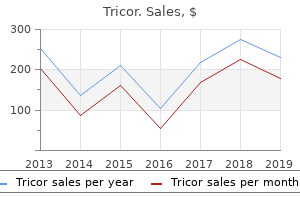
Tricor
"Generic 160 mg tricor, cholesterol under 130".
By: B. Stan, M.B.A., M.B.B.S., M.H.S.
Medical Instructor, A. T. Still University Kirksville College of Osteopathic Medicine
As standards of living are increasing across the world cholesterol test and coffee buy tricor 160mg lowest price, the amount of waste generated by cities has grown accordingly cholesterol test smoking purchase tricor 160mg. Large transportation terminals such as ports cholesterol ratio nz buy 160 mg tricor with amex, airports and railyards are dominant elements of the urban landscape high cholesterol foods to eat purchase tricor visa, including logistics zones where freight is distributed to extensive markets. Transport terminals and logistics zones are also generators of goods movements that may impact urban circulation (the last mile). Gate access at large intermodal terminals, such as ports, can lead to congestion (queuing) and local disruptions. Two actors, private and common carriers, handle commercial freight transportation. Private carriers are at the same time bene cial cargo owners (manufacturers or retailers) using their own transportation assets (eet and workforce). Common carriers service any customer on a contractual basis, which also leads to the opportunity to consolidate cargo and deliveries, which can bene t smaller users. The share of private carriers is dominant for urban freight distribution in developing countries while in developed countries common carriers account for about half of urban deliveries. The issue of dualism remains prevalent in urban freight distribution as it underlines different modes of operation between distribution systems that are integrated to globally oriented supply chains and distribution systems linked with informal activities that are more related to the local or regional economy. This is best represented by owner-drivers, or small independent truckers acting as subcontractors to large carriers for the nal distribution of goods in urban areas. Dualism is therefore illustrative of a coexistence of modern and traditional means of freight distribution within the same metropolitan area. Another aspect of dualism is related to an active informal transportation sector that supplies the needs of lower income segments of the population, a very important component of city logistics services in developing countries. Docherty (eds) Transport Geographies: Mobilities, Flows and Spaces, London: Blackwell, pp. Giuliano (eds) (2004) the Geography of Urban Transportation, 3rd edition, New York: Guilford Press. Miller (2000) Urban Transportation Planning: A Decision-Oriented Approach, New York: McGraw-Hill. The mobility of people and freight and levels of territorial accessibility are at the core of this relationship. Economic opportunities are likely to arise where transportation infrastructures are able to answer mobility needs and ensure access to markets and resources. From the industrial revolution in the nineteenth century to globalization and economic integration processes of the late twentieth and early twenty- rst centuries, regions of the world have been affected differently by economic development. International, regional and local transportation systems alike have become fundamental components of economic activities. However, even if transportation has positive impacts on socioeconomic systems, there are also negative consequences such as congestion, accidents and mobility gaps. Transportation is also a commercial activity derived from operational attributes such as transportation costs, capacity, ef ciency, reliability and speed. When transport systems are ef cient, they provide economic and social opportunities and bene ts that result in positive multiplier effects such as better accessibility to markets, employment and additional investments. When transport systems are de cient in terms of capacity or reliability, they can have an economic cost such as reduced or missed opportunities. Ef cient transportation reduces costs, while inef cient transportation increases costs.
The three clinicians involved in this research project cholesterol levels mg/dl order tricor 160mg online, Drs Weisel cholesterol hdl definition order 160mg tricor fast delivery, Feindel and Patterson cholesterol chart in canada cheap tricor 160 mg mastercard, have been involved in guideline preparations at both the national and international level cholesterol test singapore order tricor 160mg line. This research has also spawned another group at Sick Kids Hospital who are looking at paediatric transplants. The information produced by Dr Weisel and his colleagues was helpful to the paediatric surgeons who needed information on how to better protect transplant organs. Dr Rao explained that depending on the location of the donor, he often does not take heart down to four degrees Celsius, on ice. If the donor is coming from 1-2 hours away he will put the heart in a cold preservation saline solution, without ice. One of the solutions that were evaluated during the case study grant for lung preservation is known as low molecular weight dextran solution. Blood cardioplegia is used by most transplant centres in North America, although researchers are still looking to optimise results by exploring different additives and their appropriate doses. Solutions and approaches need to be adapted for the type of operation to ensure feasibility and safety. This surgical intervention has been tested at various levels from small-scale trials to large-scale trials and is now widely used. The concepts used by the team with regard to the vascular endothelial cells have been further adapted to different situations, such as preserving the brain during heart or even brain surgery, since the brain also involves endothelial functions. Scientific advances in heart surgery have reduced the mortality rate from about ten percent to a current rate of about one to two percent. Problems of organ rejection and immunosuppression still remain for heart transplant recipients, affecting long-term mortality. Better preservation of endothelial function at the time leading up to and during transplantation has been shown to improve long-term results. Furthermore, in the late 1980s and early 1990s when heart transplantation was new, there was about a ten to twenty percent incidence of primary graft dysfunction, where the heart did not function well and required a lot of support. This grant was initially submitted in this time period when clinicians were trying to better preserve the organs. This is due in part to better management of recipient and donor and better selection criteria of both recipient and donor. The success rate of lung transplants has also increased although in more modest numbers, as shown in Figure 28-4. Survival was calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method, which incorporates information from all transplants for whom any follow-up has been provided. Since many patients are still alive and some patients have been lost to follow-up, the survival rates are estimates rather than exact rates because the time of death is not known for all patients. The half-life is the estimated time point at which 50 percent of all of the recipients have died. These findings will help researchers understand how to better affect long-term outcomes at the time of transplant. Table 28-2 shows, in point form and by impact category, some of the impacts, described more fully above, that have emerged from this grant. Weisel, `Adenosine Pretreatment for Prolonged Cardiac Storage: an Evaluation with St. Whincup and Ebrahim, were clinical epidemiologists at the Department of Public Health and Primary Care, Royal Free Hospital School of Medicine, London. The aim was to examine the management of risk factors for stroke in primary care in patients aged 60 years and older. Some elements of the project proceeded exactly as planned but others did not, partly as a result of emerging findings and partly because of the reduced time and funding. The first of two journal publications that resulted from this project described a simple scoring system that was based on their analysis and could be used in general practice to identify men who would benefit from further intervention. This showed that there was scope to increase the benefits of stroke prevention in primary care by focusing on the management of patients at high absolute risk. Although the intervention did result in better identification of the risk factors, it did not seem to bring about the improvements in management that they had identified as being desirable. Nevertheless, the original project made an impact in various other ways, including on other further research. Members of the team gave a range of conference presentations and engaged in other dissemination activities aimed at particular healthcare providers.
Buy tricor 160 mg amex. Lecture - 14 Lipids and Membranes II.
In her interview cholesterol check glasgow discount tricor amex, Dr Ariane Mackey said that her experience on this project indirectly assisted her career in research by putting her in contact with other researchers and statisticians cholesterol quantity in food cheap tricor. She is also investigating a new medicine for treating high levels of cholesterol cholesterol ratio mg/dl cheap 160mg tricor with amex, carotid stenosis cholesterol test normal buy tricor online now, acute stroke and neuroprotection/neurological interventions. Dr Christina Wolfson is currently Professor and Director for the Division of Clinical Epidemiology at McGill University. She says that participating in this work was important for her at the time because she did not have tenure. She described this project as good evidence to show the university that she was capable of collaborative work. The established team continues to attract neurology residents and fellows who are integrated into the research team. Other researchers in the United States and Italy were investigating markers for cardiovascular disease. The team concluded that their findings were not robust enough, as they did not emerge from randomised controlled trials. Further studies with larger samples, as well as multiple randomised controlled trials, would have been required to confirm their findings. There has been some very good work from the Framingham Group on prognostic markers in addition to traditional risk factors. The proper statistics on patients with hypertension, diabetes and so on shows that the incremental value derived to prognosticate from these markers is very little. To date, no effective markers have been found and excitement has diminished in this field of study. The new trend is moving towards imaging and the use of imaging investigative tools to look at the growth and instability of arteric plaques. Table 4-2 shows, in point form and by impact category, some of the impacts, described more fully above, that have emerged from this grant. Interview with the author, Montreal, 30 July 2008 [audio recording in possession of author]. The research project was conducted at the University of Newcastle in collaboration with hospitals in the region (eg John Hunter Hospital) and with clinicians, patients and patient groups. The project investigated what happened to people after heart attack (or myocardial infarction) or hospital admission for other serious heart diseases, with the aims of identifying risk factors that could be modified and examining how effective different drugs were (known as secondary prevention). The follow-up study involved linkage of records and questionnaire responses for more than 7,000 subjects. The primary outputs from the case study grant were the seven directly attributable publications, with the key findings being that changes in risk factors were influencing changes in mortality and incidence. Among the specific findings it showed the benefit from beta blockers after myocardial infarction and no effect on the risk of recurrent myocardial infarction and death with the use of calcium antagonists. Funds for the heart attack study did not cover follow-up beyond 28 days from onset of symptoms. The aim was to identify those patient characteristics and secondary preventative activities that are associated with better (or worse) long-term outcomes and also to enable comparison of reinfarction and survival rates in the two centres and relate these to differences in medical care and other factors.
The applicability and dynamics of land use models is related to issues such as the age cholesterol levels different units discount tricor 160mg online, size and the locational setting of a city cholesterol levels reduce naturally discount 160 mg tricor amex. For instance cholesterol definition in hindi purchase 160mg tricor overnight delivery, concentric cities are generally older and of smaller size cholesterol lowering diet nz buy tricor 160mg on-line, while polycentric cities are larger and relate to urban development processes that took place more recently. While most of the conceptual approaches related to transportation and land use relationships have been developed using empirical evidence related to North America and Western Europe, this perspective does not necessarily apply to other parts of the world. A dualism in land uses has been observed in cities in developing countries where on one hand processes such as economic development and motorization are creating an urban landscape that is common in advanced economies. On the other hand an informal landscape of shantytowns represents a land use structure that is not effectively captured by conventional land use models. Each component of the system is constantly evolving due to changes in technology, policy, economics, demographics and even culture or values. As a result, the interactions between land use and transportation are played out as the outcome of the many decisions made by residents, businesses and governments. The eld of urban dynamics has expanded the scope of conventional land use models, which tended to be descriptive, by trying to consider relationships behind the evolution of the urban spatial structure. This has led to a complex modeling framework including a wide variety of components. Among the concepts supporting urban dynamic representations are retroactions, whereby one component changes its in uence on others. The changes will in uence the initial component back, either positively or negatively. This is the most stable component of urban dynamics, as changes are likely to modify the land use structure over a rather long period of time. This comes as little surprise since most real estate is built to last at least several decades. The main impact of land use on urban dynamics is its function as a generator and attractor of movements. This is also considered to be a rather stable component of urban dynamics, as transport infrastructures are built for the long term. This is particularly the case for large transport terminals and subway systems that can operate for a very long period of time. The main contribution of the transport network to urban dynamics is the provision of accessibility. The most dynamic component of the system since movements of passengers or freight re ect changes almost immediately. Movements thus tend more to be the outcome of urban dynamics than a factor shaping them. They account for signi cant inducement effects over urban dynamics since many models often consider employment as an exogenous factor. This is speci cally the case for employment that is categorized as basic, or export-oriented, which is linked with speci c economic sectors such as manufacturing. Commuting is a direct outcome of the number of jobs and the location of workplaces. They act as the generators of movements, because residential areas are the sources of commuting. Since there are a wide array of incomes, standards of living, preferences and ethnicity, this diversity is re ected in the urban spatial structure. The issue about how to articulate these relations remains, particularly in the current context of interdependency between local, regional and global processes. Globalization has substantially blurred the relationships between transportation and land use as well as its dynamics. The main paradigm is concerned with factors once endogenous to a regional setting that have become exogenous.