limb or the whole body. Convulsions are confined to a group of muscles or localized sensory disturbance depending on the area of cortex involved in the seizure, without loss of consciousness. Simple partial or complex partial seizures secondarily generalized the partial seizure occurs first and evolves into generalized tonic-clonic seizures with loss of consciousness. Most of the cases of epilepsy are primary (idiopathic), some may be secondary to trauma/ surgery on the head, intracranial tumour, tuberculoma, cysticercosis, cerebral ischaemia, etc. Experimental models these models for testing antiepileptic drugs have also shed light on the etiopathogenesis of epilepsy. Chronic focal seizures Produced by application of alumina cream on the motor cortex of monkey. Kindled seizures Brief bursts of weak electrical impulses are applied to the brain (especially amygdala) intermittently over days. After-discharges increase progressively and tonicclonic seizures are produced after 1015 shocks. This indicates that seizures have a self perpetuating and reinforcing effect: more neuronal circuits are facilitated and recruited in the seizure process. Newer drugs Phenobarbitone Primidone Phenytoin Fosphenytoin Carbamazepine Oxcarbazepine Ethosuximide Valproic acid (sodium valproate) Divalproex Clonazepam Diazepam Lorazepam Clobazam Lamotrigine Gabapentin Pregabalin Topiramate Zonisamide Levetiracetam Vigabatrin Tiagabine Lacosamide. However, benzodiazepines, carbamazepine, valproic acid and the newer drugs are chemically diverse. The higher anticonvulsant: hypnotic ratio of phenobarbitone may be due to its minimal effect on Ca2+ channels and glutamate release compared to hypnotic barbiturates. With continued use of phenobarbitone sedation wanes off but not anticonvulsant action. It has a wide spectrum of anticonvulsant property-raises seizure threshold as well as limits spread and suppresses kindled seizures. Phenobarbitone has slow oral absorption and a long plasma tЅ (80120 hours), is metabolized in liver as well as excreted unchanged by kidney. Steady-state concentrations are reached after 23 weeks, and a single daily dose can be used for maintenance. Long term administration (as needed in epilepsy) may produce additional side effects like-behavioral abnormalities, diminution of intelligence, impairment of learning and memory, hyperactivity in children, mental confusion in older people. Rashes, megaloblastic anaemia and osteomalacia (similar to that with phenytoin) occur in some patients on prolonged use.
Vincristine (oncovin) It is a rapidly acting drug gastritis diet ��������� discount 10 mg reglan with amex, very useful for inducing remission in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia gastritis diet ��� buy reglan 10mg cheap, but is not good for maintenance therapy chronic gastritis metaplasia buy reglan 10 mg cheap. It also causes ataxia gastritis diet ��������� purchase reglan 10mg visa, nerve palsies, autonomic dysfunction (postural hypotension, paralytic ileus, urinary retention) and seizures. Bone marrow depression Vinorelbine this is a newer semisynthetic vinblastine analogue with similar mechanism of action inhibiting microtubule assembly and causing metaphase arrest. As a single agent or combined with others, its primary indication is non-small cell lung cancer. It binds to -tubulin and enhances its polymerization: a mechanism opposite to that of vinca alkaloids. This stability results in inhibition of normal dynamic reorganization of the microtubule network that is essential for interphase and mitotic functions. Cytotoxic action of paclitaxel emphasizes the importance of tubulin-microtubule dynamic equilibrium. The approved indications of paclitaxel are metastatic ovarian and breast carcinoma after failure of first line chemotherapy and relapse cases. Pretreatment with dexamethasone, H1 and H2 antihistaminics is routinely used to suppress the reaction. It has been found effective in breast and ovarian cancer refractory to first line drugs. Small cell cancer lung, pancreatic, gastric and head/neck carcinomas are the other indications. Major toxicity is neutropenia (more than paclitaxel), but neuropathy is less frequent. Topotecan is used in metastatic carcinoma of ovary and small cell lung cancer after primary chemotherapy has failed. Docetaxel is formulated in polysorbate medium which produces less acute hypersensitivity reactions. Estramustine It is a complex of estradiol with a nitrogen mustard normustine, which has weak estrogenic but no alkylating property. However, it binds to -tubulin and interferes with its organization into microtubules exerting antimitotic action. Estramustine gets concentrated in prostate and the only indication is advanced or metastatic prostate cancer that is nonresponsive to hormone therapy. It is orally active, undergoes first pass metabolism in liver into active as well as inactive metabolites, which are mainly eliminated in faeces. A small amount is hydrolysed into estradiol and normustine producing myelosuppression and estrogenic adverse effects, viz. Irinotecan is primarily indicated in metastatic/advanced colorectal carcinoma; also in cancer lung/cervix/ ovary and stomach. Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, haemorrhage, bodyache and weakness are the other adverse effects. Prominent adverse effects are vomiting, stomatitis, diarrhoea, erythema and desquamation of skin, alopecia and bone marrow depression. Maximum action is exerted at S phase, but toxicity is usually exhibited in G2 phase. Marrow depression, alopecia, stomatitis, vomiting and local tissue damage (on extravasation) are other adverse effects. Epirubicin has been primarily used as a component of regimen for adjuvant therapy of breast carcinoma. Other indications are gastroesophageal, pancreatic, hepatic and bladder carcinoma. Alopecia, hyperpigmentation of skin and oral mucosa, painful oral ulcers, fever and g. Daunorubicin (Rubidomycin), Doxorubicin these are anthracycline antibiotics having antitumour activity. However, utility of daunorubicin is limited to acute myeloid as well as lymphoblastic leukaemia (in which it is highly active), while doxorubicin, in addition, is effective in many Mitoxantrone It is an anthracycline derivative related to doxorubicin with lower cardiotoxicity, probably because it does not produce quinone type free radicals. Clinical utility is relatively narrow, restricted mostly to acute myeloid leukaemia, advanced hormone refractory prostate cancer and occasionally in breast and hepatic carcinoma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Zolpidem is nearly completely metabolized in liver (tЅ 2 hr) gastritis diet ����������� purchase reglan us, and has short duration of action gastritis diet sheet order reglan 10 mg fast delivery. It is indicated for short-term (12 weeks) use in sleep onset insomnia as well as for intermittent awakenings gastritis diet butter purchase cheap reglan on line. Because the plasma tЅ is short gastritis low blood pressure generic 10mg reglan with mastercard, next day sedation is minimal, but morning sedation or prolongation of reactiontime can occur if it is taken late at night. Dose: 510 mg (max 20 mg) at bedtime; Ѕ dose in elderly and liver disease patients. As hypnotic A hypnotic should not be casually prescribed for every case of insomnia. Understanding the pattern and cause of insomnia in the specific patient is important, and use of a variety of other measures can avoid unnecessary hypnotic medication. Some important points are outlined below: · A hypnotic may be used to shorten sleep latency, to reduce nocturnal awakenings, or to provide anxiolytic effect the next day when insomnia is accompanied with marked element of anxiety. The next day effects are either due to prolonged sedation (longer acting drugs) or rebound anxiety (shorter acting drugs). The subjective impression that quality of sleep was poor is the major criterion of insomnia. It could be a long-term (monthsyears), short-term (weeks) or transient (a day or two, mostly situational) problem. It is rapidly absorbed; oral bioavailability is ~30% due to first pass metabolism; is rapidly cleared by hepatic metabolism with a tЅ of 1 hour. As such it is effective only in sleep-onset insomnia; does not prolong total sleep time or reduce the number of awakenings. Because of brevity of action, it can be taken late at night (> 4 hour before waking time) without causing morning sedation. Surprisingly, despite very short action, no daytime anxiety or rebound insomnia has been observed, and hypnotic effect does not fade on nightly use. The patient may have a personality disorder, but often there is no specific stress factor. He may have used hypnotics for long periods or may be alcoholic or have some somatic disease. Measures like aerobic exercise, training at mental relaxation, avoiding anxiety about past/future performance while in bed, attempting sleep when sleepiness is maximum, avoiding napping at daytime, maintaining regular sleep-wake timings and other sleep-hygiene measures, coffee/alcohol restriction, treatment of concurrent somatic illness, psychotherapy and controlled sleep curtailment may succeed. Patients of obstructive sleep apnoea have poor sleep and feel sleepy during the day. A slowly eliminated drug is preferable because rebound insomnia and withdrawal symptoms are least marked with such drugs. Short-term insomnia (321 days) Emotional problem (occupational stress, bereavement) and physical illness are the usual causes. Cautious use of low doses of an appropriate drug for the type of sleep disturbance may be made. Transient insomnia (13 days) Due to alterations in the circumstances of sleep. A rapidly eliminated hypnotic or one with marked distribution is to be preferred to avoid residual effects the next morning. Fixed dose combinations of sedative/hypnotic/anxiolytic drugs with analgesic-antipyretics has been banned in India. Flumazenil is absorbed orally; oral bioavailability is ~16%, but it is not used orally. Resedation generally occurs within 1 hour (more with diazepam than with midazolam): supplemental doses of flumazenil may be given. This may allow early discharge of patients after diagnostic procedures and facilitates postanaesthetic management. Agitation, discomfort, tearfulness, anxiety, coldness and withdrawal seizures are the occasional side effects.
To describe features of gastritis burping buy discount reglan 10mg, recognize gastritis medical definition reglan 10 mg on-line, and evaluate posterior vitreous detachments and retinal detachments gastritis diet ������������� order generic reglan. To perform slit lamp biomicroscopy with the Hruby gastritis help purchase reglan uk, +78, +90 lenses, 3-mirror contact lens, and trans-equator (pan-funduscopic) contact lens. To describe principles of retinal detachment recognition, various types of retinal detachment. To describe the findings of major studies in retinal diseases, including the following: a. To describe the fundamentals of, evaluate, and treat (or refer) peripheral retinal disease and vitreous pathology. To diagnose, treat, and recognize the complications of retinopathy of prematurity. To describe, recognize, and evaluate hereditary retinal and choroidal diseases. To describe the indications for and perform basic laser treatment for diabetic retinopathy. To perform ophthalmoscopic examination with contact lenses, including pan-funduscopic lenses. To describe the indications for and interpret basic electrophysiological tests. To perform fundus drawings of the retina, showing complex vitreoretinal relationships and findings. To describe indications, techniques, and complications of pars plana vitrectomy and to assist in a retinal surgery or perform the procedure under supervision. To apply in clinical practice the most advanced knowledge of retinal anatomy and physiology. To describe the indications for laser photocoagulation, including photodynamic therapy for the most complex retinal pathology. To describe the findings of the major studies in retinal diseases and describe the indications and exceptions for application to individual patients: a. To apply in clinical practice understanding of the most complex peripheral retinal disease and vitreous pathology. To evaluate, treat or refer the more complex cases of retinopathy of prematurity. To evaluate, treat or refer the most complex forms of retinal vascular disease: a. To evaluate and treat or refer the uncommon manifestations or presentations of the following macular diseases: a. To apply in clinical practice the more complex techniques for retinal detachment repair: a. To apply in clinical practice the more complex principles of surgical management of diabetic retinopathy. To evaluate and treat or refer the etiologically more complex or uncommon cases of posterior uveitis. To perform indirect ophthalmoscopy with scleral indentation in complex retinal cases. To perform ophthalmoscopic examination with pan-funduscopic or other lenses in complex retinal conditions. To perform posterior segment photocoagulation in more complicated retinal cases: a. To perform detailed fundus drawings of the retina with vitreoretinal relationships in the most complex retinal cases. To perform laser therapy or cryotherapy of retinal holes and other more complex retinal pathology. To describe basic principles of history taking and examination of patients with uveitis, and related diseases. To describe typical features and differential diagnosis of anterior uveitis, including infectious.
Trusted 10mg reglan. Prolapsing Gastric Mucosa At Gastrostomy.