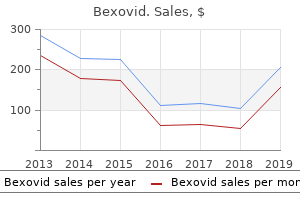
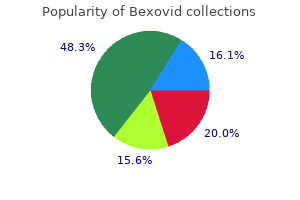
Bexovid
"Bexovid 200 mg without a prescription, hiv infection time frame".
By: H. Javier, MD
Clinical Director, Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine
Parasympathetic Injuries the oculomotor nerve is vulnerable in head injuries (herniated uncus) and can be damaged by compression by aneurysms in the junction between the posterior cerebral artery and posterior communicating artery hiv infection animation video buy cheap bexovid on line. The preganglionic parasympathetic fibers traveling in this nerve are situated in the periphery of the nerve and can be damaged antiviral breastfeeding order 200 mg bexovid mastercard. Surface aneurysmal compression characteristically causes dilatation of the pupil and loss of the visual light reflexes oregano antiviral cheapest bexovid. The autonomic fibers in the facial nerve can be damaged by fractures of the skull involving the temporal bone hiv infection rates white females purchase 200 mg bexovid fast delivery. The vestibulocochlear nerve is closely related to the facial nerve in the internal acoustic meatus, so clinical findings involving both nerves are common. Involvement of the parasympathetic fibers in the facial nerve may produce impaired lacrimation in addition to paralysis of the facial muscles. The glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves are at risk in stab and bullet wounds of the neck. The parasympathetic secretomotor fibers to the parotid salivary gland leave the glossopharyngeal nerve just below the skull; therefore, they are rarely damaged. The parasympathetic outflow in the sacral region of the spinal cord (S24) may be damaged by spinal cord and cauda equina injuries, leading to disruption of bladder, rectal, and sexual functions (see p. Degeneration and Regeneration of Autonomic Nerves the structural changes are identical to those found in other areas of the peripheral and central parts of the nervous system. Functional recoveries following sympathectomy operations can be explained only by the assumption either that the operative procedure was inadequate and nerve fibers were left intact or 3 the enophthalmos of Horner syndrome is often apparent but not real and is caused by the ptosis. However, the smooth muscle, the orbitalis, situated at the back of the orbit, is paralyzed, and involvement may be responsible. It is usually caused by a neurosyphilitic lesion interrupting the fibers that run from the pretectal nucleus to the parasympathetic nuclei (Edinger-Westphal nuclei) of the oculomotor nerve on both sides. The fact that the pupil constricts with accommodation implies that the connections between the parasympathetic nuclei and the constrictor pupillae muscle of the iris are intact. Adie Tonic Pupil Syndrome In Adie tonic pupil syndrome, the pupil has a decreased or absent light reflex, a slow or delayed contraction to near vision, and a slow or delayed dilatation in the dark. This benign syndrome, which probably results from a disorder of the parasympathetic innervation of the constrictor pupillae muscle, must be distinguished from the Argyll Robertson pupil (see above), which is caused by neurosyphilis. Adie syndrome can be confirmed by looking for hypersensitivity to cholinergic agents. These cholinergic agents do not cause pupillary constriction in mydriasis caused by oculomotor lesion or in drug-related mydriasis. Depending on the level of the cord injury,the patient may or may not be aware that the bladder is full; there is no voluntary control. The automatic reflex bladder occurs after the patient has recovered from spinal shock, provided that the cord lesion lies above the level of the parasympathetic outflow (S24). Since the descending fibers in the spinal cord are sectioned, there is no voluntary control. Stretch receptors in the bladder wall are stimulated as the bladder fills, and the afferent impulses pass to the spinal cord (S24). Efferent impulses pass down to the bladder muscle,which contracts; the sphincter vesicae and the urethral sphincter both relax. The autonomous bladder is the condition that occurs if the sacral segment of the spinal cord is destroyed or if the cauda equina is severed. The bladder wall is flaccid, and the capacity of the bladder is greatly increased. The bladder may be partially emptied by manual compression of the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall,but infection of the urine and back pressure effects on the ureters and kidneys are inevitable. Defecation Following Spinal Cord Injuries the act of defecation involves a coordinated reflex that results in the emptying of the descending colon, pelvic colon, rectum, and anal canal. It is assisted by a rise in the intra-abdominal pressure brought about by contraction of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. The involuntary internal sphincter of the anal canal normally is innervated by postganglionic sympathetic fibers from the hypogastric plexuses,and the voluntary external sphincter of the anal canal is innervated by the inferior rectal nerve. The desire to defecate is initiated by stimulation of the stretch receptors in the wall of the rectum. Following severe spinal cord injuries (or cauda equina injuries), the patient is not aware of rectal distention.
For example hiv infection by touching blood discount bexovid 200mg without a prescription, a cerebral embolism may follow the formation of a blood clot on the ventricular wall of a patient with coronary thrombosis antiviral group purchase bexovid cheap. It follows that a neurologic examination in many patients should be accompanied by a more general physical examination involving other systems data on hiv infection rates generic 200 mg bexovid mastercard. Muscle Wasting Muscle wasting occurs within 2 to 3 weeks after section of the motor nerve hiv infection through food buy cheap bexovid. In the limbs, it is easily tested by measuring the diameter of the limbs at a given point over the involved muscle and comparing the measurement obtained with that at the same site on the opposite limb. A 20-year-old man was seen in the emergency department following an automobile accident. A diagnosis of fracture dislocation of the fourth thoracic vertebra was made, with injury to the spinal cord as a complication. A laminectomy was performed to decompress the spinal cord in order to avoid permanent injury to the tracts of the cord. Multiple sclerosis is an example of a demyelinating disease of the nervous system. Many other diseases of the nervous system also have the common pathologic feature of destruction of the myelin sheaths of nerve fibers. How does myelination normally take place in peripheral nerves and central nervous system tracts? The myelin sheath is said to be formed in the peripheral nervous system by the rotation of Schwann cells on the axon so that the plasma membrane becomes wrapped around the axon in a spiral. In the central nervous system, do the oligodendrocytes rotate on the axons in a similar manner to form myelin? A 26-year-old man was involved in a street brawl and received a knife wound to the right arm at about the midhumeral level. Motor loss consisted of paralysis of the pronator muscles of the forearm and the long flexor muscles of the wrist and fingers, with the exception of the flexor carpi ulnaris and the medial half of the flexor digitorum profundus. As a result, the right forearm was kept in the supine position; wrist flexion was weak and accompanied by adduction. The latter deviation was due to the paralysis of the flexor carpi radialis and the strength of both the flexor carpi ulnaris and the medial half of the flexor digitorum profundus. No flexion was possible at the interphalangeal joints of the index and middle fingers, although weak flexion of the metacarpophalangeal joints of these fingers was attempted by the interossei. When the patient was asked to make a fist of his right hand, the index and, to a lesser extent, the middle fingers tended to remain straight,while the ring and little fingers flexed. The latter two fingers were weakened by the loss of the flexor digitorum superficialis. Flexion of the terminal phalanx of the thumb was lost due to paralysis of the flexor pollicis longus. The muscles of the thenar eminence were paralyzed,and the right thumb was laterally rotated and adducted. Sensory loss of the skin of the right hand involved the lateral half of the palm and the palmar aspect of the lateral three and one-half fingers. There was also sensory loss of the skin of the distal parts of the dorsal surfaces of the lateral three and one-half fingers. The skin areas involved in sensory loss became warmer and drier than normal, evidencing vasomotor changes. This was due to arteriolar dilatation and absence of sweating resulting from loss of sympathetic nervous control. When questioned, she said that 3 years previously she had experienced a weakness of the right side of the face and some degree of loss of taste sensation following a ride in an open car on a cold day. Six months later, the mother noticed that her 1-year-old son was becoming somnolent and quiet. Whereas previously he was very active and crawled around the house, he now tended to lie about the floor, uninterested in his toys. The mother decided to take him to a pediatrician when, as she put it, the child suddenly "threw a fit. When questioned further, the mother admitted that the child liked sucking the peeling paint on the railings outside the house. This was confirmed by finding that the blood lead level was in excess of 50 g per 100 mL. A 54-year-old man suddenly developed severe pain down both legs in the distribution of the sciatic nerve.
Cheap bexovid online master card. HIV/AIDS: Past Present and Future (a History Talk podcast).
The reticular formation by means of its reticulobulbar and reticulospinal tracts can control the parasympathetic and sympathetic outflows (see p hiv symptoms five years after infection purchase bexovid 200mg line. The reticular formation can influence all ascending pathways to the supraspinal levels (see p antiviral cream contain 200mg bexovid. The reticular formation can influence the degree of wakefulness of an individual (see p true hiv infection stories buy discount bexovid 200mg line. The limbic system is made up of the subcallosal how long do hiv infection symptoms last order bexovid online now, the cingulate, and the parahippocampal gyri, the hippocampal formation, the amygdaloid nucleus, the mammillary bodies, and the anterior thalamic nuclei. The efferent connections of the hippocampus arise from large pyramidal cells of the cortex. The efferent fibers in the fornix pass anterior to the interventricular foramen (see p. Some of the efferent fibers from the hippocampus end in the anterior nuclei of the thalamus (see p. The limbic system indirectly influences the activity of the endocrine system (see p. Ascending and descending excitatory influences in the brain stem reticulum: A re-examination. The tremors involved all of the fingers and the thumb and were present at rest but ceased during voluntary movement. On examination, the patient tended to perform all his movements slowly, and his face had very little expression and was almost masklike. When asked to stand up straight, the patient did so but with a stooped posture, and when he walked, he did so by shuffling across the examining room. The neurologist made the diagnosis of Parkinson disease, based on her knowledge of the structure and function of the basal ganglia and their connections to the substantia nigra of the midbrain. She was able to prescribe appropriate drug therapy, which resulted in a great improvement in the hand tremors. A 316 C H A P T E R O B J E C T I V E to describe the basal nuclei, their connections, and their functions and relate them to diseases commonly affecting this area of the nervous system the basal nuclei play an important role in the control of posture and voluntary movement. Unlike many other parts of the nervous system concerned with motor control, the basal nuclei have no direct input or output connections with the spinal cord. Caudate Nucleus the caudate nucleus is a large C-shaped mass of gray matter that is closely related to the lateral ventricle and lies lateral to the thalamus. The lateral surface of the nucleus is related to the internal capsule,which separates it from the lentiform nucleus. The head of the caudate nucleus is large and rounded and forms the lateral wall of the anterior horn of the lateral ventricle. The head is continuous inferiorly with the putamen of the lentiform nucleus (the caudate nucleus and the putamen are sometimes referred to as the neostriatum or striatum). Just superior to this point of union, strands of gray matter pass through the internal capsule,giving the region a striated appearance, hence the term corpus striatum. The body of the caudate nucleus is long and narrow and is continuous with the head in the region of the interventricular foramen. The body of the caudate nucleus forms part of the floor of the body of the lateral ventricle. The tail of the caudate nucleus is long and slender and is continuous with the body in the region of the posterior end of the thalamus. It follows the contour of the lateral ventricle and continues forward in the roof of the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle. Clinicians and neuroscientists use a variety of different terminologies to describe the basal nuclei. The subthalamic nuclei, the substantia nigra, and the red nucleus are functionally closely related to the basal nuclei, but they should not be included with them. The interconnections of the basal nuclei are complex, but in this account, only the more important pathways are considered. The basal nuclei play an important role in the control of posture and voluntary movement.
Susto is attributed to a traumatic or frighten ing event that causes the soul to leave the body hiv infection rates manchester buy bexovid 200mg with visa, thus resulting in illness and unhappiness; ex treme cases may result in death traitement antiviral zona order bexovid 200mg amex. Symptoms include appetite or sleep disturbances antiviral yonkis purchase 200 mg bexovid with visa, sadness antiviral immune response buy genuine bexovid online, lack of motivation, low self-esteem, and somatic symptoms. Recognized in Japan and among some American Japanese, this "interpersonal fear" syndrome is characterized by anxiety about and avoidance of interpersonal circumstances. The individual presents worry or a conviction that his or her appearance or social interactions are inadequate or offensive. Other cultures have similar cultural descriptions or syndromes associ ated with social anxiety. Instruments that have been normed for, adapted to , and tested on specific cultural and linguistic groups should be used. Instruments that are not normed for the population are likely to con tain cultural biases and produce misleading results. Subsequently, this can lead to misdiag nosis, overdiagnosis, inappropriate treatment plans, and ineffective interventions. Thus, it is important to interpret all test results cautious ly and to discuss the limitations of instruments with clients from diverse ethnic populations and cultures. Do you want an assessment that requires a clini cian to administer it, or can the client com plete the instrument himself or herself? Is the assessment process devel opmentally and culturally appropriate for your client? Choosing Instruments Numerous instruments screen for trauma his tory, indicate symptoms, assess trauma-related and other mental disorders, and identify relat ed clinical phenomena, such as dissociation. One instrument is unlikely to meet all screen ing or assessment needs or to determine the existence and full extent of trauma symptoms and traumatic experiences. The following sec tions present general considerations in select ing standardized instruments. Instrument Quality An instrument should be psychometrically adequate in terms of sensitivity and specificity or reliability and validity as measured in sever al ways under varying conditions. Do you need a standardized screening or assessment instru ment for clinical purposes? There are now four cluster symptoms, not three: reexperiencing, avoidance, arousal, and persistent negative alterations in cognitions and mood. Examples of measures: Life Stressor Checklist-Revised (Wolfe & Kimerling, 1997); Trauma History Questionnaire (Green, 1996); Traumatic Life Events Questionnaire (Kubany et al. Other Trauma-Related Symptoms Key question: Does the client have other symptoms related to trauma? These include depressive symptoms, self-harm, dissociation, sexuality problems, and relationship issues, such as distrust. Note: these measures can be helpful for clinical purposes and for outcome assessment because they gauge levels of symptoms. Other Trauma-Related Diagnoses Key question: Does the client have other disorders related to trauma? These include mood disor ders, anxiety disorders besides traumatic stress disorders, and dissociative disorders. Note: For complex symptoms and diagnoses such as dissociation and dissociative disorders, inter views are recommended. Is it easily administered and scored with accompanying manuals and/or other training materials? Is technical support available for difficulties in administra tion, scoring, or interpretation of results? Is special equipment required such as a micro phone, a video camera, or a touch-screen com puter with audio? If the client initially denies a history of trauma (or minimizes it), administer the questionnaire later or delay additional trauma-related ques tions until the client has perhaps developed more trust in the treatment setting and feels safer with the thoughts and emotions that might arise in discussing his or her trauma experiences. By going over the answers with the cli ent, you can gain a deep understanding of your client, and the client receives a demonstration of your sensitivity and concern for what the client has experienced. In addition to broad screening tools that cap ture various traumatic experiences and symp toms, other screening tools, such as the Combat Exposure Scale (Keane et al.