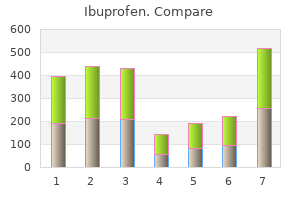
Ibuprofen
"Purchase ibuprofen 400 mg, best treatment for pain from shingles".
By: R. Treslott, M.A., M.D.
Clinical Director, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine
Paradoxically pain treatment center of franklin tennessee order ibuprofen 600 mg overnight delivery, antibodies themselves sacroiliac joint pain treatment exercises generic ibuprofen 400mg, by virtue of their exquisite specificity pain management for dogs with pancreatitis discount ibuprofen 400 mg online, might offer the best possibility for the therapeutic inhibition of specific immune responses pain treatment center west hartford ct buy generic ibuprofen from india. We will also consider experimental approaches to controlling specific immune responses by manipulating the local cytokine environment or by manipulating antigen so as to divert the response from a pathogenic pathway to an innocuous one. We have discussed in Chapters 12 and 13 how the pathological responses that cause allergy, autoimmunity, or graft rejection can be prevented by innocuous, nonpathological T-cell responses. Corticosteroids are powerful anti-inflammatory drugs that alter the transcription of many genes. Corticosteroid drugs are powerful anti-inflammatory agents that are used widely to suppress the harmful effects of immune responses of autoimmune or allergic origin, as well as those induced by graft rejection. Corticosteroids are pharmacological derivatives of members of the glucocorticoid family of steroid hormones; one of the most widely used is prednisone, which is a synthetic analogue of cortisol. Cortisol acts through intracellular receptors that are expressed in almost every cell of the body. On binding hormone, these receptors regulate the transcription of specific genes, as illustrated in. The expression of as many as 1% of genes in the genome may be regulated by glucocorticoids, which can either induce or, less commonly, suppress the transcription of responsive genes. The pharmacological effects of corticosteroid drugs result from exposure of the glucocorticoid receptors to supraphysiological concentrations of ligand. The abnormally high level of ligation of glucocorticoid receptors causes exaggerated glucocorticoid-mediated responses, which have both beneficial and toxic effects. Given the large number of genes regulated by corticosteroids and that different genes are regulated in different tissues, it is hardly surprising that the effects of steroid therapy are very complex. The use of corticosteroids to control disease requires a careful balance between helping the patient by reducing the inflammatory manifestations of disease and avoiding harm from the toxic side-effects of the drug. For this reason, corticosteroids used in transplant recipients and to treat inflammatory autoimmune and allergic disease are often administered in combination with other drugs in an effort to keep the dose and toxic effects to a minimum. In autoimmunity and allograft rejection, corticosteroids are commonly combined with cytotoxic immunosuppressive drugs. Introduction of the 1,2 double bond into the A ring increases anti-inflammatory potency approximately fourfold compared with cortisol, without modifying the sodium-retaining activity of the compound. Corticosteroids are lipid-soluble molecules that enter cells by diffusing across the plasma membrane and bind to their receptors in the cytosol. Corticosteroids exert their numerous effects by modulating the transcription of a wide variety of genes. Corticosteroids regulate the expression of many genes, with a net anti-inflammatory effect. First, they reduce the production of inflammatory mediators, including cytokines, prostaglandins, and nitric oxide. Second, they inhibit inflammatory cell migration to sites of inflammation by inhibiting the expression of adhesion molecules. Third, corticosteroids promote the death by apoptosis of leukocytes and lymphocytes. The structure and metabolism of the cytotoxic immunosuppressive drugs azathioprine and cyclophosphamide. Azathioprine was developed as a modification of the anti-cancer drug 6-mercaptopurine; by blocking the reactive thiol group, the metabolism of this drug is slowed down. It is slowly converted in vivo to 6mercaptopurine, which is then metabolized to 6-thio-inosinic acid, which blocks the pathway of purine bio-synthesis. Cytotoxic drugs cause immunosuppression by killing dividing cells and have serious side-effects. The two cytotoxic drugs most commonly used as immunosuppressants are azathioprine and cyclophosphamide. They were developed originally to treat cancer and, after observations that they were cytotoxic to dividing lymphocytes, were found to be immunosuppressive as well. The use of these compounds is limited by a range of toxic effects on tissues that have in common the property of continuous cell division. These effects include decreased immune function, as well as anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, damage to intestinal epithelium, hair loss, and fetal death or injury. As a result of their toxicity, these drugs are used at high doses only when the aim is to eliminate all dividing lymphocytes, and in these cases treated patients require subsequent bone marrow transplantation to restore their hematopoietic function.
They begin as papules and then become pearl-like umbilicated nodules that are 2 to 10 mm in diameter and have a central caseous plug that can be squeezed out pain treatment journal buy ibuprofen american express. They are most common on the trunk pain treatment for shingles buy discount ibuprofen 400 mg on line, genitalia allied pain treatment center news cheap ibuprofen 600mg online, and proximal extremities and usually occur in a cluster of 5 to 20 nodules best pain medication for uti discount ibuprofen 400mg overnight delivery. The disease is more common in children than adults, but its incidence is increasing in sexually active and immunocompromised individuals. The diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum is confirmed histologically by the finding of characteristic large, eosinophilic, cytoplasmic inclusions (molluscum bodies) in epithelial cells (see Figure 44-6B). These bodies can be seen in biopsy specimens or in the expressed caseous core of a nodule. The molluscum contagiosum virus cannot be grown in tissue culture or animal models. Lesions of molluscum contagiosum usually disappear within 2 to 12 months, presumably as a result of immune responses. The nodules can be removed by curettage (scraping) or application of liquid nitrogen or iodine solutions. Hybrid Poxviruses for Gene Delivery and Vaccines the vaccinia and canarypox viruses are being used as expression vectors to produce live recombinant/hybrid vaccines for more virulent infectious agents (Figure 44-7). For this process, a plasmid is constructed to contain the foreign gene that encodes the immunizing protein, and this gene is flanked by specific poxvirus gene sequences to promote recombination. This plasmid is inserted into a host cell, which is then infected with the poxvirus. The foreign gene is incorporated into the Molluscum Contagiosum (Box 44-4) Molluscum contagiosum is a common disease affecting 3% to 20% of the population. Immunization with the recombinant poxvirus results from expression of the foreign gene and its presentation to the immune response, almost as if by infection with the other agent. A vaccinia hybrid virus containing the G protein of rabies virus soaked onto a bait food and dropped into forests has been used successfully to immunize raccoons, foxes, and other mammals. Experimental vaccines for human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B, influenza, and other viruses have also been prepared using these techniques. Hybrid vaccinia viruses are also being used for oncolytic agents to selectively kill tumors and for gene replacement therapy. Which infectious agents would be appropriate for a vaccinia hybrid vaccine, and why Poxviruses have a large, complex structure with several membranes, lateral bodies, and other structures. Unlike other viruses with small interlocking capsid pieces, synthesis and assembly of complex structures require complex interactions to ensure that all the necessary enzymes and structures are included in final package. Immunity to smallpox infection develops from the local innate responses to the more systemic antibody and T-cell responses. Because the virus has spread throughout the body by this time and infected many tissues, the immune response (especially cell-mediated immunity and inflammation) can cause great damage when trying to eliminate the infected cells. In a vaccinated person, antibody is present in the bloodstream to block the spread of the virus by viremia. T-cell responses are activated within 1 to 4 days from memory cells, and these responses can successfully limit cell-cell spread, kill infected cells, and resolve the infection. Elimination of smallpox was made possible by an excellent vaccine that leaves a scar as evidence of vaccination, a very active World Health Organization, and because the virus has the following properties: exclusive human host range (no animal vectors to control), single serotype shared with animal viruses such as vaccinia, and presence of symptoms in every infected individual, which facilitated quarantine procedures. Vaccinia has been developed into an attenuated virus that will not cause significant human disease (in immunocompetent hosts).
The basic compound is an organic acid with a -lactam ring obtained from culture of the mold Penicillium chrysogenum midwest pain treatment center llc ibuprofen 600 mg generic. If the mold is grown by a fermentation process pain management treatment options purchase 600mg ibuprofen with mastercard, large amounts of 6-aminopenicillanic acid (the -lactam ring is fused with a thiazolidine ring) are produced pain treatment center of greater washington 600mg ibuprofen otc. Biochemical modification of this intermediate yields antibiotics that have increased resistance to stomach acids back pain treatment videos generic 600mg ibuprofen overnight delivery, increased absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, resistance to destruction by penicillinase, or a broader spectrum of activity that includes gram-negative bacteria. Penicillin G is inactivated by gastric acid; thus it is used mainly as an intravenous drug for the treatment of infections caused by the limited number of susceptible organisms. Penicillin V is more resistant to acid and is the preferred oral form for the treatment of susceptible bacteria. Penicillinase resistant penicillins such as methicillin and oxacillin are used to treat infections caused by susceptible staphylococci. Unfortunately, resistance to this group of antibiotics has become commonplace in both hospital-acquired and community-acquired staphylococcal infections. Ampicillin was the first broadspectrum penicillin, although the spectrum of activity against gram-negative rods was limited primarily to Escherichia, Proteus, and Haemophilus species. The inhibitors irreversibly bind and inactivate susceptible bacterial -lactamases (although not all are bound by these inhibitors), permitting the companion drug to disrupt bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cephalosporins and Cephamycins the cephalosporins (Table 17-3) are -lactam antibiotics derived from 7-aminocephalosporanic acid (the -lactam ring is fused with a dihydrothiazine ring) that was originally isolated from the mold Cephalosporium. The cephamycins are closely related to the cephalosporins, except that they contain oxygen in place of sulfur in the dihydrothiazine ring, rendering them more stable to -lactamase hydrolysis. The cephalosporins and cephamycins have the same mechanism of action as the penicillins; however, they have a wider antibacterial spectrum, are resistant to many -lactamases, and have improved pharmacokinetic properties. The cephalosporins have enhanced activity against gram-negative bacteria compared with the penicillins. This activity, in turn, varies among the different "generations" of cephalosporins. The activity of narrowspectrum, first-generation antibiotics is primarily restricted to Escherichia coli, Klebsiella species, Proteus mirabilis, and oxacillin-susceptible grampositive cocci. Many of the expandedspectrum, secondgeneration antibiotics have additional activity against Haemophilus influenzae, Enterobacter, Citrobacter, and Serratia species, and some anaerobes, such as Bacteroides fragilis. The broadspectrum, third-generation antibiotics and extendedspectrum, fourth-generation antibiotics are active against most Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Extended-spectrum antibiotics offer the advantage of increased stability to -lactamases. Unfortunately, gramnegative bacteria have rapidly developed resistance to most cephalosporins and cephamycins (primarily as the result of -lactamase production), which has significantly compromised the use of all these agents. In recent years, resistance to carbapenems mediated by production of carbapenemases has become widespread. The class B carbapenemase is a metallo-lactamase (requires zinc for activity), is widely distributed in gram-negative bacteria, and also cannot be detected reliably by conventional susceptibility tests. Finally, the class D carbapenemases are primarily found in Acinetobacter, are detected by conventional susceptibility tests, and encode resistance to all -lactam antibiotics. This group of carbapenemases is important because Acinetobacter strains producing this carbapenemase are generally resistant to all antibiotics, with few exceptions. Glycopeptides Vancomycin, originally obtained from Streptomyces orientalis, is a complex glycopeptide that disrupts cell wall peptidoglycan synthesis in growing gram-positive bacteria. Vancomycin interacts with the d-alanine-d-alanine termini of the pentapeptide side chains, which interferes sterically with formation of the bridges between peptidoglycan chains. Vancomycin is used for the management of infections caused by oxacillin-resistant staphylococci and other gram-positive bacteria resistant to -lactam antibiotics. Vancomycin is inactive against gram-negative bacteria, because the molecule is too large to pass through the outer membrane pores and reach the peptidoglycan target site. Intrinsic resistance is also found in some species of enterococci that contain a d-alanined-serine terminus. The genes for this resistance (primarily vanA and vanB), which also mediate changes in the pentapeptide terminus, can be carried on plasmids and have seriously compromised the usefulness of vancomycin Carbapenems and Monobactams Other classes of -lactam antibiotics (Table 17-4) are the carbapenems. The carbapenems are important, widely prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics that are active against many groups of organisms. In contrast, the monobactams are narrow-spectrum antibiotics that are active only against aerobic, gram-negative bacteria.
Order ibuprofen 600mg free shipping. Shwetha Is Happy With Her Treatment For Back Pain At Veda Wellness Center Nisarga Mane.
The appropriate response when a patient expresses concerns about another physician is to have the patient address those concerns with that physician directly pain medication for the shingles buy ibuprofen uk. If the problem is with a member of your office staff milwaukee pain treatment center milwaukee wi purchase ibuprofen overnight delivery, tell the patient you will speak to that individual pain treatment doctors purchase ibuprofen toronto. Although it is important to obtain feedback from patients arthritis pain treatment guidelines buy ibuprofen now, directly after a patient has expressed concerns about another physician is not the correct time to do so. Leukemias are an abnormal proliferation of cells arising from the bone marrow and are characterized by their lymphoid or hematopoietic lineage as well as by the level of differentiation seen. Multiple myeloma is a blood dyscrasia characterized by a hyperproliferation of plasma cells, which are recognized by their off-center, clock-face nuclei. Multiple myeloma usually affects older individuals and typically involves bone (lytic lesions). It is associated with prominent serum and urinary protein abnormalities (hyperglobulinemia and Bence Jones protein). Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is also a lymphoproliferative neoplasm that arises in the lymph nodes but is not characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells. Acetazolamide inhibits the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, which is important in the reabsorption of sodium, bicarbonate, and chloride in the proximal tubule. Ethacrynic acid is a phenoxyacetic acid derivative that essentially has the same action as furosemide. It is used in patients who are likely to be allergic to furosemide, and it is contraindicated in this patient because it will worsen her metabolic alkalosis. Furosemide is a strong diuretic that inhibits the Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransporter of the thick ascending loop of Henle and, like the thiazides, is contraindicated in this patient because it will worsen her metabolic alkalosis. Hodgkin lymphoma is a lymphoproliferative neoplasm that typically affects young adults, especially men, and presents with fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infectious mononucleosis is caused by Epstein-Barr virus and demonstrates characteristic atypical (reactive) lymphocytes on a blood smear. Clinical characteristics include prominent sore throat, fever, fatigue, generalized lymphadenopathy, and often hepatosplenomegaly. Hydrochlorothiazide inhibits sodium chloride reabsorption in the early distal tubule. It is contraindicated in this patient because it leads to hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis, which would only worsen her acid-base balance. It passes through the diaphragm with the aorta and azygous vein posteriorly at the level of T12. The right chest, back, arm, neck, and head, however, are drained via the right lymphatic duct, which empties into the angle between the internal jugular and subclavian veins. With symptoms of swelling in the right upper quadrant of the body, one must consider disruption of this structure, especially in a patient with a history of surgery and/or radiation in the right breast and axilla. The thoracic duct drains all of the lymph in the body except that from the right upper quadrant, which includes the right arm and right side of the face. Therefore, a lesion of the thoracic duct could not explain the edema in this patient. Metastatic disease to bone is common in advanced breast cancer, and most metastatic disease occurs in the central skeleton (vertebrae, pelvis, ribs, upper legs, and upper arms). This method is considered one of the four mature defense mechanisms, along with altruism, humor, and suppression. Displacement is an immature defense mechanism in which avoided ideas and feelings are transferred to a neutral person or object. An example of this is a woman who is angry at her boss and instead yells at her sister on the phone. Projection is an immature defense mechanism in which an unacceptable internal impulse is attributed to an external source. An example of this is a man who is attracted to another woman and accuses his wife of cheating on him. Reaction formation is an immature defense mechanism in which a warded-off idea or feeling is replaced by an unconsciously derived emphasis on its opposite. Suppression is another mature defense mechanism in which unwanted feelings are voluntarily (unlike other defenses) withheld from conscious awareness.
Replication is complete when the two replication forks meet 180 degrees from the origin neck pain treatment physiotherapy order ibuprofen 600 mg overnight delivery. Topoisomerases are essential to the bacteria and are targets for the fluoroquinolone antibiotics pain treatment center syracuse ny purchase discount ibuprofen online. Bacterial Growth Bacterial replication is a coordinated process in which two equivalent daughter cells are produced pain treatment guidelines 2010 buy ibuprofen 400 mg without a prescription. B zona pain treatment effective 400mg ibuprofen, the conformation of the inactive repressor protein is changed after its binding by the co-repressor tryptophan. C, the trp operon is also under the control of an attenuation-antitermination mechanism. Upstream of the structural genes are the promoter (P), the operator, and a leader (L), which can be transcribed into a short peptide containing two tryptophans (W), near its distal end. However, in the presence of little or no tryptophan the ribosomes stall in region 1 when translating the leader peptide because of the tandem of tryptophan codons. Then regions 2 and 3 can pair, forming the antiterminator hairpin and leading to transcription of the trp genes. Ribosomes are cannibalized for deoxyribonucleotide precursors, peptidoglycan and proteins are degraded for metabolites, and the cell shrinks. Similar signals may initiate sporulation in species capable of this process (see Chapter 12). During the logarithmic (log) or exponential phase, the bacteria will grow and divide with a doubling time characteristic of the strain and determined by the conditions. The number of bacteria will increase to 2n, in which n is the number of generations (doublings). The culture eventually runs out of metabolites, or a toxic substance builds up in the medium; the bacteria then stop growing and enter the stationary phase, followed by the death phase. During the death phase, some bacteria stop dividing but remain viable and are often insensitive to antibiotics. Bacterial membrane, peptidoglycan synthesis, and cell division are linked together such that inhibition of peptidoglycan synthesis will also inhibit cell division. Commencement of chromosome replication also initiates the process of cell division, which can be visualized by the start of septum formation between the two daughter cells (Figure 13-8; see also Chapter 12). New initiation events may occur even before completion of chromosome replication and cell division. Toxin and protease are produced to kill host cells and supply the colony with food, and the colony produces a biofilm for protection. Cell wall thickness and adhesion factors are less important within the colony and are repressed. Multiple growing forks may be initiated in a cell before complete septum formation and cell division. Most of these mutations have little effect on the bacteria or are detrimental, but some mutations may provide a selective advantage for survival of the bacteria when challenged by the environment, the host, or antibiotic therapy. A single base change can result in a transition in which one purine is replaced by another purine or in which a pyrimidine is replaced by another pyrimidine. A transversion in which, for example, a purine is replaced by a pyrimidine and vice versa may also result. This type of mutation occurs because more than one codon may encode an amino acid. A missense mutation results in a different amino acid being inserted in the protein, but this may be a conservative mutation if the new amino acid has similar properties. Conditional mutations, such as temperature-sensitive mutations, may result from a conservative mutation that changes the structure or function of an important protein at elevated temperatures. A small deletion or insertion that is not in multiples of three produces a frameshift mutation. This results in a change in the reading frame, usually leading to a useless peptide and premature truncation of the protein. Null mutations, which completely destroy gene function, arise when there is an extensive insertion, deletion, or gross rearrangement of the chromosome structure. Replication requires extension of the cell wall and replication of the chromosome and septum formation.