Periactin
"Order periactin 4 mg with amex, allergy medicine 773".
By: C. Lukjan, M.S., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine at Arkansas State University
Serum thyroglobulin represents a very sensitive index of a state of thyroid hyperstimulation (27) allergy symptoms food allergies causes periactin 4 mg discount. Systematic screening for congenital hypothyroidism allergy testing tulsa cheap periactin 4 mg with amex, if already available allergy treatment with acupuncture buy genuine periactin on line, is a particularly sensitive tool in the evaluation of the iodine status of a population and in the monitoring of iodine supplementation programmes (40) 621 allergy symptoms purchase periactin 4 mg with amex. As iodine has often been leached from the soil by glacial action and water washing out the soluble iodine, mountainous areas are particularly susceptible, but as already noted, by no means the exclusive sites of iodine-deficient populations. Traditionally, populations living close to the sea have been less at risk because marine foods, including seaweed, tend to be high in iodine. Other ways of replacing iodine have been through supplementation, tinctures of iodine, iodized oil, both intramuscular injections and oral, and by adding it to foods, especially salt but also water supplies and other food vehicles. Overwhelmingly, salt iodization is the intervention of choice, with the others ancillary to reach hard-to-access populations at high risk. Salt iodization has been a remarkably successful intervention as it is feasible, cheap, safe, rapidly effective and widely accepted. There is also now considerable experience in many different countries, cultures and hence dietary practices. As noted, iodized salt is the most appropriate measure for iodine deficiency control because it is used by all sections of a community, is consumed at roughly the same level throughout the year and because its production is often confined to a few centres which facilitates quality control at the level of production (27,66). Although slightly more expensive than iodide, the iodate salt is preferred, especially for moist, tropical conditions and where storage conditions are likely to be less than optimal, because it is less soluble and more stable than iodide. While most countries of the world use the iodate form, several countries in Europe. The preconditions needed to ensure adequate salt iodization availability and consumption include: · local production and/or importation of iodized salt in a quantity that is sufficient to satisfy the potential human demand (approximately 45 kg/person per year); · 90% of salt for human consumption (whether local or imported) must be iodized according to government standards for iodine content; · the percentage of food-grade salt with an iodine content of at least 15 ppm, in a representative sample of households, must be equal to or greater than 90%; and · iodine estimation at the point of production or importation, and at the wholesale and retail levels, must be determined by titration; at the household level, it may be determined by either titration or certified kits (27). Assuming an average salt consumption of 10 g of salt/capita per day, a loss of iodine of some 20% between production and retail and another 20% during food processing (67), to achieve the recommended level of iodine of 150 µg per person for adults, iodine in the salt should be in the range of 2040 mg/kg (2040 ppm) (68). To avoid losses as high as 75% over a period of nine months, waterproof packaging is required, as re-emphasized in the recent amended Codex Alimentarius. Sixty-six per cent of households of the surveyed countries have access to iodized salt, as compared to 5 to 10% in 1990 (20). A variety of iodized oils have been used including most commonly, Lipiodol, a poppy seed oil containing 40% iodine per weight. Over the past six or seven decades, iodized oil has been extensively used, initially in Papua New Guinea and thereafter in Africa, China and Latin America, and in many of the most severe endemic areas in the world (71), as well as in Europe. More than 20 million doses of iodized oil have been administered since 1974, initially by injections and subsequently orally, with very few side-effects, including during pregnancy (73). In the groups most susceptible to the effects of iodine deficiency, women of reproductive age, pregnant women and children less than 2 years, iodine supplements such as iodized oil are recommended where salt iodization coverage is inadequate (29). Since 1942, the main carrier for iodine in the Netherlands has been the salt in bread. Iodized water has been successfully used in several countries such as the Central Asian Republics, Italy (Sicily), Mali, and Thailand. A limiting factor of this approach, especially in terms of costeffectiveness, is the question of availability of one single source of iodine for the whole population and for the livestock (75). Sugar has been iodized in pilot studies in Guatemala and the Sudan, and iodized tea has been used in China. Indirect iodization has also been shown to be effective in correcting iodine deficiency. Adding potassium iodate into irrigation water has been reported as highly successful in Xinjiang, China: for example, the infant mortality rate dropped by 50% (76). Milk has adventitiously had its iodine content raised in many dairy-producing countries consequent to the use of iodophors in the dairy industry. A change in dairy practice would reverse the situation and increase the likelihood of iodine deficiency in those populations. The salt licks used by animals in much of European stock-raising should be fortified with iodine but often are not. However, if the added iodine becomes part of the ecological system, cost-effectiveness is improved, and sustainability likely; quality control, however, may be harder to ensure. These other options to increase iodine intake will become increasingly important within the next few years as a result of the policy adopted by many countries to reduce salt consumption intake to 5 g/day in order to prevent hypertension and cardiovascular diseases.
People may need more regular testing if they · have had a thyroid problem before allergy medicine ok for breastfeeding discount periactin 4mg mastercard, such as goiter or thyroid surgery · have a family history of thyroid disease · have pernicious anemia allergy forecast waukesha wi buy periactin 4 mg online, a B12 deficiency; type 1 diabetes; or primary adrenal insufficiency allergy generator buy discount periactin 4mg on-line, a hormonal disorder · eat large amounts of food containing iodine allergy shots cvs purchase cheap periactin line, such as kelp, or use iodinecontaining medications such as amiodarone, a heart medication · are older than age 60 · were pregnant or delivered a baby within the past 6 months Getting tested routinely helps uncover thyroid problems-especially subclinical problems. Others prefer to leave it untreated but monitor their patients for signs that the condition is worsening. Hyperthyroidism in the Aging Population Hyperthyroidism is more common in people older than age 60 and is often caused by thyroid nodules. For this reason hyperthyroidism in this age group is sometimes misdiagnosed as depression or dementia-loss of intellectual abilities, sometimes with emotional disturbance and personality changes. For example, older adults with hyperthyroidism may seem disinterested or withdraw socially. Older adults with hyperthyroidism may lose their appetites, whereas younger people with the condition tend to have increased appetites. Untreated hyperthyroidism can also speed the bone-thinning disease osteoporosis, particularly in women, and increase the likelihood of bone fractures. That normal enlargement, combined with fatigue, makes a new thyroid problem easy to miss. A rapid and irregular heartbeat, a slight tremor, and unexplained weight loss or failure to have normal pregnancy weight gain are signs that hyperthyroidism could be developing. This inflammation of the thyroid gland affects about 4 to 10 percent of women in the first year after giving birth. Women with postpartum thyroiditis often develop hypothyroidism before the thyroid gland is completely healed. Postpartum thyroiditis sometimes goes undiagnosed because the symptoms are mistaken for postpartum blues-the exhaustion and moodiness that sometimes follow delivery. If symptoms of fatigue and lethargy do not go away within a few months or a woman develops postpartum depression, she should talk with her health care provider. She may have developed a permanent thyroid condition and will need to take medication. With suspected hyperthyroidism, health care providers take a medical history and perform a thorough physical exam. Health care providers may conduct additional tests to help confirm the diagnosis or determine the cause of hyperthyroidism. With hyperthyroidism, the levels of one or both of these hormones in the blood are higher than normal. The aim of treatment is to bring thyroid hormone levels to a normal state, thus preventing long-term complications, and to relieve uncomfortable symptoms. Beta blockers act quickly to relieve many of the symptoms of hyperthyroidism, such as tremors, rapid heartbeat, and nervousness, but do not stop thyroid hormone production. However these women should continue to be monitored for recurrence of thyroid problems following delivery. Studies have shown that mothers taking antithyroid medications may safely breastfeed. However, they should take only moderate doses, less than 10-20 milligrams daily, of the antithyroid medication methimazole. Almost everyone who receives radioactive iodine treatment eventually develops hypothyroidism. But health care providers consider this an acceptable outcome because hypothyroidism is easier to treat and has fewer long-term complications than hyperthyroidism. Although iodine-131 is not known to cause birth defects or infertility, radioiodine therapy is not used in pregnant women or women who are breastfeeding. Experts recommend that women wait a year after treatment before becoming pregnant. Radioiodine Therapy Radioactive iodine-131 is a common and effective treatment for hyperthyroidism. Because the thyroid gland collects iodine to make thyroid hormone, it will collect the radioactive iodine from the bloodstream in the same way. This presurgical treatment prevents a condition called thyroid storm-a sudden, severe worsening of symptoms-that can occur when hyperthyroid patients have general anesthesia. When part of the thyroid is removed-as a treatment for toxic nodules, for example- thyroid hormone levels may return to normal.
Cheap periactin 4 mg with visa. Prison Break 5x09 "Behind the Eyes" SEASON FINALE REACTIONS.
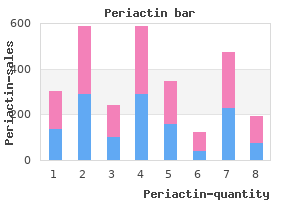
Because exposures in these incidents are thought to have been largely from oral ingestion of radioiodine allergy shots make you feel worse purchase genuine periactin line, these studies are discussed in detail in Section 3 allergy medicine starts with l order 4 mg periactin amex. This condition would be highly unlikely in iodine-induced hypothyroidism secondary to inhalation of iodine allergy treatment atlanta generic periactin 4mg line. However allergy symptoms for gluten order periactin 4 mg without prescription, one epidemiological study examined health outcomes of infants of mothers who resided in the Belarus region before or after the Chernobyl accident (Petrova et al. The occurrence of thyroid cancers has also been studied in populations exposed to radioiodine released from nuclear bomb tests at the Nevada Test Site and from operational releases of radioiodine from the Hanford Nuclear Site. Although the inhalation of radioiodine occurred in these incidents, oral ingestion of radioiodine is thought to have been the major contributor to thyroid radiation doses. The estimated cumulative gamma radiation dose on these islands ranged from 69 to 175 rad (0. Later studies suggest that external radiation contributed approximately 4 16% of total thyroid dose (Hamilton et al. Internal exposures to the thyroid, resulting primarily from radioiodines, were much higher. Nursing infants would also have received internal exposures from ingestion of radioiodine in breast milk. Although these measurements allowed back extrapolation of the initial internal 131I exposures, shorter-lived radioiodine species (132I, 133I, 135I) could not be detected in the urine sample. These isotopes are thought to have contributed 23 times the thyroid radiation dose of 131I (Conard 1984). Sixty-six nuclear bomb tests were conducted in the Marshall Islands during the period 19461958. The external radiation exposures were contributed largely by isotopes of cesium. Estimates of thyroid radiation doses have been derived from external thyroid gland scans that measure radiation (mostly gamma) from radioiodine in the thyroid. These measurements suggest that radioiodine doses to the thyroid gland were highest in small children at the time of the release, and were highest in locations nearest to the nuclear plant where people were not evacuated rapidly. Estimated median doses received in populations residing approximately 200 km from the plant. Although inhalation of airborne radioiodine is likely to have occurred after the accident, the major contributors to the absorbed thyroid radiation dose are thought to have been from ingestion of milk and leafy vegetables contaminated from atmospheric deposition of radioiodine. Endemic goiter in the Belarus population due to iodine deficiency (Gembicki et al. Thyroid dose estimates, particularly peak dose rates, are largely based on extrapolations from thyroid gland 131I measurements made within 1 to several weeks after the major release from the Chernobyl plant and ground monitoring of atmospheric deposition of radiocesium. One set of measurements of thyroid gland radioactivity came from postmortem measurements of thyroid glands from 416 people collected over the period from May 3 (8 days after the initial release) to August 4, 1986 in Bratislava (Beno et al. Back extrapolation of thyroid gland activities and consideration of temporal trends in both the thyroid gland data and atmospheric deposition allowed the estimation of transfer coefficients relating atmospheric deposition of radioiodine (kBq/m2) and thyroid dose (µSv); the coefficients were 641 µSv/kBq-m2 in exposed children and 221 µSv/kBq-m2 in exposed adults (Beno et al. Based on this approach, and radiocesium measurements made in Belarus, thyroid radiation doses received in Belarus may have ranged from 0. In Gomel, where the highest incidence of thyroid cancer in children has been reported, estimated doses were 1. Almost all of the internal radiation exposure of the thyroid gland was received in the first 3 months after the accident, during which time, the 131I activity decreased to <0. These tests were followed by nine surface detonations during the period 19621968 and approximately 809 below-ground tests, of which 38 were determined to have resulted in off-site releases of radioactive materials. Geographicspecific geometric mean lifetime doses are estimated to have ranged from 0. Thyroid radiation doses have been estimated using a dosimetry model developed in the Hanford Environmental Dose Reconstruction Project (Shipler et al. Deaths related to thyroid cancers (or to other cancers or causes) following the accident continue to be studied and possible associations between mortality and radioiodine exposures may eventually become evident. However, papillary carcinomas that occur in young children, the predominant age group for thyroid cancers observed after the Chernobyl accident, are more fatal then when they occur in adults (Harach and Williams 1995). The major systemic effects of exposures to radioiodine are on the thyroid gland; however, other systemic effects have been observed, including inflammation of the salivary glands (sialadentitis), following relatively high exposures to radioiodine such as those used for ablative treatment of thyroid cancers.
Insight into the molecular basis of pathogen abundance: group A Streptococcus inhibitor of complement inhibits bacterial adherence and internalization into human cells allergy symptoms joints discount periactin 4mg otc. Nonpolar inactivation of the hypervariable streptococcal inhibitor of complement gene (sic) in serotype M1 Streptococcus pyogenes significantly decreases mouse mucosal colonization allergy xanax best order periactin. Streptococcal inhibitor of complement inhibits two additional components of the mucosal innate immune system: secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor and lysozyme allergy treatment in infants buy periactin 4mg amex. Acquisition of regulators of complement activation by Streptococcus pyogenes serotype M1 allergy meds for dogs order periactin uk. Streptolysin O promotes group A Streptococcus immune evasion by accelerated macrophage apoptosis. Nad glycohydrolase acts as an intracellular toxin to enhance the extracellular survival of group A streptococci. Vascular dysfunction and ischemic destruction of tissue in Streptococcus pyogenes infection: the role of streptolysin O-induced platelet/ neutrophil complexes. Role of streptolysin O in a mouse model of invasive group A streptococcal disease. Incompetence of neutrophils to invasive group A Streptococcus is attributed to induction of plural virulence factors by dysfunction of a regulator. Reduced virulence of group A streptococcal Tn916 mutants that do not produce streptolysin S. Cytocidal effect of Streptococcus pyogenes on mouse neutrophils in vivo and the critical role of streptolysin S. A two-component regulatory system, CsrR-CsrS, represses expression of three Streptococcus pyogenes virulence factors, hyaluronic acid capsule, streptolysin S, and pyrogenic exotoxin B. Cytotoxic effects of streptolysin O and streptolysin S enhance the virulence of poorly encapsulated group A streptococci. Fc-receptor and M-protein genes of group A streptococci are products of gene duplication. Many group A streptococcal strains express two different immunoglobulin-binding proteins, encoded by closely linked genes: characterization of the proteins expressed by four strains of different M-type. Evasion of phagocytosis through cooperation between two ligandbinding regions in Streptococcus pyogenes M protein. Protective immune response against Streptococcus pyogenes in mice after intranasal vaccination with fibronectin-binding protein SfbI. Nonimmune interaction of the SfbI protein of Streptococcus pyogenes with the immunoglobulin G F(ab=)(2) fragment. A novel, anchorless streptococcal surface protein that binds to human immunoglobulins. IdeS, a highly specific immunoglobulin G (IgG)cleaving enzyme from Streptococcus pyogenes, is inhibited by specific IgG antibodies generated during infection. IgG protease Mac/IdeS is not essential for phagocyte resistance or mouse virulence of M1T1 group A Streptococcus. Insight of host immune evasion mediated by two variants of group A Streptococcus Mac protein. EndoS and SpeB from Streptococcus pyogenes inhibit immunoglobulin-mediated opsonophagocytosis. Study of the IgG endoglycosidase EndoS in group A streptococcal phagocyte resistance and virulence. EndoS2 is a unique and conserved enzyme of serotype M49 group A Streptococcus that hydrolyzes N-linked glycans on IgG and alpha1-acid glycoprotein. The SpeB virulence factor of Streptococcus pyogenes, a multifunctional secreted and cell surface molecule with strepadhesin, laminin-binding and cysteine protease activity. Temporal production of streptococcal erythrogenic toxin B (streptococcal cysteine proteinase) in response to nutrient depletion. Substitution of cysteine 192 in a highly conserved Streptococcus pyogenes extracellular cysteine protease (interleukin 1beta convertase) alters proteolytic activity and ablates zymogen processing. Role for a secreted cysteine proteinase in the establishment of host tissue tropism by group A streptococci.