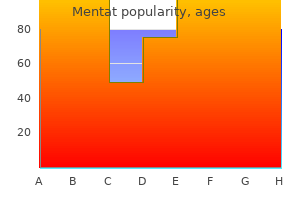
Mentat
"Buy genuine mentat, x medications".
By: G. Myxir, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
O "A pattern deviation" refers to an inward angle of deviation that increases in upgaze and decreases in downgaze treatment regimen mentat 60caps on-line. O "V pattern deviation" refers to an inward angle of deviation that decreases in upgaze and increases in downgaze treatment room cheap mentat 60caps with amex. Usually the disorder manifests itself at the age of two and leads to sensory adaptation syndromes in the form of unilateral strabismus treatment yeast diaper rash order mentat. This form of acute late strabismus with normal sensory development is encountered far less frequently than other forms medicine 2632 discount mentat 60 caps without prescription. As binocular vision is already well developed, affected children cannot immediately suppress the visual images of the deviating eye. As a result, they suffer from sudden double vision at the onset of strabismus, which they attempt to suppress by closing one eye. Clinical experience has shown that moderate and severe hyperopia will be detected more frequently than in the congenital form. Binocular vision is well developed in late strabismus with normal sensory development. Surgery within three to six months will allow the patient to maintain or regain stereoscopic vision. Microstrabismus: this is defined as unilateral esotropia with a minimal cosmetic effect, i. Binocular vision is partially preserved despite anomalous retinal correspondence and amblyopia. For this reason, treatment is limited to occlusion therapy to correct the amblyopia. For example in accommodative esotropia, the angle of deviation is larger with close objects than with distant objects. The disorder is corrected with bifocal eyeglasses, which in the case of accommodative esotropia have a strong near-field correction (Fig. However, the angle of deviation may also improve to the point that the visual axes are parallel with good binocular vision. The arrow indicates the dividing line between the distance and nearfield portions. As it is usually acquired, the disorder is encountered more often in adults than in children, who more frequently exhibit esotropia. Exotropia less frequently leads to amblyopia because the strabismus is often alternating. Occasionally what is known as "panorama vision" will occur, in which case the patient has an expanded binocular field of vision. In intermittent exotropia, an angle of deviation is present only when the patient gazes into the distance; the patient has normal binocular vision in near fixation (Figs. This form of strabismus can occur as a latent disorder in mild cases, meaning that the intermittent exotropia only becomes manifest under certain conditions, such as fatigue. O Secondary exotropia occurs with reduced visual acuity in one eye resulting from disease or trauma. Vertical deviations are usually associated with esotropia or exotropia, for example in infantile strabismus. Primary oblique muscle dysfunction and dissociated vertical deviation are common in this setting. Primary oblique muscle dysfunction is characterized by upward vertical deviation of the adducting eye during horizontal eye movements. The respective non-fixating eye or the eye occluded in the cover test will be elevated. The corneal reflexes are symmetrical in normal binocular vision or pseudostrabismus; in esotropia, exotropia, and vertical deviation, they are asymmetrical. As the examiner cannot rely on patient cooperation at this age, examination techniques requiring minimal patient cooperation are necessary.
Infants with birth weight below 1000 g are at increased risk of developing the disorder treatment nurse discount mentat 60 caps without a prescription. Retinopathy of prematurity is not always preventable despite optimum care and strict monitoring of partial pressure of oxygen medicine 750 dollars buy mentat 60caps on-line. Etiology: Preterm birth and exposure to oxygen disturbs the normal development of the retinal vasculature symptoms hepatitis c cheap mentat 60 caps otc. This results in vitreous hemorrhage medicine bow wyoming order 60 caps mentat with amex, retinal detachment, and, in the late scarring stage, retrolenticular fibroplasia as vessels and connective tissue fuse with the detached retina. Findings and symptoms: After an initially asymptomatic clinical course, vitreous hemorrhage or retinal detachment will be accompanied by secondary strabismus. A plus stage includes dilated and tortuous vasculature of the posterior pole in addition to the other changes. Diagnostic considerations: the retina should be examined with the pupil dilated four weeks after birth at the latest. Differential diagnosis: Other causes of leukocoria such as retinoblastoma or cataract (see Table 11. Prophylaxis: Partial pressure of oxygen should be kept as low as possible, and ophthalmologic screening examinations should be performed. This can be classified into four types: O Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment results from a tear, i. Blood, lipids, or serous fluid accumulates between the neurosensory retina and the retinal pigment epithelium. In rare cases, secondary retinal detachment may also result from a tear due to other disorders or injuries. Proliferative vitreoretinopathy frequently develops from a chronic retinal detachment (see Chapter 11, Vitreous Body). Epidemiology: Although retinal detachments are relatively rarely encountered in ophthalmologic practice, they are clinically highly significant as they can lead to blindness if not treated immediately. Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (most frequent form): Approximately 7% of all adults have retinal breaks. This indicates the significance of posterior vitreous detachment (separation of the vitreous body from inner surface of the retina; also age-related) as a cause of retinal detachment. The annual incidence of retinal detachment is one per 10 000 persons; the prevalence is about 0. There is a known familial disposition, and retinal detachment also occurs in conjunction with myopia. Exudative, tractional, and tumor-related retinal detachments are encountered far less frequently. Round breaks: A portion of the retina has been completely torn out due to a posterior vitreous detachment. This will occur only where the liquified vitreous body separates, and vitreous humor penetrates beneath the retina through the tear. The retinal detachment occurs when the forces of adhesion can no longer withstand this process. Tractional forces (tensile forces) of the vitreous body (usually vitreous strands) can also cause retinal detachment with or without synchysis. In this and every other type of retinal detachment, there is a dynamic interplay of tractional and adhesive forces. This develops from the tensile forces exerted on the retina by preretinal fibrovascular strands (see proliferative vitreoretinopathy) especially in proliferative retinal diseases such as diabetic retinopathy. Subretinal fluid with or without hard exudate accumulates between the neurosensory retina and the retinal pigment epithelium. Either the transudate from the tumor vasculature or the mass of the tumor separates the retina from its underlying tissue. A posterior vitreous detachment that causes a retinal tear may also cause avulsion of a retinal vessel. The patient will perceive this as "black rain," numerous slowly falling small black dots. The patient will perceive a falling curtain or a rising wall, depending on whether the detachment is superior or inferior.
Recognize and diagnose mitochondrial diseases and manage their cardiovascular manifestations 2 symptoms after embryo transfer order 60 caps mentat otc. Recognize and diagnose fatty acid oxidation disorders symptoms 7 days pregnant order mentat paypal, and manage their cardiovascular manifestations 3 treatment zit purchase generic mentat. Understand the genetic basis medicine you cant take with grapefruit discount generic mentat uk, natural history, and management of cardiovascular manifestations of glycogen storage diseases 4. Understand the genetic basis, natural history, and management of the cardiovascular manifestations of the mucopolysaccharidoses 5. Understand the genetic basis, natural history, and management of the cardiovascular manifestations of the mucolipidoses 6. Understand the genetic basis, natural history, and management of the glycoproteinoses 7. Understand the genetic basis, natural history, and management of the cardiovascular manifestations of the lipidoses D. Recognize indications and contraindications for cardiac transplantation in a patient with cardiomyopathy 2. Recognize indications and contraindications for cardiac transplantation in a patient with single ventricle 3. Recognize and understand the mechanism of the side effects of usual immunosuppressive drugs given to cardiac transplant recipients (in particular steroids, and calcineurin inhibitors) 5. Know special problems of infection and lymphoproliferative disease in an immunosuppressed patient who has undergone cardiac transplantation 6. Know current 1-year and 5-year survival rates following cardiac transplantation for infants and adolescents 7. Recognize the clinical and angiographic features of graft vasculopathy, including the setting in which it occurs 9. Know the etiology of major types of congenital and acquired pericardial disorders 2. Recognize the clinical features and laboratory manifestations of postpericardiotomy syndrome b. Know the indications for surgical pericardial stripping procedure in a patient with constrictive pericarditis F. Plan appropriate management (including genetic counseling) of a patient with cardiac tumor 4. Formulate a differential diagnosis for pulmonary hypertension based upon history, physical examination, and testing 2. Know major problems of unoperated complex cardiac disease (eg, single ventricle) in adolescents 5. Know how to manage unoperated complex cardiac disease (eg, single ventricle) in adolescents 7. Understand the pathophysiology of pulmonary hypertension secondary to congenital heart disease 9. Understand the secondary causes of pulmonary hypertension unrelated to congenital heart disease 12. Interpret a fetal echocardiogram, including developing a differential diagnosis 4. Recognize the etiology and genetic syndromes associated with congenital heart disease in the fetus 5. Know the indications and limitations of fetal echocardiography on the diagnosis of congenital heart disease 6. Understand the role of routine fetal ultrasonography in screening for fetal heart disease 7. Understand the indications, limitations, and types of fetal intervention for congenital heart defects and arrhythmias 8. Know the echocardiographic / Doppler findings in a fetus that signify abnormal flow and fetal distress 3. Recognize chromosomal abnormalities associated with congenital heart disease in the fetus 2. Recognize extracardiac malformations in the fetus associated with congenital heart disease 3.
Purchase mentat paypal. Medicinal Cannabis Used to Treat Addiction Withdrawal Symptoms..