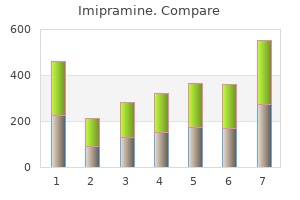
Imipramine
"Purchase imipramine cheap online, 0503 anxiety and mood disorders quiz".
By: S. Diego, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Associate Professor, Eastern Virginia Medical School
Any special technical modification should be written on the request form for the technical staff to review papa roach anxiety generic 75 mg imipramine with amex. Reporting studies In general anxiety symptoms blurred vision generic imipramine 50mg fast delivery, reporting sessions should contain the following features: (a) Physicians should review the studies before the patient leaves the floor and order further delayed scans where necessary anxiety job purchase generic imipramine canada, write a preliminary report for all inpatients and contact the referring physician with the results in the case of an emergency anxiety 24 hour hotline generic 25mg imipramine amex. Reports should be made after further consultation (if applicable), reviewed, signed and mailed or delivered within 24 hours. Such centres would only take on other functions, such as research and teaching, at a later stage. Within this context, the general issues that need to be considered are the location of the laboratory, building specifications, staff, training (Section 2. An advantage to this is that the two types of tests are often complementary in the diagnostic follow-up of patients with commonly encountered disorders such as those related to the thyroid. In vitro tests, being simpler and less expensive, are often set up first and in vivo work introduced at a later stage. Provisions should, therefore, be made at the initial planning stage for future in vivo activities (with a gamma camera, etc. On the other hand, in places where the two branches of nuclear medicine activity occupy separate premises there is little, if any, decrease in their effectiveness. Other suitable locations are university medical faculties (usually associated with teaching hospitals), medical research institutes or similar institutions, provided they are oriented towards patient service. Premises should generally provide working conditions that are hygienic and spacious, and may include special features depending on the extent to which radionuclides are used. A patient reception area with a waiting room and an area for taking blood samples should be available. If the laboratory has medically qualified staff who carry out examinations or dynamic tests such as intravenous insulin stimulation, the reception area should be equipped with a couch, resuscitation trolley and other special facilities. It is essential to reserve an area for record keeping and the sorting and labelling of samples that, depending on the tests required, may be taken in the laboratory or obtained from outside. It is essential to entrust a responsible person with this duty where the consequences of error - wrong patient, wrong test - could be irremediable. It should be spacious enough to accommodate the number of technicians employed, be well ventilated and have a constant and reliable supply of electricity and clean water. Floors and bench-tops should be smooth and of non-absorbent material to facilitate cleaning and decontamination in the event of chemical or radioactive spillage. A separate washbasin, labelled to this effect, should be reserved for the washing of hands of laboratory personnel, with its use prohibited for any other purpose. Sensitive electronic equipment, such as counters, computers and analytical balances, needs to be stored in airconditioned surroundings, particularly where the outside environmental conditions are hot, humid, dusty or otherwise unfavourable. A storage room for buffer chemicals, solvents, test tubes and other consumables that are often procured in bulk quantities would avoid cluttering up the main laboratory and provide greater workspace. If reagent production activities are developed to the stage of polyclonal antisera and monoclonal antibodies, access will be required to an animal house and supportive veterinary care. This is not necessary if the laboratory uses only readymade tracers obtained elsewhere in quantities of approximately 50 mCi (1. The importance of standard radiation safety practices such as the monitoring of personnel and the work area, and the prohibition of food, drink or smoking in the laboratory, is to be highlighted. The use of drip trays lined with absorbent paper is a wise precaution when handling radioactive solutions and minimizes the effect of accidental spillage. In a well managed laboratory, the areas designated for assays are separated from those reserved for other activities such as patient reception, record keeping and computing. In most modern centres, seminar rooms and other general areas are located at some distance from laboratory workbenches and no one wearing a laboratory coat is allowed to enter them. Solid waste including contaminated glassware, syringes, vials and pipette tips that are no longer usable should be stored in a marked container or bin for three half-lives before final disposal by incineration under proper conditions. This should be stored refrigerated in the radiochemical laboratory (hot laboratory) where the iodination facility and tracer purification system are also located. Whatever is left over or is no longer usable may be stored in a special area of the hot laboratory provided with lead shielding, for two to three half-lives, after which it may be disposed of into the sewage system. The proper recording of the receipt, dispensing and, finally, disposal of radioiodine should be a statutory requirement. This is more important than an ordinary stock book that records the receipt and issue of other consumables.
In non-palpable masses anxiety symptoms zollinger order imipramine with visa, localization by ultrasonography is recommended and the ultrasonographer should mark the location of the breast mass anxiety symptoms jaw spasms purchase imipramine now. Internal mammary lymph nodes anxiety symptoms bloating generic imipramine 50mg, however anxiety 6th sense order imipramine 25mg online, have less chance of being visualized with intradermal injection. Dose and volume injected the following procedure should be applied: (a) Injection around the tumour: -Patients imaged on the day of surgery require 18. Warming the saline to body temperature helps reduce the pain at the injection site that is frequently experienced by patients. This is followed by static acquisition for 5 min in the lateral and anterior projections. If the nodes are still not seen, static images should be repeated after two hours. A transmission scan is recommended using either 99mTc or 57Co flood sources to outline the body contours. Display of data Attention should be paid to the following points: - Dynamic images are summed and displayed representing 1 or 2 min each. Intra-operative procedures the intra-operative procedures are summarized below: (a) the surgeon injects Methylene Blue (Blue Patent V) around the breast mass. Using a surgical probe (radiation detection), the surgeon locates the sentinel node in the axilla and determines that it is the same node visualized with the Methylene Blue technique to trace the lymphatic system. Any node with activity higher than twice the background activity should be excised. If the primary tumour was not removed and the purpose of surgery is only to excise the sentinel node, the site of injection should be shielded with lead in order to decrease the background activity and to avoid saturation and electronic jamming of the detector. Internal mammary lymph nodes can be excised from the third and fourth intercostal space next to the outer border of the sternum. Patient selection Only cases with the following characteristics should be investigated: - Early stage malignant melanomas of the skin of no more than 3 mm in thickness; - No invasion of the subcutaneous tissue and no clinically palpable regional lymph nodes present; - Referral usually after an excisional biopsy or a wide surgical excision of the lesion. Radiopharmaceuticals the following radiopharmaceuticals are used for sentinel node localization: - Technetium-99m antimony tin colloid; 350 5. These can be used for fast visualization of the lymphatic channels and sentinel nodes provided the patient is due to enter the operating room soon. The first node seen after injection is the sentinel node and this should be properly marked on the skin. The following procedure should be observed: (a) Route of injection: -Intradermal injections, within 1 cm of the edge of the lesion or the scar at four corners and 90o apart, can be used. Mode of acquisition: -An anterior dynamic image should be taken every 30 s for 45 min, followed by static images for 5 min in the anterior and lateral projections. Region to be imaged: Depending on the location of the lesion, clinical judgement should be used in identifying the region to be imaged. Markers over the site of the sentinel node should be attempted using a point 57Co source, and an ink mark on the skin should be performed. Reporting: Details should be included on the site of injection and the radiopharmaceutical used, as well as on the location and number of sentinel nodes visualized. Preparation for the surgical probe: -The battery of the probe should be fully charged. Most probes are currently covered by disposable, sterile plastic tubing for use in the operating room, usually supplied by the manufacturer or obtained commercially. Principle Radioimmunodetection or radioimmunoscintigraphy uses tumour targeting antibodies or antibody fragments, labelled with a radionuclide suitable for external imaging, for the detection of specific cancers. Monoclonal antibodies have been developed against a variety of antigens associated with tumours and have been shown to target tumours with minimal side effects. Numerous radionuclides suitable for external imaging have been conjugated to antibodies, or antibody fragments, and the radioimmunoconjugates have been shown to be stable in vivo. Antibody fragments have been conjugated with 99mTc, allowing same or next day imaging. Intact immunoglobulin conjugated with 111 In permits imaging as late as a week after administration. Clinical indications Radioimmunoscintigraphy has been shown to be of benefit in the detection of occult disease, in the management of patients with potentially resectable disease, and for the evaluation of lesion recurrence and therapeutic response. Radiolabelled antibody imaging in prostate cancer has been shown to be useful in risk stratification and in patient selection for loco-regional therapy.
There are no abnormal morphologic changes such as bleeding anxiety symptoms head 75mg imipramine with mastercard, nerve fiber edema anxiety symptoms vibration discount imipramine 25mg overnight delivery, and hyperemia; visual acuity and visual field are normal anxiety or heart attack cheap imipramine 75mg online. Because of their location in the innermost layer of the retina anxiety 12 signs generic 50 mg imipramine with visa, they tend to obscure the retinal vessels. When this tissue takes the form of veil-like membrane overlying the surface of the optic disk, it is also referred to as an epipapillary membrane. Ophthalmoscopy can reveal superficial drusen but not drusen located deep in the scleral canal. In the presence of optic disk drusen, the disk appears slightly elevated with blurred margins and without an optic cup. Abnormal morphologic signs such as hyperemia and nerve fiber edema will not be present. However, bleeding in lines along the disk margin or subretinal peripapillary bleeding may occur in rare cases. This impedes axonal plasma flow, which predisposes the patient to axonal degeneration. Deep drusen can cause compressive atrophy of nerve fibers with resulting subsequent visual field defects. Optic disk drusen may be diagnosed on the basis of characteristic ultrasound findings of highly reflective papillary deposits. Fluorescein angiography findings of autofluorescence prior to dye injection are also characteristic. Epidemiology: Epidemiologic data from the 1950s describe papilledema in as many as 60% of patients with brain tumors. Since then, advances in neuroradiology have significantly reduced the incidence of papilledema. Etiology: An adequate theory to fully explain the pathogenesis of papilledema is lacking. Current thinking centers around a mechanical model in which increased intracranial pressure and impeded axonal plasma flow through the narrowed lamina cribrosa cause nerve fiber edema. However, there is no definite correlation between intracranial pressure and prominence of the papilledema. Nor is there a definite correlation between the times at which the two processes occur. However, severe papilledema can occur within a few hours of increased intracranial pressure, such as in acute intracranial hemorrhage. Therefore, papilledema is a conditional, unspecific sign of increased intracranial pressure that does not provide conclusive evidence of the cause or location of a process. In approximately 60% of all cases, the increased intracranial pressure with papilledema is caused by an intracranial tumor; 40% of all cases are due to other causes, such as hydrocephalus, meningitis, brain abscess, encephalitis, malignant hypertension, or intracranial hemorrhages. The patient should be referred to a neurologist, neurosurgeon, or internist for diagnosis of the underlying causes. Every incidence of papilledema requires immediate diagnosis of the underlying causes as increased intracranial pressure is a life-threatening situation. The incidence of papilledema in the presence of a brain tumor decreases with increasing age; in the first decade of life it is 80%, whereas in the seventh decade it is only 40%. Papilledema cannot occur where there is atrophy of the optic nerve, as papilledema requires intact nerve fibers to develop. Special forms: O Foster Kennedy syndrome: this refers to isolated atrophy of the optic nerve due to direct tumor pressure on one side and papilledema due to increased intracranial pressure on the other side. Possible causes may include a meningioma of the wing of the sphenoid or frontal lobe tumor. Possible causes may include penetrating trauma or fistula secondary to intraocular surgery. Symptoms and diagnostic considerations: Visual function remains unimpaired for long time.
Buy imipramine 50 mg with visa. Sanders sides incorrect quotes•gacha life 1000 sub special Halloween edition.
In many cases anxiety verses discount imipramine 25mg with amex, an interrupted periosteal rim will surround the expanded portion of bone anxiety fear buy genuine imipramine line. This pattern may be seen in locally aggressive tumors and in lowgrade malignancies anxiety nursing diagnosis discount imipramine master card. Due to the minute size of radiolucencies the lesion may be difficult to see and to delineate on the plain film anxiety 5 things you can see 75 mg imipramine amex. Generally, the more rapidly growing a lesion, the more difficult it is to see on plain film. The periosteum responds to traumatic stimuli or pressure from an underlying growing tumor by depositing new bone. The radiographic appearances of this response reflect the degree of aggressiveness of the tumor. This is seen in malignant bone tumors and in some other rapidly growing lesions such as aneurysmal bone cyst, or in reactive processes (osteomyelitis, and subperiosteal hematoma). Other types of periosteal reaction in response to a rapidly growing lesion include "onion-skinning" and spiculated "hair-on-end" types. Malignant osteoid can be recognized radiologically as cloudlike or ill-defined amorphous densities with haphazard mineralization. Mature osteoid, or organized bone, shows more orderly, trabecular pattern of ossification. Radiologically, it is usually easier to recognize cartilage as opposed to osteoid by the presence of focal stippled or flocculent densities, or in lobulated areas as rings or arcs of calcifications. Whatever the pattern, it only suggests the histologic nature of the tissue (cartilage) but does not reliably differentiate between benign and malignant processes. Always obtain a list of differential diagnoses from a radiologist, make a habit of reviewing the films, and develop a good working relationship with an orthopedic surgeon. On physical examination, there was some local tenderness and soft tissue swelling over the proximal and mid thirds of the left humerus. Characteristic Radiological Findings q Plain radiograph shows a large ill-defined, destructive, diaphyseal intramedullary lesion with permeative pattern of bone destruction and periosteal reaction of a "hair-on-end" type. Although the radiological features listed here (poor margination, permeative bone destruction, periosteal "hair-on-end" reaction and soft tissue involvement) are very common in this entity, they are not entirely specific, and just indicate the presence of a rapidly growing, most likely malignant, destructive tumor. Pathological Findings q Biopsy material showed a highly cellular, infiltrative neoplasm consisting of sheets of tightly packed, round cells with very scant cytoplasm ("round blue cell tumor"). The clue here is in the cytological appearance and pattern consisting of sheets of primitive cells with little histologic evidence of differentiation. Most common skeletal sites include diaphyses of femur, tibia and humerus, and also pelvis and ribs (Askin tumor of the chest). Response to pre-operative chem otherapy, as assessed by the degree of histologic tumor necrosis is a major independent prognostic factor. Studies have also shown that during tumor progression, secondary molecular alterations may occur, which often involve genes regulating cell cycle. The histological response to chemotherapy as a predictor of the oncological outcome of operative treatment of Ewing sarcoma. He stated that the mass had been present for several years and did not change in size. Characteristic Radiological Findings: q Plain radiograph demonstrated a pedunculated bony outgrowth at the proximal tibial metaphysis. Pathological Findings: the specimen consisted of a pedunculated lesion, 3 x 3 x 2cm, with a lobulated cartilage cap measuring up to 0. Few small islands of similarly appearing cartilage were present in the stalk and at the resection margin. Solitary osteochondromas may be either primary due to a developmental anomaly of bone, or secondary following trauma. Unlike primary osteochondromas, secondary lesions are often seen in the phalanges of the hands and feet and have their peak incidence in the 3rd and 4th decades of life. Multiple osteochondromas represent an autosomal dominant hereditary disorder and are associated with bone deformities.
Using the optimal parameters anxiety nursing interventions order imipramine 50 mg otc, it was observed that the overall trends and magnitudes were reproduced during combined loading (Fig 2B) anxiety 1-10 rating scale buy on line imipramine. Using the optimized parameters anxiety symptoms difficulty swallowing order generic imipramine on-line, it was also observed that the model predicted load response was generally comparable in the dominant shear loading direction (anterior) with very good agreement in the superior loading direction anxiety symptoms in spanish cheap imipramine 50 mg with mastercard. Further plantar tissue validation will also be performed for additional loading tools and loading scenarios [3]. Given the availability of data, this study could also be extended to include forefoot passive response, effectively modeling whole foot structural response. To the authors knowledge, this study is the first to optimize nonlinear elastic material parameters using dominant and off-axis loads in a 3D model and including a validation attempt with an additional dataset. The results have important implications for the accurate prediction of shear response in plantar tissue and lend more insight into the biomechanics of this important structure. Figure 2: Comparison of experimental reaction forces with the model predicted values using the optimized material properties A) compression B) combined loading of compression and anterior-posterior shear. LifeModeler was used to compute the contact force between the triquetrum and hamate throughout the hammering path based on the amount of intersection of the two surface meshes. Contact force location and orientation were reported in a capitate-based inertial coordinate system because it aligned well with the dorsal-volar and proximaldistal directions of the hamate. It was shown that the articulation of the triquetrum on the hamate was roughly helicoidal as the triquetrum rotated around the convex surface of the hamate. It was qualitatively observed that the triquetrum maintains a distal course along the hamate until it reaches a prominent distal ridge at which point it begins a volar course. However it is difficult to determine whether or not the triquetrum is interacting with the distal ridge of the hamate using standard kinematic measures. We found that as the triquetrum moved distally on the hamate the contact force shifted from its location on the oval articular surface of the hamate to the distal ridge. The orientation of the force vector also shifted from a more dorsal to a volar direction. Primary limitations in this study include the imposed penetration of the articular surfaces of the triquetrum and hamate, as well the lack of adjacent carpal articulations and ligament constraints. Future work will include these structures and the use of kinematics to train a model for forward dynamics simulation. We qualitatively observed that at the strike position of the hammering task, the contact force vector was located on or near the distal ridge of the hamate. Our visual understanding of the triquetrum translating along an oblique path over the hamate from proximal and dorsal to distal and volar as the wrist Figure 2. Three views of the contact force as it sweeps through the range of wrist positions (Bottom Panel). As the triquetrum moved distally on the hamate, the force vector shifted from a distal location and more dorsal orientation (red vector) to a proximal location and a more volar orientation (blue vector). A common treatment for patients involves removal of the degenerated disc and fusion of the adjacent vertebral bodies. However, previous research has shown that as many as 25-92% of patients treated with fusion have disc degeneration at the adjacent levels within 10 years after surgery [2,3]. It has been hypothesized that this degeneration results from changes in motion at vertebral segments adjacent to the fusion site [2]. Thus, the objective of this study was to compare the dynamic, three-dimensional (3D) motion of the cervical spine in control subjects and cervical fusion patients. Biplane x-ray images were acquired at 60 Hz during two motion tasks: axial neck rotation and neck extension. For the axial neck rotation task, subjects rotated their neck from a position of maximal right rotation to maximal left rotation. For the neck extension task, subjects moved their neck from a position of full flexion (chin against chest) to full extension. Motion at C4-C5 and C6-C7 was measured for each subject, as these represented the vertebral motion segments above (C4-C5) and below (C6-C7) the fusion site for the fused subjects.