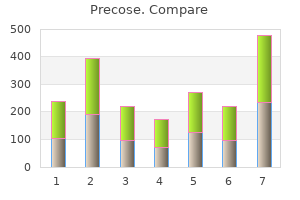
Precose
"25 mg precose with amex, diabetic neuropathy icd 9".
By: B. Navaras, M.S., Ph.D.
Program Director, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker M.D. School of Medicine
Nerve blocks are the key to being able to perform dental extractions in the standing horse under a constant-rate intravenous infusion of an anesthetic agent diabetes type 2 effects generic precose 50mg line. With the use of regional nerve blocks most horses can have productive noninvasive and invasive dental procedures under standing sedation diabetes prevention blog precose 50 mg otc. General anesthesia is still necessary for intractable patients diabetes test zeist 25mg precose fast delivery, surgeries requiring computed tomography at most North American institutions and practices diabetes mellitus neuropathy generic 50 mg precose with amex, and extractions or maxillofacial surgeries requiring precise, delicate surgical technique. When placing a regional nerve block, achieving effectiveness while reducing risk is paramount. The following descriptions give systematic directions to perform the major nerve blocks associated with extractions. Three nerve blocks will be discussed: the maxillary nerve block, the mental nerve block, and the inferior alveolar nerve block. This intersection point provides an estimate of the location of the mandibular foramen on the medial aspect of the coronoid process. This indicates the depth of needle insertion on the medial aspect of the mandible to reach the foramen. The use of a nerve stimulator, in the horse, has not been published but is used in multiple academic institutions. The use of the nerve stimulator gives the clinician confirmation of appropriate deposition of anesthetic, reducing the volume of anesthetic required, thus decreasing possible impacts to adjacent nerves like the lingual nerve. The masticatory reflex is believed to be the result of stimulation of the inferior alveolar nerve resulting in the jaw-opening reflex and the reflex inhibition of jaw-closing muscles similar to that described in detail in the cat. If no nerve stimulation guidance is chosen, use the 6-inch, 20-gauge Tuohy needle to perform the block. Positioning of the needle and delivery of anesthetic is the same for stimulation-guided and nonguided blocks. At this angle, the needle should first contact bone on the dorsal aspect of the pterygoid fossa. Equipment Needed Sharpie and straight-edge Clippers Betadine and saline soaked gauze for prep tray Sterile gloves Tuohy epidural needlesc (spinal needles used historically) -3. This block will provide analgesia to the ipsilateral mandible and mandibular teeth in addition to all soft-tissue structures innervated by the mental nerve. The mandibular third incisor-canine-second premolar interproximal space provides a visible marker for the location of this line. If necessary, completely remove the needle and attempt a slightly different angle/placement. Technique 2 A second technique for anesthetizing the inferior alveolar nerve intraorally has been published in the literature. The study evaluated the efficacy of the intraoral block on client horses and reported the findings. Determination of efficacy was based on the ability to perform the necessary dental procedure. If the reader is interested in performing intraoral inferior alveolar blocks, it is strongly recommended that they refer to the paper for anatomical guidance, needle positioning, and encountered complications. The mental foramen nerve block anesthetizes the rostral portion of the inferior alveolar nerve as it branches into the rostral inferior alveolar nerve that innervates the canine and incisor teeth and the mental nerve at the level of the mental foramen. If the block is delivered to the rostral inferior alveolar nerve, then the ipsilateral canine and incisor teeth will be anesthetized in addition to the skin and lip rostral to the mental foramen. Only the mental nerve (skin and lip) will be anesthetized if the local anesthetic is not delivered through the mental foramen into the mandibular canal. Mental foramen positioning is 1/3 of the horizontal distance of the incisor-premolar space from the second premolar and 1/3 of the vertical distance in the mandible from the dorsal surface of interproximal space at the level of the foramen.

Atrial fibrillation in left ventricular noncompaction with and without neuromuscular disorders is associated with a poor prognosis diabetes prevention games buy 25mg precose amex. Clinical features of isolated ventricular noncompaction in adults long-term clinical course diabetes insipidus and diabetes mellitus order precose mastercard, echocardiographic properties blood glucose 86 mg dl cheap 50mg precose overnight delivery, and predictors of left ventricular failure diabetes signs symptoms and treatment order precose 25mg free shipping. Genotype-positive status is associated with poor prognoses in patients with left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy. Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy: cardiac, neuromuscular, and genetic factors. Isolation of pulmonary vein and superior vena cava for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in a young adult with left ventricular non-compaction. Life-threatening event risk in children with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: a multicenter international study. Practice variation in anticoagulation prescription and outcomes after device-detected atrial fibrillation. Progression to chronic atrial fibrillation after pacing: the Canadian Trial of Physiologic Pacing. Detection of new atrial fibrillation in patients with cardiac implanted electronic devices and factors associated with transition to higher device-detected atrial fibrillation burden. Subclinical device-detected atrial fibrillation and stroke risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Newly detected atrial high rate episodes predict long-term mortality outcomes in patients with permanent pacemakers. Atrial high-rate episodes and risk of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with cardiac implantable electronic devices. Detection of previously undiagnosed atrial fibrillation in patients with stroke risk factors and usefulness of continuous monitoring in primary stroke prevention. Atrial high rate episodes in patients with cardiac implantable electronic devices: implications for clinical outcomes. Randomized trial of atrial arrhythmia monitoring to guide anticoagulation in patients with implanted defibrillator and cardiac resynchronization devices. Diabetes mellitus is a strong, independent risk for atrial fibrillation and flutter in addition to other cardiovascular disease. Atrial flutter: clinical risk factors and adverse outcomes in the Framingham Heart Study. Moving the tipping point: the decision to anticoagulate patients with atrial fibrillation. Clinical outcomes of solitary atrial flutter patients using anticoagulation therapy: a national cohort study. Celikyurt U, Knecht S, Kuehne M, Reichlin T, Muehl A, Spies F, Osswald S, Sticherling C. Incidence of new-onset atrial fibrillation after cavotricuspid isthmus ablation for atrial flutter. Newonset atrial fibrillation after cavotricuspid isthmus ablation: identification of advanced interatrial block is key. Prediction of uneventful cardioversion and maintenance of sinus rhythm from direct-current electrical cardioversion of chronic atrial fibrillation and flutter. Initial energy setting, outcome and efficiency in direct current cardioversion of atrial fibrillation and flutter. Safety and efficacy of advanced atrial pacing therapies for atrial tachyarrhythmias in patients with a new implantable dual chamber cardioverter-defibrillator. Conduction block in the inferior vena caval-tricuspid valve isthmus: association with outcome of radiofrequency ablation of type I atrial flutter. Scaglione M, Caponi D, Ebrille E, Di Donna P, Di Clemente F, Battaglia A, Raimondo C, Appendino M, Gaita F. Very long-term results of electroanatomic-guided radiofrequency ablation of atrial arrhythmias in patients with surgically corrected atrial septal defect. Association of left atrial function with incident atypical atrial flutter after atrial fibrillation ablation. Mechanisms of organized left atrial tachycardias occurring after pulmonary vein isolation. Wasmer K, Monnig G, Bittner A, Dechering D, Zellerhoff S, Milberg P, Kobe J, Eckardt L.
The choices facing current veterinary school graduates are not rosy metabolic diseases biochemistry 25mg precose fast delivery, and the equine industry in general may be near a reckoning point in terms of tackling this issue diabetes insipidus low urine osmolality purchase precose with a visa. This review describes diagnostic techniques and findings to facilitate early identification and treatment of mares with compromised pregnancy diabetes prevention needs assessment purchase precose from india. Based on retrospective studies of pathology cases in Kentucky and Europe diabetes in bichon frise dogs cheap precose 25 mg free shipping, the primary cause of pregnancy loss is placentitis/fetal sepsis. Because clinical presentation of these and other conditions is subtle and nonspecific, identification of compromised pregnancies and correct classification of high-risk mares in time for successful intervention represents a serious challenge to the equine industry. Identifying the High-Risk Mare It is generally recommended that all mares be evaluated periodically throughout pregnancy. Mares should be vaccinated for equine herpesvirus 1 using a killed vaccine at 5, 7, and 9 months of gestation, which provide convenient junctures for evaluation of pregnant mares. Clinical and Diagnostic Findings Consistent with Elevated Gestational Risk mended to examine mares in late autumn or early winter (November/December in the northern hemisphere) to confirm pregnancy prior to the breeding season. The examination should include observation of overall maternal health and ambulation, a complete physical examination, and an evaluation of the pregnancy through either palpation or transrectal ultrasonography. Careful attention should be given to vulvar conformation and evidence of vulvar discharge at this time. Due to the weight of the fetus and fetal fluids in late gestation, the cervix can be displaced cranially, exacerbating risk of urine pooling, pneumovagina and fecal contamination of the caudal reproductive tract. Mares that exhibit white crystalline accumulations just below the ventral commissure of the vulva should be suspected to experience some degree of urine pooling, while pneumovagina can often be diagnosed as vaginal distention via transrectal palpation or based on the characteristic aspiration of air when the vulvar lips are gently separated. Glandular development should be differentiated from edema or fat deposition in the mammary gland, which can occur routinely and are not indicative of larger problems. In addition, any mare with a history of late-term pregnancy loss or subfertility should be included in this group (Table 1). Common Differential Diagnoses for High-Risk Mares Exam Parameter History Diet Physical exam Findings Consistent with Elevated Gestational Risk Previous pregnancy loss/neonatal disease Recent systemic disease Fescue exposure Systemic infection Equine asthma Colic Laminitis Body-wall defect Poor perineal conformation Urine crystals evident on ventral commissure Pneumovagina Vulvar discharge Persistently inactive fetus Posterior presentation 9 months Twins (generally diagnosed via transabdominal ultrasonographic examination) Increased uteroplacental thickness Increased fluid echogenicity Precocious glandular development or secretions more than 3 weeks before term Serosanguinous mammary discharge Excessive edema extending from mammary glands along ventral body wall External genitalia Internal genitalia Mammary glands Mares with high-risk pregnancy should undergo additional scrutiny and owners should be made aware of specific signs of pregnancy compromise, including precocious mammary development, vulvar discharge, abrupt changes in body shape, or abrupt changes in attitude and appetite if these are not already apparent. Because abortion frequently occurs in the absence of any premonitory signs, mares experiencing a high-risk pregnancy should receive regular screening examinations at least monthly, with specific attempts to identify and characterize gestational disease in order to guide therapeutic choice. As suggested above, placentitis contributes to approximately one third of late-term abortions and fetal loss. Three types of placentitis have been described, broadly classified as ascending placentitis, diffuse placentitis, and focal mucoid (also called nocardioform) placentitis. Isolated bacteria include Streptococcus equi subspecies zooepidemicus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Streptococcus equisimilis, and Staphylococcus and Enterobacter species, as well as Rhodococcus equi, Neorickettsia risticii, and Arcanobacterium hippocoleae. A, Ascending placentitis is characterized by avillous, thickened chorioallantois in the region of the cervix, with necrotizing inflammation on histology. B, Tenacious brown exudate covers a denuded portion of chorionic membrane from a mare that delivered a premature, compromised foal due to nocardioform placentitis. C, Fungal placentitis, characterized by a diffusely thin, discolored chorion with multifocal raised nodular lesions. However, careful screening may identify ultrasonographic signs of uteroplacental disease or fetal stress, while hematologic parameters may also change prior to abortion. Focal mucoid, nocardioform placentitis has been described as a cause of abortion and premature delivery worldwide, including North America, Europe, South Africa, Australia, and New Zealand. B and C, From cases of ascending placentitis with separation of the chorioallantois from the endometrium present. Focal placentitis can be diagnosed by identifying the characteristic thickening and separation of the chorioallantois via transabdominal ultrasound.
Cheap 25 mg precose free shipping. Type II Diabetes Explained.
Building upkeep Equipment Computer equipment and software Inventory Other: 534 2019 Vol diabetic pump supplies purchase on line precose. Introduction You have decided to take the leap and hire your first (or more) paraprofessionals for your practice diabete 500 cause buy 50 mg precose overnight delivery. Now it is time to design the job descriptions diabetic diet quick weight loss discount 25 mg precose, which are foundational to team success diabetes test strips free cheap 25mg precose amex, and outline the hiring process to include pre-employment background checks, series of interview questions, and an outstanding job announcement. Job Description Veterinary team job descriptions are "living documents," growing and changing as employees develop their careers. Once employees have a couple of years under their belts, their passions and professional goals will be defined and reflected in their performance reviews and upgraded job descriptions. This document is updated to accurately reflect their passions, education, advanced skill sets, and dedication to client service. However, if you are looking to hire a credentialed veterinary technician with years of experience and an interest in equine medicine, then the job description will reflect those skills, level of achievement, and varied responsibilities. Job descriptions are valuable tools for hiring, performance reviews, establishing expectations of the job, and documentation. You may want to add responsibilities to fill in the gaps and distribute duties for less duplication. Download the following team exercise to help create job descriptions: A Day in the Life Exercise catalystvetpc. Some practices may not have job descriptions, so links to a few resources that can help you in creating job descriptions are below. Job description for an equine veterinary technician may be found on BalanceCareers Academy of Equine Veterinary Nursing Technicians has 23 active members at time of print. Avoid violence in the workplace- keep in mind the statistics show drug users arrive for work with their problems in tow. Reduces costs associated with bad hiring because you will be decreasing your chances of hiring somebody with a drug problem or addiction or history of theft. Interview Questions Before your job post goes live, completely outline your hiring process. This will help the person overseeing the procedure stay on task and sets your practice up for success by being consistent among candidates and avoiding discrimination. Job description Salary or hourly wage/benefits package/signing bonus Job announcement to include background and drug screening Solid criteria in reviewing cover letter and resume for desired qualifications Thanks and no thanks correspondence Email questions Telephone interview questions and request for a video/test In-person interview questions Letter of Employment Pre-Employment Background Checks Designing interview questions is another aspect of the hiring process in which wheels have already been created. Always introduce the same questions at the same time during the interview process. Interview questions for veterinary practice managers: interviewquestions247. Your clients are opening their barns or maybe their homes to a complete stranger-your veterinary team member. Are they appropriately credentialed and current as a veterinarian, veterinary technician, or veterinary assistant Give an example of when you had to work with someone who was difficult to get along with. Who knew so much preparation had to go into the hiring of a veterinary team member You may consider cheerful videos of the services you provide, which is another reason why you need a practice manager. It should engage and motivate the candidate to apply and continue along the hiring process. Be straightforward with job title, company introduction, job description, and qualifications. Create a pool of resources, focusing heavily upon the current sphere of influence-schools, other veterinary hospitals, salespeople, industry representatives. Generate a protocol for distributing and collecting applications, resumes, and cover letters. Critique all applicants in the same manner, review of resume, interview, skill sets, etc.

Patients can have undiagnosed liver disease or other syndromes that affect the coags blood sugar jinx purchase precose line. Informed consent: the attending physician is responsible diabetes symptoms black skin order precose online now, however at times housestaff will be responsible that documentation is achieved on the chart diabetes impact factor 25 mg precose fast delivery, i diabetes test symptoms order precose no prescription. The consent should be placed on chart and witnessed by nursing staff, not performed by nursing staff!!! Mark and sign all required documents: Which includes the consent form, and correctly mark the surgical site, confirm with the patient the correct side!!! Signout with on call staff pending laboratory evaluations/testsinform on call house staff if this/then what (transfusion triggers, etc. Campbell ii antIcoagulants Unfractionated Heparin: From ancient Greek (hepar: liver). Recommend a lower starting dose in: trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, or metronidazole. This effect depends on the clearance of circulating prothrombin, which has an elimination half-life of about 60 hours. Structure: Complex, branched glycan (polysaccharide made of many glucose molecules) composed of chains of varying lengths (from 10 to 150 kilodaltons). Chapter 2- Commonly presCribeD meDiCations 11 Chapter 2- Commonly presCribeD meDiCations claudIcatIon agEnts: PlEtal (cilostazol) Indication: Medical management of claudication (studies report increase in walking distance from 25-100% of baseline). Mechanism of action: Phosphodiesterase inhibitor, mild antiplateletreversible inhibition. The most effective medication to increase walking distances in patients with peripheral vascular disease. Should be stopped 48 to 72 hours prior to surgery secondary to risk for hypoglycemia. Post-operatively these medications can cause hypoglycemia if initiated with poor caloric intake by patient. If you can only remember two numbers related to Doppler criteria, they would include the velocities < 50 cm/sec (seem with slow flow from either severe proximal stenosis or occlusion) and > 300 cm/sec (elevated velocities detected within or adjacent to a stenosis). Asymmetry in brachial blood pressures > 20 mmHg with reversal of blood flow in the vertebral arteries demonstrate anatomic subclavian steal. This is performed by using a hand-held continuous wave doppler probe and a manual sphygmomanometer. When the pulse is identified with the doppler probe at the ankle over the artery (dorsalis pedis or posterior tibial), inflate the cuff over the calf until the signal is lost. The high thigh should be at least the same as the brachial pressure, if less than brachial blood pressure, then consider inflow disease. Chapter 3 - noninVasiVe imaging 16 Chapter 3 - noninVasiVe imaging Peripheral arterial duplex: analysis of lower Extremity doppler arterial waveform Patterns the Doppler arterial waveforms obtained from the lower extremity may be classified into categories as an aid in interpretation. Mild disease: Lose reversal of flow first, resulting in a biphasic waveform pattern. Chapter 3 - noninVasiVe imaging 18 Chapter 3 - noninVasiVe imaging dVt Acute: Non-compressible vein, limited or no color flow, faintly echogenic, homogenous in nature, no collaterals. Chronic: Often has collaterals and is not dilated, has partial degree of occlusion, heterogenous. Subsequent imaging should be at 6 months and then again at 12 months, assuming no critical abnormalities are detected after interventions or in de novo lesions. Pad Procedures Similarly, we closely follow vein bypass patients with 1 month, 6 month, and 12 month exams, but more frequently with abnormal findings, i.