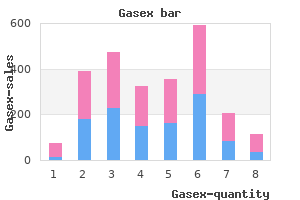
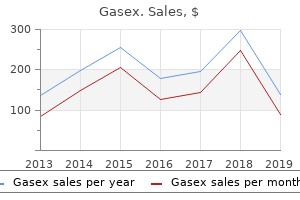
Gasex
"Gasex 100 caps without a prescription, gastritis aguda".
By: X. Lars, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Deputy Director, University of Vermont College of Medicine
Isolated Systolic Hypertension this is said to be present when systolic blood pressure is > 140 mm Hg and diastolic blood pressure is < 90 mm Hg gastritis je cheapest generic gasex uk. Cardiovascular System 89 Accelerated Hypertension A significant recent increase in blood pressure over previous hypertensive levels gastritis symptoms tongue generic gasex 100 caps fast delivery, associated with evidence of vascular damage on fundoscopic examination gastritis diet âêàíòàêòå generic 100 caps gasex overnight delivery, but without papilloedema gastritis zantac order gasex in india. Labile Hypertension Patients who sometimes, but not always have arterial pressure within the hypertensive range, are classified as having labile hypertension. The cuff is then deflated even more slowly, and the pressure is again noted when Korotkoff sound becomes audible throughout the respiratory cycle. Normally the difference between the two pressures should not exceed 10 mm Hg during quiet respiration. Paradox: Heart sounds are still heard over the precordium at a time when no pulse is palpable at the radial artery. Transient Hypertension this may be seen in Acute cerebrovascular accidents Acute myocardial infarction Acute glomerulonephritis Pregnancy Acute intermittent porphyria. It is systemic hypertension seen for a transient phase of time when the patient is under stress or when he is having a disorder with a transient hypertensive phase, as may occur in the above-mentioned conditions. However, a patient with pheochromocytoma may be normotensive, hypotensive or hypertensive. Pulsus alternans is present if there is an alteration in the intensity of Korotkoff sound. The right internal jugular vein is selected because it is larger, straighter and has no valves. Thus, the vertical height of the column of blood in the neck can be estimated from the sternal angle, to which 5 cm is added to obtain an estimate of mean right atrial pressure in centimeters of blood. This estimation may be erroneous in patients with deformed chest walls or malpositioning of the heart. Markers of Rheumatic Fever Joint swelling (Migrating polyarthritis involving major joints, leaving no residual deformities) Erythema marginatum Subcutaneous nodules. Abdominal Jugular Reflux Firm compression is given in the periumbilical area for 30 seconds. Abdominal jugular reflux is positive in right or left heart failure and/or tricuspid regurgitation. In the absence of these conditions, a positive abdominal jugular reflux suggests an elevated pulmonary artery wedge or central venous pressure. In congenital heart disease look for: Cyanosis Clubbing Polycythaemia Hypertelorism Low set ears High arched palate Webbed neck Syndactyly, Polydactyly, Arachnodactyly (Polydactyly: Trisomy 13 to 1 and 18. Precordial bulge indicates the presence of right ventricular hypertrophy presenting since early childhood. Pulmonary artery pulsation Apical Impulse Apical impulse is the lower most and outer most point of definite cardiac impulse with a maximum perpendicular thrust to the palpating finger. Normal apical impulse is produced by left ventricle and the left ventricular portion of the interventricular septum. Suprasternal pulsation Supraclavicular pulsation 94 Manual of Practical Medicine. Golden Rules Before commenting on the position and character of apical impulse, look for the presence of chest wall or spinal deformities, and the tracheal position. When the apical impulse is not localisable on the left side, palpate the right hemithorax for its presence (dextrocardia or pseudo-dextrocardia) 3. Tapping apical impulse Behind the rib or sternum Dextrocardia Palpable S1 (closing snap). Heaving apical impulse is one in which there is increase in both amplitude and duration. Parasternal impulse can be seen in Right ventricular enlargement or Left atrial enlargement Causes of Right Ventricular Enlargement Volume overload: Fast, ill-sustained parasternal impulse- Left to right shunts.
Alternatively gastritis test order gasex 100 caps mastercard, Na1 can leak back from the paracellular space into the lumen gastritis diet ïî÷òà generic 100 caps gasex with visa, providing a recycling system for Na1-coupled transport of glucose gastritis with fever generic gasex 100caps line. Conversely gastritis ulcer disease discount gasex online amex, natriuretic hormones, such as dopamine, inhibit proximal tubule NaCl reabsorption (15). Hormonal factors regulate largely transcellular NaCl flux via modulation of the Na1 transporters (16). This increases the protein concentration and oncotic pressure in the postglomerular blood, which along with the lower hydrostatic pressure jointly promote proximal fluid to move into the peritubular capillary. Thus, in the absence of an appropriate buffer, the daily production of H1 will decrease the body pH to ,3 within an hour, which is clearly not compatible with life. Unlike the thick ascending limb or distal convoluted tubule, there are no dedicated "NaCl" transporters in the proximal tubule. The proximal tubule uses parallel arrays of symporters and antiporters to affect NaCl entry. Cl2 exit is less well defined utilizing a va3 riety of transporters and possibly a Cl2 channel. Finally, the most abundant base equivalent in urine is citrate22/32, whose urinary excretion is also exclusively regulated by the proximal tubule (19). Unlike NaCl reabsorption, luminal acidification is mediated by dedicated 3 acid-base transporters. The titration of 3 trivalent citrate to its bivalent form facilitates citrate reabsorption. Titration of divalent to monovalent phosphate reduces phosphate absorption and allows the titrated phosphate to function as 4 a H1 carrier in the urine. There are 3 3 three generic mechanisms by which changes in luminal and cell pH can alter apical transporters. Therefore, the proximal tubule plays an essential role in net acid excretion because a large fraction of the urinary buffers is already titrated by the end of the proximal tubule. Thus, the sequential positioning of the two transporters that favor capacity and affinity in the early and late tubule, respectively, creates an effective mechanism to ensure that,1% of the filtered glucose exits the proximal tubule. Both transporters facilitate the passive movement of glucose from the proximal tubular cells to the interstitial space. The proximal tubule metabolizes little or no glucose, which is compatible with the very low hexokinase in this segment (34). In normal acid-base balance, the arterial-venous difference for glucose across the kidney is zero or slightly positive, which reflects substantial proximal tubule gluconeogenesis counterbalanced by glucose consumption by the rest of the nephron segments (35). Amino Acid Transport the renal transport of amino acids is a complex process due to the range of structures and ionic properties of the free amino acids in the plasma (36,37). Previous micropuncture studies established that the filtered glutamine is nearly quantitatively reabsorbed from the lumen of the early proximal tubule (39). The transporters that mediate the export of amino acids across the basolateral membrane are less well characterized. The two antiporters contribute to the maintenance of normal intracellular levels of amino acids. However, net efflux requires the participation of a uniporter that facilitates the passive export of neutral Other Solute Transport Another primary function of the proximal tubule is the recovery of metabolites from the glomerular filtrate. Approximately 180 g of glucose (1000 mEq) and 50 g of amino acids (400 mEq) are filtered by the human kidney per day. The process of transepithelial transport normally accomplishes the recovery of 99. As mentioned previously, this process requires the asymmetric association of distinct transporters in the apical and basolateral membranes. Typically, a secondary active Na 1 -dependent transporter in the brush border membrane uses the Na1 gradient to accomplish the initial uptake of solutes. By contrast, the subsequent transport of the solutes across the basolateral membrane frequently utilizes a Na1-independent passive transporter. Important examples of transepithelial transport are those involved in the recovery of glucose, glutamine, citrate, and phosphate. Glucose Transport Two distinct Na1-dependent transporters mediate the uptake of glucose from the lumen of the proximal tubule (30).
So in compressive lesions there is early pupillary loss and ischaemic lesions there is pupillary sparing gastritis or gastroenteritis quality gasex 100caps. Complete Ptosis this occurs with third nerve lesions due to paralysis of the levator palpabrae superioris gastritis in spanish generic gasex 100 caps without prescription, innervated by the third nerve gastritis diet õîðîñêîï best buy for gasex. Pupils < 3 mm size in average condition of illumination are called miotic and pupils > 5 mm are called mydriatic chronic gastritis recipes buy discount gasex 100caps. Pin point pupil is said to be present when the pupillary size is less than or equal to 1 mm. Infancy Lesion of third cranial nerve (midbrain lesion) Drugs like atropine and pethidine Blindness due to optic nerve damage (optic atrophy). Light source is directed to one eye and the consensual light reflex is noted in the other eye. Consensual light reflex is elicitable because of the bilateral innervation of the Edinger-Westphal nucleus by the fibres carrying the light reflex. Light Reflex Light reflex pathway: the light reflex is carried by the visual pathway up to the optic tracts, after which the fibres carrying this reflex are relayed to the EdingerWestphal nucleus, bilaterally, and from here through the ciliary ganglion to the sphincter pupillae by the ciliary nerves. Reaction to Accommodation Accommodation reflex pathway: the afferent stimulus for this reflex is carried from the retina via the optic nerve, tract and radiation to the calcarine cortex of the occipital lobe. From here, fibres pass to the frontal lobe and from here the corticobulbar fibres go to the third nerve nucleus (nucleus of the medial rectus and the Edinger-Westphal nucleus). This reflex comprises of adduction (convergence) of the eyes when patient looks at a near object, accompanied by pupillary constriction. Argyll-Robertson pupil (absent light reflex and preserved accommodation reflex) i. Reversed Argyll-Robertson pupil (absent accommodation reflex and preserved light reflex) i. Binocular diplopia: In this condition, diplopia occurs only when both eyes are open. The defective movement of the affected eye results in the image of the object falling on two different points on the retinae of the two eyes. The real image is closer to the eye and is distinct, whereas the false image is farther away from the eye and is indistinct. Red glass test: this test is performed to detect the affected eye in patients with diplopia. A red glass is placed over each eye, one at a time, and the patient is asked to look at an object, placed in the direction which produces diplopia with both eyes. When the red glass is placed over the normal eye, the patient visualises the true image as red. When the red glass is placed over the affected eye, the patient visualises the false image as red. Strabismus or Squint It is an abnormality of ocular movement, in which the visual axis do not meet at the point of fixation. Primary deviation: the deviation of the axis of the affected eye from the parallelism with that of the normal eye is called primary deviation. Secondary deviation: If the patient is made to fix an object in a direction requiring the action of the affected muscle Ocular Movements the ocular movements are tested by first asking the patient to look in different directions on command. The patient is instructed to follow the moving object with his eyes and not to move his head. Parietal and temporo-mesencephalic-pontine pathway: this pathway is concerned with pursuit eye movements. This pathway originates in the posterior parietal lobe and adjacent superior temporal sulcus and anterior temporal lobe. Fibres descend unilaterally to the pons to join the medial longitudinal fasciculus at about the level of the sixth nerve nucleus. Paralysis of conjugate upward gaze is found with a lesion of midbrain at the level of superior colliculus. Paralysis of conjugate downward gaze is found with lesion of midbrain at the level of inferior colliculus and lower brainstem. Internuclear ophthalmoplegia is a result of lesions in the medial longitudinal fasciculus. Upper Motor Neuron (Supranuclear) Lesions Supranuclear Pathway the third, fourth and sixth cranial nerves have two supranuclear pathways. Fronto-mesencephalic-pontine pathway: this pathway is concerned with voluntary conjugate eye movements (saccades).
Syndromes
- Numbness, tingling, or a "pins and needles" feeling
- Hematoma (a buildup of blood outside the blood vessels)
- Your carotid artery is opened. The surgeon removes the plaque inside the artery.
- Swollen spleen and liver
- If you are pregnant or have a weakened immune system, DO NOT eat soft cheeses, especially soft cheeses imported from countries outside the U.S.
- Medicines to lower eye pressure, given by mouth and through a vein (by IV)
- People who live in hot climates may need a small amount of extra table salt.
- Give support to the pregnant woman and her family
Patients have normal liver serum tests and histology and there are no systemic symptoms gastritis diet 8 plus gasex 100caps low cost. Patients when placed on a diet of 300 Kcal without lipids for 24-48 hours chronic gastritis food allergy buy gasex 100caps low price, have an elevation of bilirubin by 100% or by 1 gastritis diet ÷åëîâåê cheap gasex 100caps with visa. Treatment Occasionally phenobarbitone in a dose of 180 mg/day in divided doses for 2 weeks can be given to enhance the activity of glucuronyl transferase gastritis diet vegetable soup buy 100 caps gasex free shipping. Bromsulphthalein excretion is normal at 45 minutes and there is secondary rise at 120 minutes. Bromsulphthalein excretion is abnormal at 45 min and no secondary rise at 120 min. Viral Hepatitis Viral hepatitis is caused by five main agents mainly hepatitis A, B, C, D and E viruses. Dubin-Johnson Syndrome It is an autosomal recessive disorder resulting in conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia secondary to a defect in canalicular transport of organic anions. First generation assays detect antibodies 1-3 months after the onset of hepatitis. In severe acute hepatitis B treatment with Lamivudine at 100 mg/d orally may tried. In acute hepatitis C, antiviral therapy with interferon alpha 3 million units subcutaneously thrice weekly helps in reducing the rate of chronicity. Mortality is high in patients with other diseases like carcinoma, lymphoma or chronic liver disease. The portal tracts are infiltrated with inflammatory cells (lymphocytes, macrophages, plasma cells). The infiltrate is limited to portal tracts and does not spill out into the hepatic parenchyma. Pathologically, it is characterised by piecemeal necrosis and fibrosis extending from the portal tracts into the hepatic parenchyma leading to cirrhosis. Chronic lobular hepatitis: It refers to lobular inflammation with spotty necrosis. Alpha interferon Prednisone, azathioprine withdraw drug Prednisolone Azathioprine 2. It is also useful in lamivudine resistant cases and can safely be given in the presence of de-compensated liver disease. Hepatitis A vaccine: An inactivated protein vaccine (Harvix) grown in human diploid cells. Clinical Features It occurs most often in women (10-30 years and late middle age). The common symptoms are fever, fatigue, intermittent jaundice, weight loss, and pruritus. Liver Abscess Liver is the organ commonly involved in the development of abscesses. In developing countries, abscesses are due to parasitic infection (amoebic, echinococcal, other protozoal or helminthic organisms). Organisms reaching the liver via the portal vein (amoebiasis, appendicitis, actinomycosis of right iliac fossa). Via arterial supply (septicaemia, pyaemia, faciocervical actinomycosis, infected hydatid cyst). Sterile pleural effusions Contiguous spread from liver Frank rupture into pleural space Hepatobronchial fistula (good prognosis) Rupture into peritoneum, pericardium (grave prognosis). Water sanitation; take fruits and vegetables after washing and after removing the skin. These drugs are given along with a luminal agent (paromomycin 500 mg tid for 10 days or diloxanide furoate 500 mg tid for 10 days). In abscesses following pelvic/ intraperitoneal source of infection, anaerobes or mixed flora are common. It may end up with fibrosis and end stage liver disease in the absence of significant alcohol consumption 5.
Order gasex online. Doxinate Tablet Review | Uses Side Effects & Precautions Before Use in Hindi.